Context:
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) has taken a significant step in combating the drug menace by disposing of a massive 1,44,000 kilograms of illegal drugs.
- Usage of psychotropic substances: Apart from narcotics, India has been experiencing a significant rise in the use of psychotropic substances and medicinal preparations among addicts since late 1990.
Factors Behind Drug Menace in India:
- Geographical reasons:
- Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle: India’s geographical location sandwiched between the two, makes it an ideal route for the transportation of heroin. It infiltrates the country through the international, land and maritime borders, with the western international border along Pakistan being a focal point.
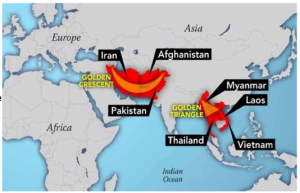
- Golden Triangle: It refers to the area where the borders of Thailand, Laos, and Myanmar meet at the confluence of the Ruak and Mekong rivers. Myanmar is the world’s second-largest illicit supplier of morphine and heroin, producing 80 per cent of the world’s heroin.
- Golden Crescent: The Golden Crescent, on the other hand, is a major global opium production site in Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, from where drugs are smuggled into India through Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
|
-
- Proximity to sea: India shares borders with several countries that are major drug producers and transit points, including Afghanistan and Myanmar. Its long and porous borders make it an attractive transit point for drug traffickers.
- Drug trafficking through sea routes in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, estimated to account for around 70% of the total illegal drugs smuggled into India
2. Technological reasons:
-
- Digital tools and drones:Drugs are now being smuggled across these borders using new digital tools and drones.Also, drug gangs now use couriers, packages, and the mail to sneak drugs in and deliver them.
- Darkweb: The increased use of couriers or postal services is directly linked to increased Dark Web activity in India. Dark Web is used to buy illicit substances which are often paid in crypto currency.
3. Organized Crime:
-
- Nexus between drug traffickers, organized criminal networks and terrorists: Terrorists exploit established trafficking routes, collaborating with well-entrenched criminal groups to infiltrate borders with arms and explosives, exacerbating security challenges.Money generated through drug trade has been used to fund various insurgent and terrorist movements.
- For example, 1993 serial bomb blasts in Mumbai, Pathankot attack on 31st December 2015 highlight a close nexus between drug traffickers and anti-national elements.
- Corruption: Drug traffickers are known to bribe law enforcement officials and other government officials to facilitate their operations. This has further enabled drug trafficking to thrive in India.
4. Socioeconomic reasons:
-
- Lack of education: Poor aspirations of the youth, which are not fulfilled due to low quality of education imparted to the lower income groups in rural and urban government schools of the state, leave them disillusioned and susceptible to drugs.
- Vicious cycle: The drug addicts from poor families, in order to meet the expenses of their daily dose, get entangled in drug-peddling, the rising unemployment among youths have further led to disillusionment.
5. Smuggling of Synthetic drugs and precursor chemicals: India manufactures a lot of synthetic drugs and precursor chemicals which are smuggled out of the country.
6. Poor Law enforcement: India’s law enforcement agencies are understaffed, lack specialised training and equipment, and are often unable to detect or interdict drug shipments.The agencies are more involved in dealing with peddlers and distributors and often fail to catch the drug mafia.
Case in Point:
- J & K :It is estimated that 15% of the finances of Jammu and Kashmir militants came from drug sales.
- Northeast: Insurgent organizations are directly involved in drug trafficking to secure quick funds, while larger groups collect protection money from drug peddlers in return for safe passage of drug consignments through their territories.
|
Challenges /Impact of drug abuse in India:
- Smuggling of weapons: The international borders of the country used by drug traffickers are used for smuggling in weapons as well as terrorists into the country.
- Financing of terror activities: Illicit drug sales generate substantial funds that are often diverted to finance terrorist activities.
- Law and order issues:The wide availability of narcotics and drugs contributes to increased domestic demand, leading to dysfunctional behavior and creating law and order problems in society.
- Economic impact : The substantial economic toll from drug abuse includes losses in production and resources diverted for caring and rehabilitating drug addicts.
- Undermining role of state: The trafficking nexus can subvert and corrupt state institutions, further undermining the political process, as they gain control over the illegal drug trade.
- Facilitation of organised crime: Drug trafficking facilitates other organised criminal enterprises such as human trafficking and narco terrorism, all of which use the same networks and routes to smuggle people, arms and contraband.
- Loss of demographic dividend: Increase in violence and crime is the direct impact of drug abuse. Addicts resort to crime to pay for their drugs. Substance abuse can lead to the removal of inhibitions and impair judgment, individual productivity and potential.
- Adverse social impact: A partner’s addiction may affect the entire family straining interpersonal relationships, stability, and lead to violence, child abuse, economic insecurity, deprivation of schooling, and the risk of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Psychological impact: Drug addiction not only affects the financial stability of individuals but also gives rise to conflicts within families, causing immense emotional distress for all its members.
Govt measures/Response to counter drug menace:The Ministry of Home Affairs is cracking down on drugs in three different ways:
-
- Strengthening institutional structures,
- Empowerment of all agencies related to control of narcotics and strengthening the coordination among them
- Launching an awareness campaign.
Other measures are listed below-
- Legislative:
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940: It regulates the import, manufacture and distribution of drugs in India.The primary objective of the act is to ensure that the drugs and cosmetics sold in India are safe, effective and conform to state quality standards.
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985: It prohibits a person from the production/manufacturing/cultivation, possession, sale, purchasing, transport, storage, and/or consumption of any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- Prevention of Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1988: Under the act, It is illegal for a person to produce/manufacture/cultivate, possess, sell, purchase, transport, store, and/or consume any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- Institutional measures:
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB): It is under the Ministry of Home Affairs and is responsible for coordination in illicit drug control as well as compiling the cases of drug trafficking in the country as reported to it by various agencies.
About Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB):
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) is the chief law enforcement and intelligence agency of India responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substances.
- It was created on 17 March 1986 to enable the full implementation of the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) and fight its violation through the Prevention of Illicit Trafficking in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1988).
|
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment: The nodal Ministry for drug demand reduction has taken the following steps:
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) for 2018-2025: It aims at reduction of adverse consequences of drug abuse through a multi-pronged strategy involving education, deaddiction and rehabilitation of affected individuals and their families.
- Scheme for Prevention of Alcoholism and Substance (Drug) Abuse: Under this scheme, financial assistance is given to Voluntary Organizations and other eligible agencies for setting up/running Integrated Rehabilitation Centre for Addicts.
3. Other preventive government measures:
-
- Increased patrolling and surveillance: Intensive preventive and interdiction efforts along known drug routes and strict surveillance and enforcement at import and export points.
- Training programmes: Training programmes are being conducted for various law enforcement officials to combat drug menace.
- Empowering of border guarding agencies: Amongst border guarding agencies, Border Security Force (BSF), Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) and Coast Guard have been empowered to take action under the Narcotic Drugs & Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat campaign:It was launched in 2020 in 272 identified districts. It incorporates a comprehensive approach towards drug reduction including combining the supply curb by NCB, Outreach and Awareness and Demand Reduction effort by Department of Social Justice and Empowerment and treatment through Health Department.
- Strengthening anti-narcotic units: Financial assistance has been provided to eligible States for strengthening their anti-narcotic units.
- Narco Co-ordination Centre (NCORD): it has been constituted under Director General,Narcotics Control Bureau to provide a common platform for concerted actions by all the Drug law enforcement agencies and other stakeholders.
4. International efforts:
-
- The International Drug Control Conventions.
- The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961): The Convention aims to combat drug abuse by coordinated international action. It seeks to limit the possession, use, trade, distribution, import, export, manufacture and production of drugs exclusively to medical and scientific purposes. It also combats drug trafficking through international cooperation to deter and discourage drug traffickers.
- Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971: The Convention on Psychotropic Substances establishes an international control system for psychotropic substances. It responded to the diversification and expansion of the spectrum of drugs of abuse and introduced controls over a number of synthetic drugs according to their abuse potential on the one hand and their therapeutic value on the other.
- United Nations Convention against illicit traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances of 1988: The Convention provides comprehensive measures against drug trafficking, including provisions against money laundering and the diversion of precursor chemicals.
- Cooperation with neighbours: In order to foster cooperation among neighbors, India is engaged in multiple bilateral and multilateral agreements to address the issue of preventing the illicit trafficking of drugs and chemicals.
Way Forward:
- Effective coordination among enforcement agencies: Promoting cooperation and collaboration between government departments in the fight against drug abuse and trafficking. For example, Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation, Border Security Force, the National Investigation Agency, etc.
- Sharing of intelligence: There is an urgent need to develop a system for sharing of information which would help the enforcement agencies connect the distributors to the source of supply.
- Focus on source of supply:. Enforcement agencies should focus mainly on tracking the network deeply and prosecuting producers and suppliers, rather than the current focus on distributors and peddlers.
- Special skills, dedicated units: There is a need to develop special skills within state police organisations dealing with drugs.
- Enhancement of punishment under Illegal Drug Control Act: Smugglers, suppliers and members of drug syndicates should be awarded enhanced punishments.
- Creating awareness among citizens: Many times, students and young people may not be aware of the harmful effects of illicit drugs. Youth, especially, suffer from insecurity and depression and fall prey to drug peddlers. There is need to create awareness among the people.
- Establishment of de-addiction centres and camps: The government agencies can establish district wise de-addiction centres and camps to help the affected youth. Rehabilitation and post care counselling can save many lives.
- Comprehensive approach: Exploring comprehensive approaches to treatment, rehabilitation, and harm reduction.
- Role of civil society: It can play an important role in preventing narcotic drug abuse through:
- Awareness programmes for students in educational institutions, youth clubs and associations to make healthy choices in life and to stay away from drugs.
- Role models such as athletes or film actors can be roped in to inspire youth to adopt healthy habits.
- Religious leaders will have a positive impact on moulding people’s behaviour
- Monitoring by parents to keep their children away from bad company.
- A mechanism to obtain the consent of a doctor for the continuous purchase of any soft drug should be developed.
- Social media campaigns to enhance awareness about the ill effects of narcotic substances.
Conclusion:
- Illicit drug trafficking is a crime which affects not only an individual but has ramifications across societies. It has the potential to destroy an entire generation. Therefore, it is the responsibility of every section of society to help enforcement agencies of the government to root out this menace.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 20 Jul 2023
20 Jul 2023
