According to the National Center for Seismology (NCS) , a shallow earthquake of 4.0 magnitude struck Delhi-NCR, with a focal depth of 5 km.
- Another 4.0 magnitude earthquake was recorded in Bihar at 8:02 AM, with a depth of 10 km.
About Earthquake
An earthquake is the shaking of the Earth’s crust caused by a sudden release of energy. This release of energy occurs along a fault, which is a break in the Earth’s crustal rocks.
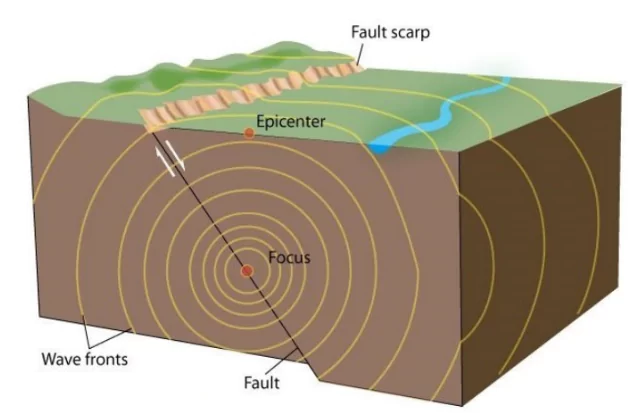
How do earthquakes occur?
- Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates.
- When two tectonic plates slide past each other, the jagged edges can get caught, and when they release, the energy is released as vibrations.
- Earthquakes can also be caused by the injection or withdrawal of magma, or explosions of chemical or nuclear devices.
Know the Terms:
- The branch of knowledge that deals with the study of earthquakes is called seismology.
- Hypocenter (Focus): The location below the Earth’s surface where the earthquake starts
- Epicenter: The location directly above the hypocenter on the surface of the Earth
|
Types of earthquakes
- Earthquakes can vary in intensity and duration, ranging from minor tremors to major seismic events.
- Earthquakes can be categorized into shallow, intermediate, and deep based on their depth.
What is a Shallow Earthquake?
- Shallow earthquakes originate between 0 to 70 km below the surface.
- Intermediate earthquakes occur at 70 to 300 km, and deep earthquakes at 300 to 700 km.
- The shallower the earthquake, the more destructive it is, as seismic waves lose less energy before reaching the surface.
- Example: A 5.6 magnitude earthquake in Indonesia (November 2022) killed over 160 people.
Earthquake Waves: Earthquake waves are basically of two types — body waves and surface waves.
- Body waves are generated due to the release of energy at the focus and move in all directions travelling through the body of the earth. Eg. P-waves and S-waves.
- The body waves interact with the surface rocks and generate new sets of waves called surface waves.
- Surface waves, also known as L-waves, travel along the earth’s surface and are the most destructive.
Difference between P and S waves
| Types of Wave |
P-waves (Primary waves) |
S-waves (Secondary waves, shear waves) |
| Speed |
Faster than S-waves |
Slower than P-waves |
| Travel path |
Can travel through liquid, gas, and solid |
Can only travel through solid |
| Vibration |
Vibrate parallel to direction of propagation |
Vibrate perpendicular to direction of propagation |
| Effect |
Cause pressure changes in the medium |
Create troughs and crests in the material |
| Shadow Zones |
The shadow zone of is P-waves
much smaller than that of the S-wave. |
The shadow zone of S-wave is
much larger than that of the P-waves. |
|
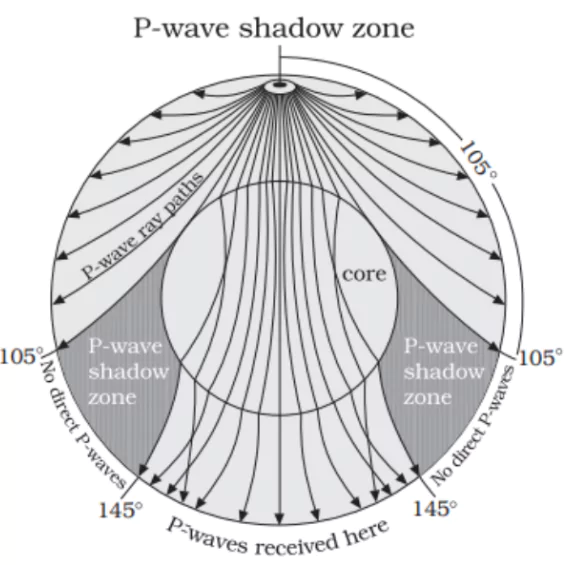 |
|
- The difference in travel time between P-waves and S-waves can be used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake.
![]() 17 Feb 2025
17 Feb 2025


