Weeks ahead of the onset of winter in India, both Punjab and Haryana have promised to “eliminate” stubble burning this year.
- The Supreme Court sought a report from the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) on incidents of stubble-burning and action taken against these occurrences.
About Stubble Burning
- It is a practice of removing agricultural waste from the field by setting on fire the straw stubble (parali) that is left on the land after harvesting of grains like paddy, wheat etc.
- It is mostly practised in the Indo-Gangetic plains of Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh to clear the fields for rabi crop sowing.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Challenges
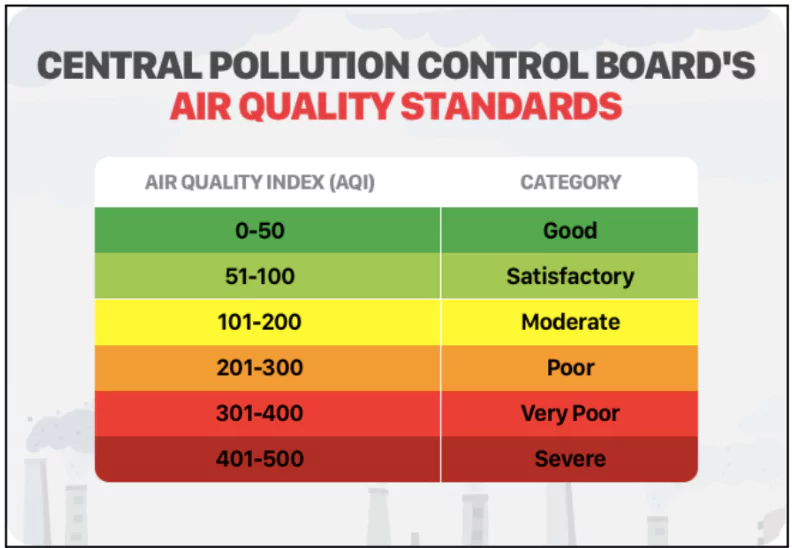
- Air Pollution: Each year, air pollution levels rise and the AQI reaches a ‘severe’ and ‘hazardous’ level.
- Harmful Health Impacts: It emits toxic pollutants in the atmosphere containing harmful gases like Carbon Monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), NH3, SO2, carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and volatile organic compounds (VOC).
- Heat Penetration: Heat generated by stubble burning penetrates into the soil, leading to the loss of moisture and useful microbes
- For instance, the heat from burning paddy straw penetrates 1 centimetre into the soil, elevating the temperature to around 400 Celsius.
- Soil Fertility: Burning husk on the ground destroys the nutrients in the soil, making it less fertile.
- Global Warming: Greenhouse gases such as CO2, N2O, O3,etc are released during Stubble burning.
Methods to Eliminate Stubble Burning
- In-Situ Management: Utilising specialised machinery or bio chemicals to manage crop residue directly in the field.
- For example The Pusa decomposer is a microbial solution that helps break down crop stubble into manure.
- Ex-Situ Management: Transporting crop residue for alternative uses, such as composting or biogas production.
- Co-Firing: Converting paddy straw into pellets and using them as a fuel source in thermal power plants.
- Promotion of Alternative Crops: Encouraging farmers to adopt crop varieties that require less stubble removal.
Policy support from Central Government:The Government has revised the Crop Residue Management guidelines enabling efficient ex-situ management of paddy straw generated in the States of Punjab, Haryana, UP and Delhi.
- Techno-commercial pilot projects: Establishment of supply chains between farmers and industries.
- Financial assistance: Government support for machinery and equipment costs (up to 65%).
- Working capital: Joint funding by industry and beneficiary or through AIF(Agriculture Infrastructure Fund ), NABARD, or other financial institutions.
- Land arrangement: Beneficiary responsible for securing and preparing storage land.
- Project proposal-based support: Financial assistance for specific machinery and equipment.
- State government approval: Projects to be approved by project sanctioning committees.
- Industry contribution: Primary promoter contributes 25% of project cost.
- Farmer or group contribution: Direct beneficiary contributes 10% of project cost.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Punjab, Haryana Commit to Eliminate Stubble Burning
- Government Commitment: The governments of Punjab and Haryana have pledged to eliminate stubble burning this winter.
- Action Plans: Both states have developed comprehensive action plans to manage crop residue through a combination of in-situ and ex-situ methods.
- Machinery and Support: Adequate machinery and support systems, including Custom Hiring Centers (CHCs), have been provided to farmers.
About Commission for Air Quality Management
- It is a Statutory body formed under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas, Act 2021.
- Composition:
- It has a Chairperson
- 5 ex-officio members (Chief Secretaries or Secretaries in charge of the department dealing with environment protection in Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.)
- 3 full time technical members;
- 3 members from non-government organisations; Technical members from CPCB, Indian Space Research Organisation, and NITI Aayog
- Objectives:
- Air pollution control: The CAQM’s main goal is to prevent, monitor, and control air pollution in the NCR.
- Research and development: The CAQM conducts research and development to identify air pollutants and improve air quality.
|
- Co-Firing Initiatives: Co-firing projects are being implemented in thermal power plants to utilise paddy straw as a fuel source
Challenges in Eliminating Stubble Burning
- Economic Incentives: Providing farmers with economic incentives to adopt alternative practices can be challenging due to budget constraints and administrative difficulties.
- Awareness Campaigns: Reaching out to all farmers in rural areas and ensuring effective communication can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Technological Limitations: The availability and affordability of suitable machinery for crop residue management can be a barrier for farmers.Social Resistance: Some farmers may resist adopting new practices due to traditional farming methods and cultural beliefs.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward
- Comprehensive Policy Framework: Developing a comprehensive policy framework that addresses both economic and environmental concerns.
- Financial Assistance: Providing financial assistance to farmers for adopting alternative practices, such as stubble incorporation or baling.
- Community Engagement: Organizing community workshops and training programs to educate farmers about the benefits of sustainable practices.
- Strict Enforcement: Implementing strict enforcement measures to discourage stubble burning and hold violators accountable.
![]() 25 Sep 2024
25 Sep 2024
