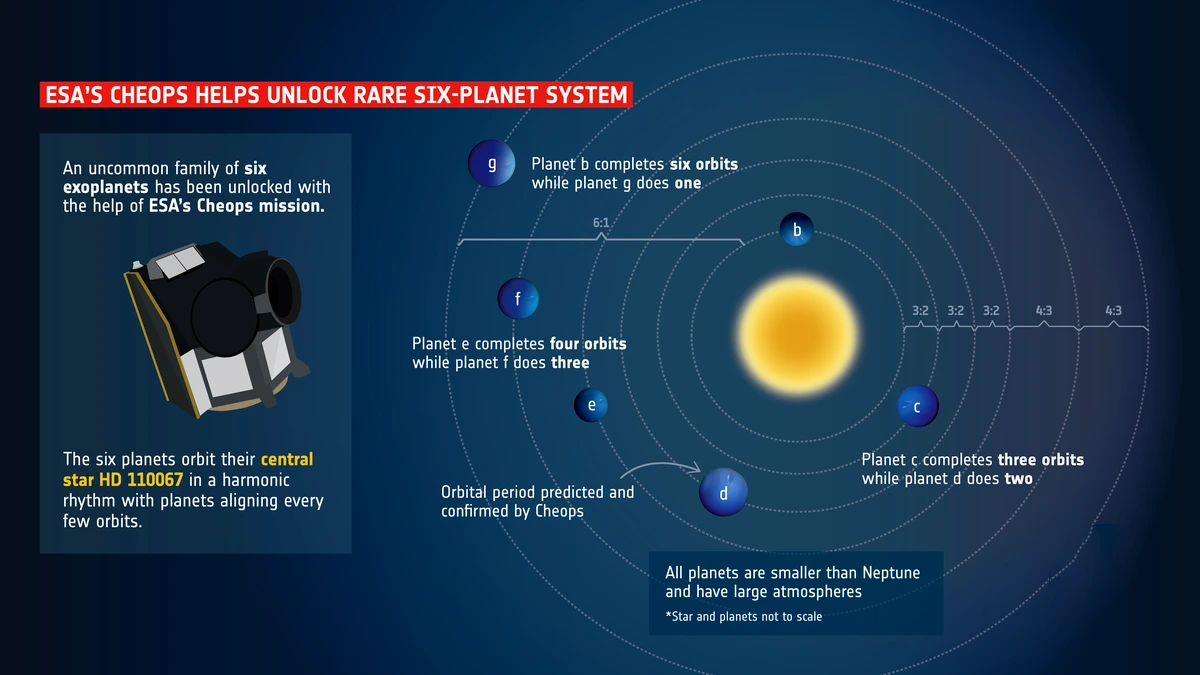
Context: Six exoplanets orbiting around a nearby bright star (HD 110067) in the Coma Berenices constellation have been discovered.
Discovery of Six Exoplanets
- The planets have radii between Earth and Neptune.
- NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) first discovered two exoplanets orbiting the star in 2020.
- TESS is a space telescope for NASA’s Explorer program, designed to search for exoplanets using the transit method in an area 400 times larger than that covered by the Kepler mission.
- Planets with radii between that of the Earth and Neptune (referred to as ‘sub-Neptunes’) are found in close-in orbits around more than half of all Sun-like stars.
What are Exoplanets?
- The word “exoplanet” is derived from the term “extrasolar planet.“
- Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars other than the sun and thus exist outside the solar system.
- Currently, the closest exoplanet to Earth is Proxima Centauri b, which orbits the star Proxima Centauri and is located 4 light-years away.
Types:
- Hot Jupiters: Hot Jupiters are gas giant exoplanets that orbit close to their stars and complete a full orbit in just a few Earth days.
- Terrestrial exoplanets: Terrestrial exoplanets are roughly Earth-size worlds outside the solar system composed of rock, silicate, water and carbon.
- Super-Earths or mini Neptunes: Super-Earths, alternatively known as mini-Neptunes, are planets that are up to twice the size of Earth.
- Rogue Exoplanets: They are also known as isolated planetary-mass objects and free-floating planets, which are worlds outside the solar system that are not gravitationally bound to stars.
About HD 110067:
- HD 110067 is a bright star in the Coma Berenices constellation (around 100 light-years away), visible from Earth’s Northern Hemisphere.
Coma Berenices constellation
- Coma Berenices, or Berenice’s Hair, is a constellation in the northern sky.
- It was named after Queen Berenice II of Egypt.
- The constellation is home to the North Galactic Pole.
- It belongs to the Ursa Major family of constellations.
|
Significance of Discovery:
- A study published in Nature has calculated the orbit details, along with estimates of their masses and densities, which offer clues about the compositions of the planets’ atmospheres.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 5 Dec 2023
5 Dec 2023

