As climate urgency grows, Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW) is gaining global interest for its potential to combine carbon capture with agricultural benefits.
| Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a way of reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which could be key to helping to tackle global warming. |
About Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW)
- Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW) is a carbon dioxide removal technique that accelerates the natural process of rock weathering to capture and store atmospheric CO₂
- ERW seeks to accelerate this natural weathering process using finely ground silicate rocks such as basalt.
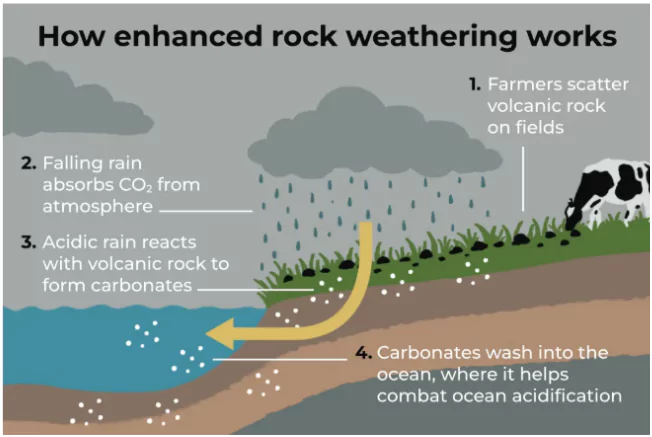
How Does It Work?
- Rock Application: Finely crushed silicate rocks are spread on land, typically agricultural fields.
- Chemical Reaction: Rainfall and soil moisture facilitate reactions where CO₂ dissolves in water to form carbonic acid, which reacts with minerals like calcium or magnesium in the rocks to form carbonates.
- Carbon Storage: The resulting carbonates are stable and can either remain in the soil or wash into rivers and oceans, where they contribute to long-term carbon storage.
- Co-Benefits: ERW can improve soil fertility by adding nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, potentially increasing crop yields. It may also reduce soil acidity.
Benefits
- Carbon Removal: ERW offers a scalable method to remove atmospheric CO₂ and lock it away for thousands of years.
- One US study: Up to 10.5 tonnes CO₂ removed per hectare over 4 years (with 50 tonnes of basalt/year)
- Soil Improvement: Increased alkalinity from basalt can enhance soil fertility, nutrient availability, and crop yields.
- Acid Neutralisation: Even when not directly reacting with CO₂, ERW may prevent soil acids from entering waterways and releasing CO₂ downstream.
- Cost-Effective Material: Basalt is abundant and often a byproduct of quarrying, making it a low-cost input.
Growing Investor Interests
- Mati Carbon, an India-based startup, won the $50 million X Prize for carbon removal.
- Google signed the world’s largest ERW deal (200,000 tonnes credits by early 2030s)
- Terradot sold 90,000 tonnes for $27 million (clients include H&M)
|
Challenges
- Overestimation Impact : Accurately measuring captured CO₂ is challenging:
- Current method: Tracks cations released during weathering
- But cations also result from non-CO₂ acids, leading to possible overestimation
- Occupational Safety: Spreading fine rock dust requires protective equipment for farm workers.
- Toxic Elements: Some silicate rocks may contain heavy metals; proper selection and handling are essential.
- Carbon Credit Integrity: If ERW projects overstate carbon removal and sell credits based on flawed data, it could undermine climate goals (net emissions increase )
Applications of ERW
ERW is being trialled in a variety of agricultural settings, including:
- Tea plantations in Darjeeling, India
- Sugarcane fields in Australia
- Oil palm fields in Malaysia
- Maize and soybean farms in the U.S.
- Brazil: First-ever verified ERW carbon credit project
![]() 25 Jun 2025
25 Jun 2025


