Dinosaurs ruled Earth’s ecosystems for millions of years, ranging from plant-eating giants like Argentinosaurus to fierce predators like Tyrannosaurus and odd creatures like Therizinosaurus with long claws.
What Are Dinosaurs?
- Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles belonging to the clade Dinosauria.
- They first appeared during the Triassic Period, about 243–233 million years ago (mya).
- They went extinct around 66 million years ago.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
History of Dinosaurs in India
- Indian is situated on the Indian plate which is a major tectonic plate that split from the gondwana land ((southern part of Pangea).
- The first dinosaur fossil was found in India in 1828, near Jabalpur in Madhya Pradesh.
- The holotype vertebrae were found by Captain William Henry Sleeman of the East India Company on Bara Simla Hill.
- In 1877, the fossil was named Titanosaurus indicus, a herbivorous dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period (145-65 mya).
- More dinosaur remains were found in India in the Lameta Formation (an area in the Narmada Valley of Central India).
- This region has revealed dinosaur nests, eggs, and skeletons.
- Significant Fossil Discoveries in India
- Barapasaurus
- Isisaurus
- Indosuchus
- Rajasaurus
|
Where Did Dinosaurs Come From?
- Proposed Origin:
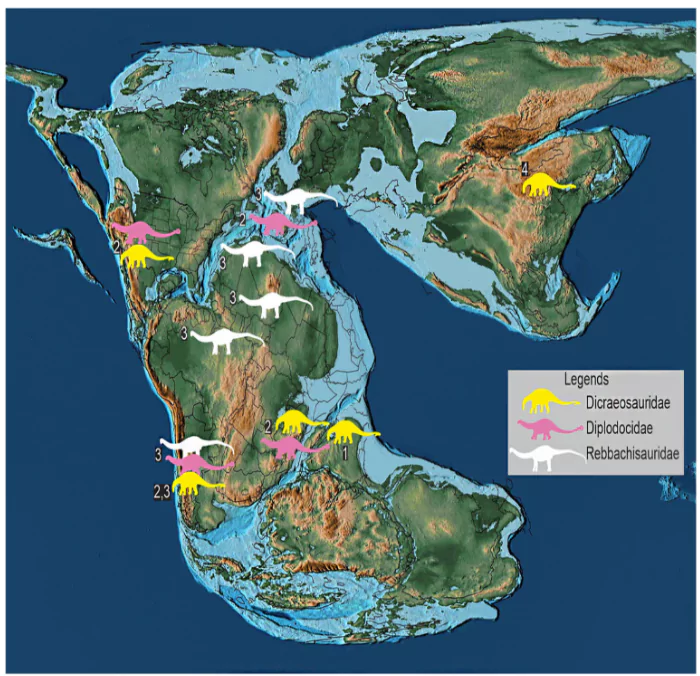
- Dinosaurs likely first appeared in the areas that are now the Sahara Desert and Amazon Rainforest.
- At that time, all the earth’s continents were part of the giant supercontinent Pangaea.
- During the Triassic Period, these areas were part of the southern portion of a massive landmass called Gondwana.
- The first dinosaur fossils on Earth were discovered in 1819 by British fossil hunter William Buckland
- Oldest Fossils Found:
- Examples include:
- Eoraptor and Herrerasaurus (Argentina).
- Saturnalia (Brazil).
- Mbiresaurus (Zimbabwe).
- These fossils are about 230 million years old, showing dinosaurs had already evolved by then.
How Did Dinosaurs Evolve?
- Mass Extinction Event: Dinosaurs evolved from primitive reptiles after a mass-extinction event about 252 million years ago caused by volcanic activity at the end of the Permian Period.
- Early Days:
- Dinosaurs started small and were less important in their ecosystems.
- Earlier, Larger animals, like crocodile relatives and mammal-like creatures, were dominant.
- Around 201 million years ago, a mass extinction wiped out many of their competitors.
- Dinosaurs adapted and became the leading land animals.
- Unique Traits:
- Dinosaurs stood upright, with legs under their bodies for efficient movement.
- They had specialized hips, bodies designed for speed and agility, and teeth suited to their diets.
- Examples of Early Dinosaurs:
- Herrerasaurus: A 6-meter-long predator.
- Eoraptor: A small, dog-sized omnivore.
- These specialised traits didn’t appear overnight. They evolved gradually over millions of years from older, more primitive reptiles.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Challenges in Tracing Dinosaur Origins
- Harsh Triassic Environment
- Extreme Climate: Around 245-230 million years ago, equatorial regions experienced extremely hot and dry conditions.
- These areas were characterized by vast deserts, savannahs, and frequent wildfires, creating a challenging environment for life.
- Survival Assumptions: It was previously thought that such harsh conditions would prevent dinosaurs from surviving and thriving.
- However, evidence suggests that early dinosaurs and their relatives were able to adapt to these extreme environments.
- Scarce Fossils
- Poor Preservation Conditions: The conditions during the Triassic period were not ideal for fossil preservation. High temperatures, aridity, and erosion reduced the chances of organic material being buried and fossilized.
- Difficult Exploration: Dense forests and vast deserts, such as those in the Amazon and Sahara, make fossil exploration challenging.
- These areas are often remote and difficult to access, hindering paleontological research.
- Fragmentary Evidence: Fossils from this period are rare and often fragmentary, making it difficult to piece together a complete picture of early dinosaur evolution.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 27 Jan 2025
27 Jan 2025

