Finance Minister called out the European Union’s initiatives such as the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and Deforestation rules as ‘unilateral’ and ‘arbitrary’
More on the news
- She highlighted that the European Union’s decision to impose a carbon tax on Indian products such as steel and cement is aimed at hurting Indian industries.
- The levy is a pretence to convert the EU’s own “dirty” steel into green at another’s cost.
- India has decided to retaliate against EU steel tariffs, which have led to trade losses of $4.41 billion from 2018 to 2023.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
“Fit for 55 in 2030 package” .
- The overall goal of the European Union (EU) in its efforts to control climate change is to achieve climate neutrality by 2050.
- To achieve this goal, the Climate Law has been enacted to ensure that all EU policies aim at climate neutrality.
- This law was implemented in July 2021 through the ‘Fit for 55 Package’. The number 55 symbolizes the target of reducing GHG at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
- This package includes legal tools to implement this goal in the fields of climate, energy, land use, traffic and taxes.
|
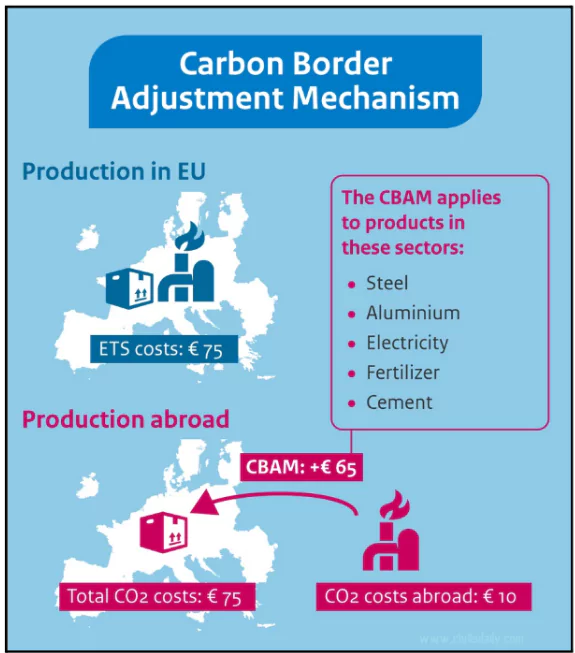
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
- It is part of the EU’s “Fit for 55 in 2030 package” .
- It aims to achieve the target of a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2030, compared to 1990 levels.
Pro and Con of CBAM implementation
Pro
- Level Playing Field: Prevents carbon leakage, ensuring that EU companies aren’t disadvantaged by competing with those from countries with less stringent climate policies.
- Incentivizes Climate Action: Encourages non-EU countries to adopt more ambitious emissions reduction targets to avoid tariffs.
- Revenue Generation: CBAM can generate revenue for the EU, which can be used to support climate mitigation and adaptation projects.
Cons
- Trade Barriers: May increase trade costs and hinder global trade, particularly for developing countries with less developed climate policies.
- Complexity: Implementing CBAM can be administratively complex, requiring accurate tracking of emissions and product life cycles.
- Retaliation: Other countries may retaliate with their own carbon border measures, leading to a trade war.
|
- Importers will be required to surrender annually the corresponding number of CBAM certificates.
- Applicability: Applied to the actual declared carbon content embedded in the goods imported to the EU.
- EU’s Emission Trading System (ETS): EU’s Carbon Border Tax is intended to work like the EU-ETS, which sets a cap on the amount of GHG emissions permitted.
- Importers will need to acquire these certificates at prices reflecting the carbon cost, incentivizing cleaner production practices globally.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Implications of CBAM
- Adverse Impact: India is among the top 8 countries that will be adversely affected by the CBAM.
- Few of its core sectors such as steel will be greatly affected by the CBAM.
- India exports 27% of its iron, steel, and aluminium products worth $8.2 billion to the EU
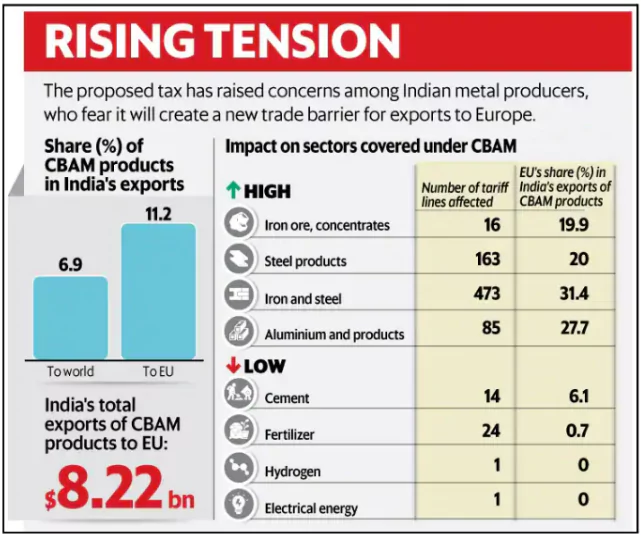 Costlier Export: The EU carbon tariffs could raise costs of Indian exports by 20% to 35%, particularly affecting iron, steel, and aluminium.
Costlier Export: The EU carbon tariffs could raise costs of Indian exports by 20% to 35%, particularly affecting iron, steel, and aluminium.- Complex process : Indian exporters are concerned about the burdensome requirements of the CBAM, which involve submitting nearly 1,000 data points regarding production methods.
- Other regulations: EU’s Deforestation Regulation, could disrupt supply chains and increase transition costs for compliant countries.
- The EU has proposed delaying the implementation of the Deforestation Regulation by one year due to pushback from several countries.
India’s Commitment to Green Transition
- India is advancing its green transition through initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for emerging sectors, including green energy.
- The government is committed to meeting its 2070 climate targets, with interim milestones set for 2030.
- There are ongoing efforts to explore new blended finance options to support funding for green projects, fostering a conducive environment for sustainable investments.
![]() 10 Oct 2024
10 Oct 2024

 Costlier Export: The EU carbon tariffs could raise costs of Indian exports by 20% to 35%, particularly affecting iron, steel, and aluminium.
Costlier Export: The EU carbon tariffs could raise costs of Indian exports by 20% to 35%, particularly affecting iron, steel, and aluminium.