![]() 7 Oct 2024
7 Oct 2024
English
हिन्दी
A team of history and archaeology scholars from the University of Mysore have embarked on an excavation of megalithic burial sites in Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka
| Aspect | Paleolithic | Mesolithic | Neolithic |
| Period | 2.5 million years ago to 10,000 BCE | 10,000 BCE to 8,000 BCE | 8,000 BCE to 3,000 BCE |
| Habitat | Caves, temporary shelters, open plains | Semi-permanent camps near water sources | Permanent settlements, farming villages |
| Key Findings | Stone tools (e.g., hand axes), cave art, early fire usage | Microliths (small stone tools), bone tools, art (petroglyphs) | Agricultural tools, pottery, domesticated plants and animals |
| Lifestyle | Hunter-gatherers, nomadic lifestyle | Transition to more sedentary life, seasonal migration | Farming, animal husbandry, social stratification, trade |
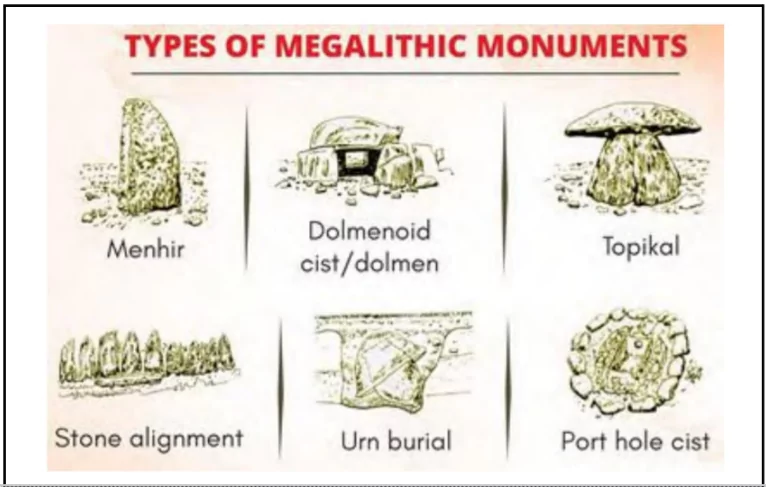 Sarcophagus Burials: Terracotta receptacles, often with lids, sometimes shaped like animals.
Sarcophagus Burials: Terracotta receptacles, often with lids, sometimes shaped like animals.| State | Burial Sites | Features/Components Found |
| Jharkhand | Seraikela | Megalithic burials, large stone structures, urn burials, associated with iron age tools and artifacts. |
| Uttarakhand | Deodhoora (Almora district) | Early human habitation, rock shelters, and megalithic burial remains. |
| Uttar Pradesh | Koldihwa (Belan Valley), Banda, Mirzapur, Prayagraj, Varanasi | Chalcolithic materials, evidence of early agricultural practices, copper tools, and pottery. |
| Kerala | Thrissur, Kunnattur | Megalithic burial sites with Topikal, urn burials, stone circles, dolmens, and pottery artefacts. |
| Kashmir | Waztal, Burzahom, Brah | Burzahom: Pit dwellings, Neolithic to Megalithic transition, animal bones, tools, and ceramics. |
| Karnataka | Maski, Hallur, Chandravalli, Hire Benakal, Coorg, Heggadehalli, Brahmagiri | Megalithic dolmens, cist burials, iron tools, pottery, skeletal remains, evidence of early agriculture. |
| Andhra Pradesh | Nagarjunakonda | Buddhist relics, stupa remains, Megalithic burials, urn burials, stone tools, and pottery. |
| Maharashtra | Junapani, Khapa, Mahurjhari, Naikund (near Nagpur), Pune | Megalithic burials, stone circles, urn burials, copper and iron tools, skeletal remains, pottery, and beads. |
| Tamil Nadu | Adichanallur, Sanur, Kodumanal, Perumbair | Urn burials, iron implements, pottery, skeletal remains, and evidence of trade with ancient civilizations. |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>