![]() 18 May 2024
18 May 2024
English
हिन्दी
India to begin formal negotiations for a free trade agreement with the Russian-led Eurasian Economic Union (EEU). The EEU has exchanged trade data with the Indian side ahead of the start of the negotiations.
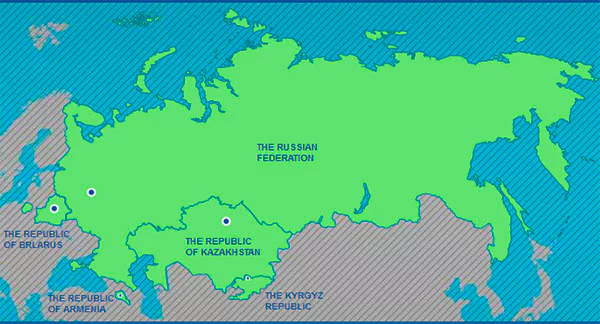
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)Free Trade Agreement is a pact between two or more countries to reduce barriers to trade ie. goods and services can be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
India and FTAs:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>