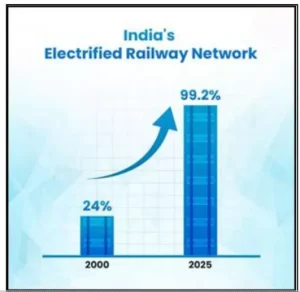
Indian Railways has become the world’s largest electrified rail network, with about 99.2% of its broad-gauge network electrified by November 2025.
About Indian Railways
- Indian Railways is operating one of the largest rail networks in the world.
- Electrification Achievement: It has achieved near-complete electrification of its broad-gauge routes, surpassing other major global railway systems.
- Mission 100% Railway Electrification:
- Under the “Mission 100% Railway Electrification,” Indian Railways is aiming for complete electrification.
- History and Timeline of Electrification:
- The electrification initiative started in 1925., but post-2014, it was accelerated under a mission-mode approach.
- Electrification pace has surged from 1.42 km/day (2004–2014) to over 15 km/day in 2019- 2025, marking a massive acceleration in modernization.
- Objective: The main goal is to eliminate diesel traction and shift to cleaner, more sustainable electric traction.
 Key Features of the Electrification Initiative:
Key Features of the Electrification Initiative:-
- Progress: 99.2% of about 70,000 km of broad-gauge network is electrified (as of November 2025).
- Full Electrification States: 25 States and UTs are fully electrified, with only ~0.8% of the network left pending
- Renewable Integration: Solar capacity increased from 3.68 MW in 2014 to 898 MW by 2025
- Technological Integration: Adoption of modern technologies like Automatic Wiring Trains and mechanized Traditional overhead electrification (OHE) foundations.
About Railway Gauges in India
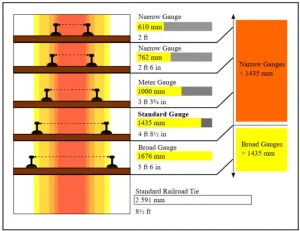
The gauge refers to the width and stability of the railway track, which directly influences the size and design of rail vehicles that can operate on it.
Broad Gauge (1676 mm)
- The most prevalent gauge used in India, covering the majority of passenger and freight routes. This gauge is considered the widest in regular use worldwide.
- They are also used at port facilities for accommodating cranes and related equipment.
Meter Gauge (1000 mm)
- Found in isolated or less trafficked branch lines. Meter gauge is gradually being converted to broad gauge. Notable example: Nilgiri Mountain Railway, a heritage route.
Narrow Gauge (762 mm and 610 mm)
- Narrow gauge railways are often used for mountainous and hilly terrains due to their suitability for steep slopes.
- Famous examples include the Kalka-Shimla Railway and Darjeeling Himalayan Railway.
Standard Gauge (1435 mm)
- In India, the standard gauge is used for urban rail systems, such as Metro, Monorail, and Trams.
- Kolkata Tram System: The only standard gauge railway line in India was the Kolkata (Calcutta) tram system.
- The standard gauge is preferred in metropolitan regions for metro lines due to the greater availability of rolling stock and better accessibility of equipment for this gauge.
![]() 7 Jan 2026
7 Jan 2026


 Key Features of the Electrification Initiative:
Key Features of the Electrification Initiative:

