WHO team reaches Rajasthan’s Deeg after 7 children die of diphtheria in a month.
Challenges in Diphtheria Vaccination
- Vaccination Efforts: Large-scale vaccination drives initiated, especially targeting children, as diphtheria is a vaccine-preventable disease.
- Resistance to Vaccination: Local population reluctant to vaccinate children due to superstition and misinformation.
- Previous Drives: Multiple vaccination drives have been organized in the past, but opposition from locals has hindered progress.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Diphtheria
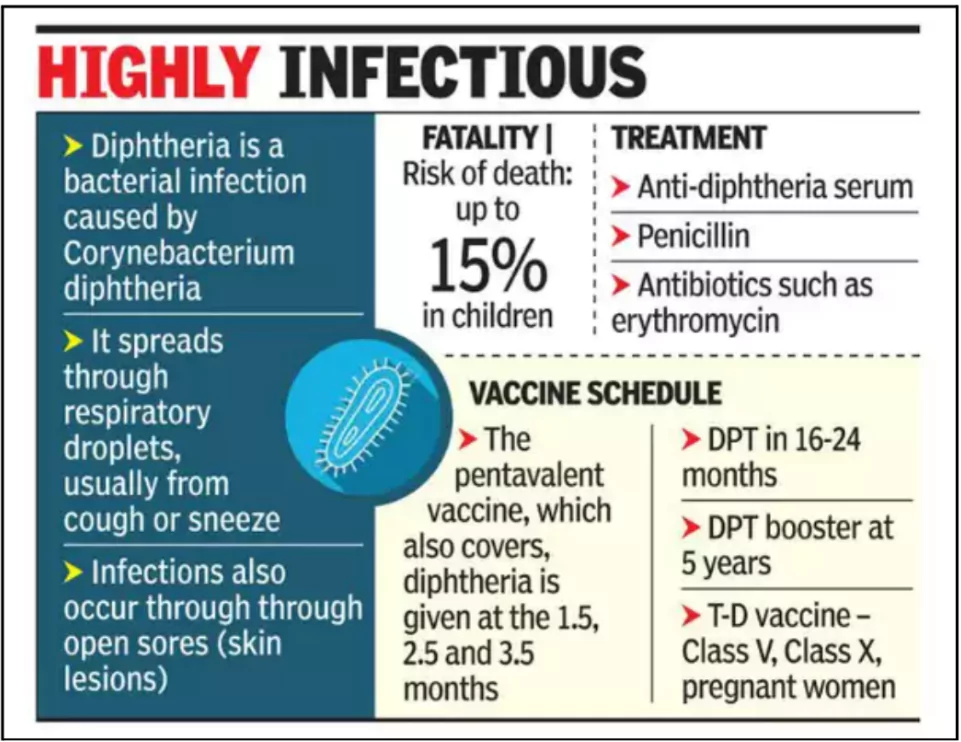
- Contagious Bacterial Infection: A serious bacterial infection caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
- The bacteria produces a toxin affecting the upper respiratory tract, heart, and nerves.
- Transmission: Spread through respiratory droplets (coughing or sneezing)
- It can also spread through contact with infected sores/ulcers.
- Symptoms: Fever, sore throat, swollen neck glands, weakness, and grey coating in the throat, making breathing difficult.
- Complications: Includes heart inflammation, nerve damage, and can be fatal in around 30% of untreated cases, especially in children under 5 years old.
- Over Fatality rate is around 15% in Children.
Prevention for Diphtheria
- Vaccine Preventable: Diphtheria is prevented by vaccines, usually given in combination with tetanus, pertussis, and other childhood diseases.
- Multiple Doses: Requires 6 doses of vaccine from infancy to adolescence for long-term protection.
- Routine Immunisation: Covered under the Universal Immunization Program in India as Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTP).
Risk Factors
- Non-immunized/Under-vaccinated Individuals: Most at risk, with outbreaks occurring when vaccination coverage drops.
- Under-vaccination Impact: Recent diphtheria outbreaks have highlighted the need for sustained high levels of vaccine coverage.
Treatment for Diphtheria
- Antitoxin & Antibiotics: Diphtheria antitoxin (DAT)neutralizes unbound toxins, while antibiotics prevent further bacterial growth.
- Supportive Care: Airway obstruction and myocarditis are monitored and treated to reduce complications.
- Contact Precaution: Close contacts of patients should receive antibiotics and vaccination if unvaccinated or under-vaccinated.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Vaccination Status for Diptheria
- Global Coverage: In 2023, 84% of children worldwide received 3 doses of diphtheria vaccine, but 16% remain under or unvaccinated.
- India Coverage: The coverage rate for DPT3(the third dose of diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus) vaccines, in India rose to an all-time of 93% in 2022.
- Coverage Variations: Significant differences in vaccination levels between and within countries.
Prevention of Diptheria
- High Coverage: Community-wide vaccination embedded in primary healthcare is the most effective prevention.
- Combination Vaccines: Diphtheria vaccines are often combined with vaccines for tetanus, pertussis, and others, increasing protection against multiple diseases.
![]() 16 Oct 2024
16 Oct 2024

