Recently, India launched DHRUV64, the nation’s first fully indigenous 1.0 GHz, 64-bit dual-core microprocessor.
About DHRUV64
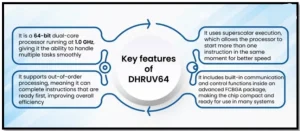
- Technical Architecture: It is a high-performance 64-bit dual-core processor based on the Reduced Instruction Set Computer-V (RISC-V) open-source architecture, which eliminates intellectual property (IP) licensing costs.
- RISC-V is an “open-source language” that allows computers to talk to hardware.
- Unlike Windows or Intel, which are “closed” and require expensive licenses, RISC-V is free for anyone to use and modify.
- Aim: To establish India as a global hub for Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM).
- Milestone Achieved: DHRUV64 is the third chip fabricated under the Digital India RISC-V (DIR-V) Programme with an overall aim to enable creation of Microprocessors for the future in India.
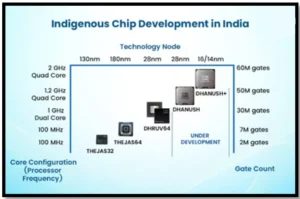
- The first chip, THEJAS32, was fabricated at the Silterra facility in Malaysia.
 The second chip, THEJAS64, manufactured domestically at Semiconductor Lab (SCL) Mohali, India.
The second chip, THEJAS64, manufactured domestically at Semiconductor Lab (SCL) Mohali, India.- In addition, the design, implementation, and fabrication of DHANUSH64 and DHANUSH64+ System on a Chip (SoC) variants are currently under development.
- Development Authority: The chip was designed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) under the Microprocessor Development Programme (MDP) initiated by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
 Strategic Applications: It is engineered for critical sectors like 5G infrastructure, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Automation, and Automotive Systems, ensuring data security and technological sovereignty.
Strategic Applications: It is engineered for critical sectors like 5G infrastructure, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Automation, and Automotive Systems, ensuring data security and technological sovereignty.- Domestic Ecosystem: Before DHRUV64, India developed several key processors to ensure digital sovereignty:
- SHAKTI (2018): Developed by IIT Madras; the first indigenous RISC-V processor.
- AJIT (2018): Developed by IIT Bombay for low-power applications.
- VIKRAM (2025): Developed by ISRO-SCL for strategic space missions.
- THEJAS64 (2025): A C-DAC developed high-performance processor preceding DHRUV64.
- Significance:
- High performance & reliability enabled by out-of-order execution and advanced fabrication.
- Strengthens indigenous processor capability for both strategic and commercial sectors.
- Boosts self-reliant microprocessor ecosystem through open-source architecture, eliminating licence costs and enabling scalable, long-term deployment.
PWOnlyIAS Extra Edge:
- Microprocessors: These are the brains of modern electronic devices such as mobiles, computers, automobiles, medical equipment, defence systems and satellites.
- Key National Programmes Supporting Indigenous Chip Design:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), 2021: Provides structured support and works with global companies to bring large semiconductor investments into the country.
- As of 2025, the mission has approved ten projects across six states, with a total investment commitment of ₹1.60 lakh crore.
- Through ISM, India is positioning itself as a competitive player in the global semiconductor ecosystem.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme, 2021: It aims to offer financial incentives as well as design infrastructure support across various stages of development and deployment of semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor linked design over a period of 5 years.
- Digital India RISC-V (DIR-V) Programme, 2022: Played a central role in advancing India’s indigenous chip design efforts.
- It enabled the development of advanced RISC-V processors in India.
- The programme aims to bring researchers, startups and industry into a shared design ecosystem, improving collaboration and innovation.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme, 2022: A capacity-building initiative implemented across 113 institutions, including 100 academic and R&D organisations and 13 startups and MSMEs.
- The programme has an outlay of ₹250 crore for a five-year period.
- It aims to generate 85,000 industry-ready manpower and create a vibrant fabless chip design ecosystem in the country.
- Indian Nanoelectronics Users Programme- idea to innovation (INUP-i2i): Enables hands-on access to national nanofabrication facilities for students, researchers, and startups.
- Focuses on practical training in chip and device fabrication, bridging the gap between design and manufacturing.
- It has trained over 8,000 personnel and supported hundreds of mid-term R&D projects.
|
![]() 17 Dec 2025
17 Dec 2025

 The second chip, THEJAS64, manufactured domestically at Semiconductor Lab (SCL) Mohali, India.
The second chip, THEJAS64, manufactured domestically at Semiconductor Lab (SCL) Mohali, India. Strategic Applications: It is engineered for critical sectors like 5G infrastructure, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Automation, and Automotive Systems, ensuring data security and technological sovereignty.
Strategic Applications: It is engineered for critical sectors like 5G infrastructure, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Automation, and Automotive Systems, ensuring data security and technological sovereignty.
