Recently, International Fatty Liver Day 2024 was celebrated as in the month of June.
International Fatty Liver Day 2024
- Theme for International Fatty Liver Day 2024 – ‘Act Now, Screen Today‘.
 This special day highlights a fatty liver disease that impacts about 1 in 4 people worldwide.
This special day highlights a fatty liver disease that impacts about 1 in 4 people worldwide.
About Fatty Liver Disease
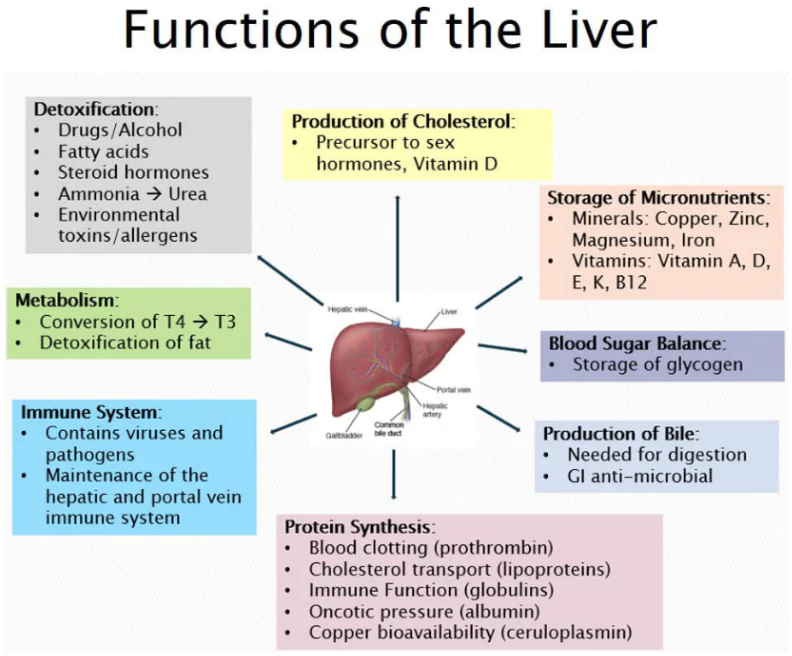
Fatty liver disease occurs when fat accumulates in the liver.
- The liver is the largest organ inside the body.
- It is closely connected to metabolic health, cardiac health, and cancer risk.
- Impact of fat: Excessive fat in the liver can lead to inflammation, causing damage and scarring.
- In severe situations, this scarring can result in liver failure.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Incidence of Fatty Liver Disease in India
- According to an AIIMS study, In India, Around 38% of Indians have fatty liver or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- In another AIIMS study, there were reports of 67 per cent deaths among patients with antituberculosis drug-related acute liver failure.
- This disease is affecting nearly 35 per cent of the children too.
|
- Reclassification: The condition is now known as ‘Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease’ (MASLD).
- Global Prevalence: This disease affects 25-30% of the global population.
- MASLD is closely linked to obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- India’s Statistics: In 2022, a study showed that 38.6% of Indian adults and 36% of obese children had fatty liver.
- There are two types of this disease.
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): It affects individuals who consume little to no alcohol.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Alcoholic Steatohepatitis): This disease arises when Fat builds up due to excessive alcohol consumption.
Risk Factors for Fatty Liver Disease
- Obesity: Being overweight, especially around the abdomen, raises the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Resistance: People with diabetes or pre-diabetes are more prone to developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Insulin Production: Excess glucose leads to high insulin levels, causing insulin resistance.
- Fat Storage: Insulin resistance promotes the storage of fatty acids in the liver, leading to fatty liver disease.
- Diet and Lifestyle: A diet high in sugar and processed foods.
- Physical Activity: Low levels of physical activity contribute to fatty liver.
- Digestive Issues: Problems with digestion also play a role.
- High Blood Cholesterol and Triglycerides
- Blood Lipids: Elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels can lead to fatty liver.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic tendency to develop fatty liver.
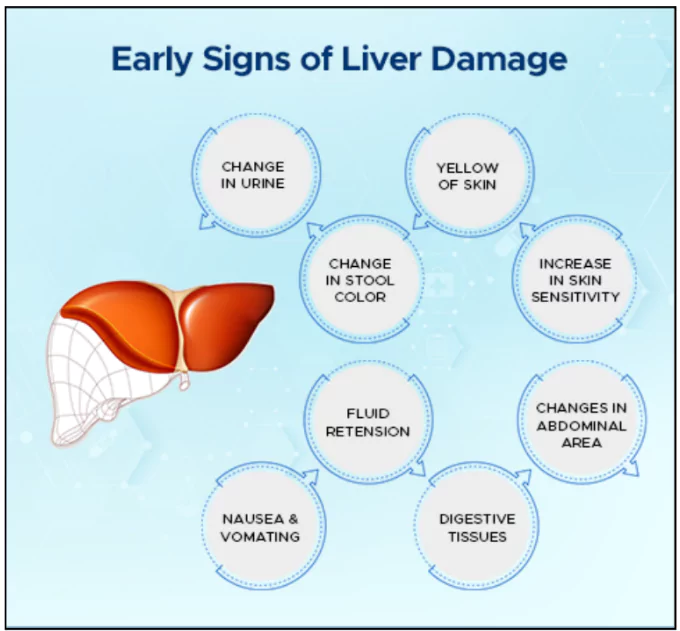
Disease Progression: Over time, fatty liver can develop into steatohepatitis and cirrhosis, which may require a liver transplant.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
![]() 14 Jun 2024
14 Jun 2024
 This special day highlights a fatty liver disease that impacts about 1 in 4 people worldwide.
This special day highlights a fatty liver disease that impacts about 1 in 4 people worldwide.