3 Papers published in the journal Nature by a team called eDyNAmiC explored how ecDNA is formed and contributes to the progression of cancer and drug resistance.
About the Study
- Subject:
- First Study: Mutation patterns in tumours before and after the formation of ecDNA was analysed to identify the role of certain factors like smoking, exposure to certain substances, and genetic mutations triggering DNA damage leading to the formation of ecDNA.
- Second Study: The violation of the Mendel’s third law of independent assortment by reporting that ecDNA is passed on in clusters to the daughter cells during cell division.
- Mendel’s Third Law: The genes on the same chromosome are inherited together while those on different chromosomes are distributed independently of one another, usually when cells divide.
- When cells divide, they duplicate the chromosomes and distribute it equally among their daughter cells.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- DNA is the genetic material present in the nuclei of cells as a double helix, supercoiled to form chromosomes along with intercalated proteins.
Types of DNA
- Autosomal DNA: It is also known as nuclear DNA, this DNA is passed down from both parents and is packaged into 22 pairs of chromosomes.
- Chromosomal DNA: It is a single, long DNA molecule containing many genes.
- The DNA in chromosomes is tightly coiled around proteins called histones, which help package and control the DNA so it fits inside the cell.
- Mitochondrial DNA: This DNA is found in the mitochondria (organelles that produce energy for the cell). It is passed down only from the mother and replicates separately from the rest of the cell.
- A-DNA: A right-handed double helix that forms when DNA is dehydrated or when protein binds to it. This form protects DNA from extreme conditions.
- B-DNA: The most common form of DNA, with a right-handed double helix structure.
- Z-DNA: A left-handed double helix with a zigzag pattern.
- It is found in bacteria, viruses, and eukaryotes, and is believed to play a role in gene regulation
|
-
- Third Study: It uncovered a potential weakness in tumours that relies on ecDNA leading to a conflict between the cellular machinery involved in making RNA and the activity of cancer cells that leads to DNA damage.
- Samples: Samples from nearly 15,000 cancer patients from U.K.’s 100,000 Genomes Project, covering 39 tumour types were analysed for the study.
- Method Used: Computational tools like AmpliconArchitect followed by AmpliconClassifier were used to identify ecDNA from whole-genome sequencing data and the Findings were validated using a method called fluorescence in-situ hybridisation (or FISH)
- FISH Technique specifically looks for certain cancer-related genes in tissue samples.
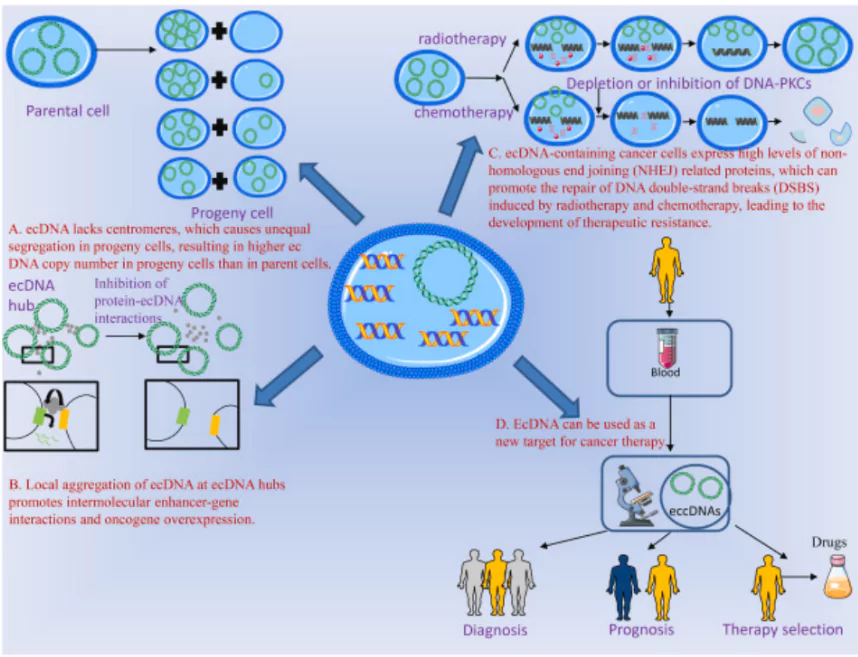
- Need: ecDNA is a major contributor to treatment resistance and poor outcome for patients with cancer
- Findings:
- Widespread Presence: It was found that ecDNA was present in about 17% of tumour samples but more so in liposarcomas, brain tumours, and breast cancers.
- The prevalence of ecDNA rose after treatments like chemotherapy, and correlated with metastasis and worse patient outcomes.
- The “Jackpot Effect”: The clustering of ecDNA in daughter cells gives cancer cells an advantage as it allows them to enhance gene interactions, support cancer growth, and preserve favourable genetic combinations over multiple life-cycles.
- Fundamental shift in Genetics Understanding: It overturns the idea that gene inheritance is entirely random when the genes are not linked by DNA strands
- It was reported that the transcription process (from DNA to RNA) facilitates the coordinated segregation of ecDNA during cell division.
- New Cancer Treatment: A drug (BBI-2779) was used to block the CHK1 Protein found that the drug selectively killed cancer cells with ecDNA, significantly reducing the number of tumours in mice with stomach cancer.
- It can provide new treatment options particularly for patients with ecDNA-driven cancers, such as glioblastoma and ovarian and lung cancers.
About ecDNA
- Extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) is a type of DNA that exists outside of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell.
- In normal human cells, the nucleus contains 23 pairs of chromosomes that enclose the DNA.
- Discovery: ecDNA was discovered in the 1960s when its presence was found in only 1.4% of tumors.
- Types: ecDNA is categorized into five types based on its sequence and size,
- Small polydispersed DNA (spcDNA), MicroDNA, t-circle/c-circle, ERC, and ecDNA
- Structure: Individual ecDNAs are large (typically greater than 500 kilobases), mobile, gene-containing (and regulatory-region-containing) circular DNA particles that can be found in the nuclei of many cancer cells
- Segregation: ecDNA lacks centromeres and segregates randomly or asymmetrically during cell division
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
- ecDNA and Cancer Biology:
- Prevalence: A study published in 2017 reveals that ecDNA is present in nearly 40% of cancer cell lines and in up to 90% of patient-derived brain tumour samples making its study pivotal for understanding cancer biology.
- Oncogenes: ecDNA is a common origin for amplified oncogenes (mutated genes capable of causing cancer) across human cancer and its presence in tumours often contain multiple copies of oncogenes that are required to activate tumour growth.
- Presence: Oncogenes are not present in chromosomes as ecDNA moves freely unlike chromosomal DNA (It is fixed within specific regions in the cell) and interacts with other ecDNA to form hubs (concentrated zones where oncogenes are expressed more)
- Cancer Growth: A 2021 study has found that when cells transcribe ecDNA to mRNA, the process causes specific oncogenes to become four-times more common in the cell than if the DNA came from the chromosomes.
- This anomaly enhances the potential to accelerate the Evolution of Tumours and help the cancer resist drugs.
Additional Reading: About DNA
![]() 4 Dec 2024
4 Dec 2024

