Astronomers have discovered winds blowing at an astonishing 33,000 km/hour on WASP-127b, making them the fastest jet-stream winds ever observed on any known planet.
- This massive gaseous planet is located about 520 light-years away in the Milky Way galaxy and orbits its star very closely.
What Are Jet Streams?
- Jet streams are narrow bands of fast-moving winds that flow from west to east in the atmosphere.
- This stream blows with winds of more than 442 km per hour, but they are not the strongest in your solar system.
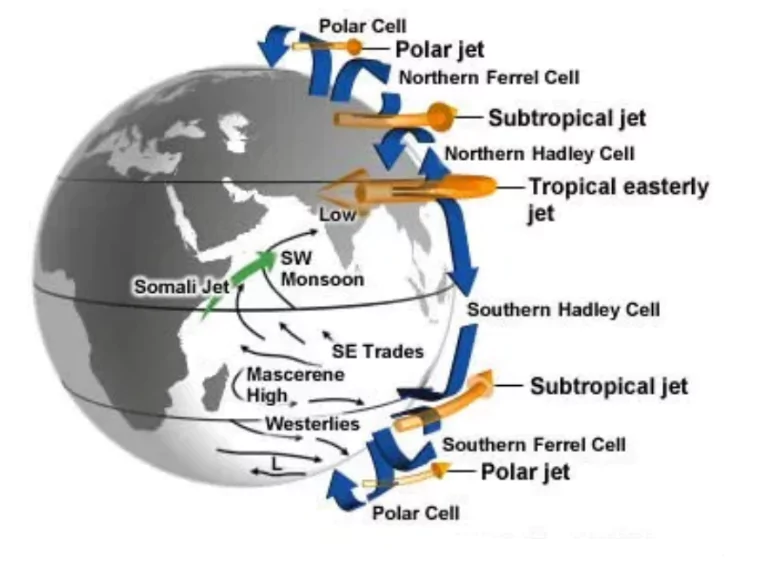
| How do jet streams affect the climate of India?
Jet streams affect the climate of India in various ways.
- Subtropical Jet Stream (STJ) affect the onset and withdrawal of the Indian monsoon.
- In summer, STJ shifts northward due to which monsoon winds bring heavy rainfall.
- In winter, STJ shifts southward which causes drier conditions.
- Westerly jet streams create western disturbances which cause winter rains in the north and north-western part of India.
- These disturbances play a significant role in agriculture by providing moisture during winter month.
- Cyclonic activity: Troughs and ridges created by jet streams can cause cyclonic activity, causing storms and heavy rainfall.
- Troughs are elongated regions of low pressure.
- Ridges are elongated region of high pressure.
|
- The Earth has four main jet streams:
- Two polar jet streams near the north and south poles.
- Two subtropical jet streams near the equator.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Why Do Jet Streams Form?
- Jet streams are created when warm air meets cold air in the atmosphere.
- The Sun heats the Earth unevenly:
- The equator is warmer because it gets more sunlight.
- The poles are colder due to less sunlight.
- When warm air rises and cold air sinks, the movement of air creates strong winds high in the atmosphere, forming jet streams.
What is WASP-127b?
- WASP-127b is a type of exoplanet called a hot Jupiter, which is a gas giant orbiting very close to its star.
- Discovery: 2016 Composition – Mainly of hydrogen and helium.It is about 30% larger than Jupiter but has only 16% of Jupiter’s mass, making it very “puffy.”
Exoplanet
- An exoplanet is a planet located outside our solar system.
- While most exoplanets orbit other stars, there are also some that drift through space without orbiting a star, known as rogue planets.
|
- The planet orbits its star once every four days at a distance that is only 5% of the Earth-Sun distance.
- This makes it extremely hot, with temperatures around 1,127°C (2,060°F).
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Unique Features of WASP-127b
- Tidally Locked Rotation
- Similar to how the moon always shows the same side to Earth, WASP-127b is tidally locked.
- One side of the planet permanently faces its star, known as the day side, while the other side remains in perpetual darkness, called the night side.
- Atmospheric Composition
- The planet’s atmosphere is primarily made up of hydrogen and helium, the lightest gases.
- It also contains traces of more complex molecules such as water and carbon monoxide, detected through advanced research.
- Temperature Variation
- The polar regions of WASP-127b are cooler compared to its equatorial regions, which experience intense heat due to constant exposure to the star’s radiation.
How Does WASP-127b Compare to Other Planets?
- Other Exoplanets: Higher wind speeds have been observed on two other exoplanets, but those winds typically flow from the day side to the night side.
- Unique Wind Pattern: WASP-127b’s winds are unique because they circle around the entire planet at the equator.
Why Are Winds So Fast on WASP-127b?
Several factors cause the intense wind speeds on WASP-127b:
- Intense Heat from the Host Star
- The planet is very close to its star, receiving strong radiation that heats its atmosphere.
- This energy creates temperature differences that drive strong winds.
- Tidal Locking
- The day side is constantly heated, while the night side remains cool.
- This creates a thermal imbalance, causing air to move rapidly.
- Low Mass and High Size
- WASP-127b is very large but not very dense, making its atmosphere “fluffy.”
- This allows wind to circulate freely and at high speeds.
- Other Dynamic Factors
- Wind patterns are shaped by complex interactions between heat, pressure, and the planet’s rotation.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Why Is This Discovery Important?
Understanding the extreme winds on WASP-127b helps astronomers learn more about:
- Atmospheric Dynamics: How atmospheres behave under different conditions.
- Planet Formation and Evolution: Insights into how such puffed-up planets come to exist.
- Exoplanet Habitability: Studying diverse exoplanets expands our knowledge about the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 28 Jan 2025
28 Jan 2025

