Context: The State of Finance for Nature report has been recently released by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
About the State of Finance for Nature Report
- Tracking finance flow to NbS: The State of Finance for Nature report tracks finance flows to nature-based solutions (NbS) and compares them with the finance needed to maximize the potential of NbS to help tackle climate, biodiversity, and degradation challenges.
- Tracking NbS Implementation: The report focuses on the current state of NbS implementation and financing, as well as the amount of funding required to meet specific Rio targets.
- Ex-limiting global warming to 1.5°C, protecting 30% of land and sea by 2030 (30×30 target), and achieving land degradation neutrality (LDN) by 2030.
Key Highlights from the State of Finance for Nature Report
- Private nature-negative finance:
- Nature Negative Finance Flows: It estimates the scale of nature-negative finance flows from both public and private sector sources globally which is around US$7 trillion per year.
- Private finance flows having a direct negative impact on nature include US$5 trillion, which is 140 times larger than private investments into NbS.
- Nature-negative financial flows refer to finance flows for activities that could potentially hurt nature.
- Industries contributing to most of the negative financial flows: Construction, electric utilities, real estate, oil and gas, and food and tobacco.
- 43 percent of financing that harmed nature was associated with the destruction of forests, wetlands, and other natural habitats.
- Public nature negative finance:
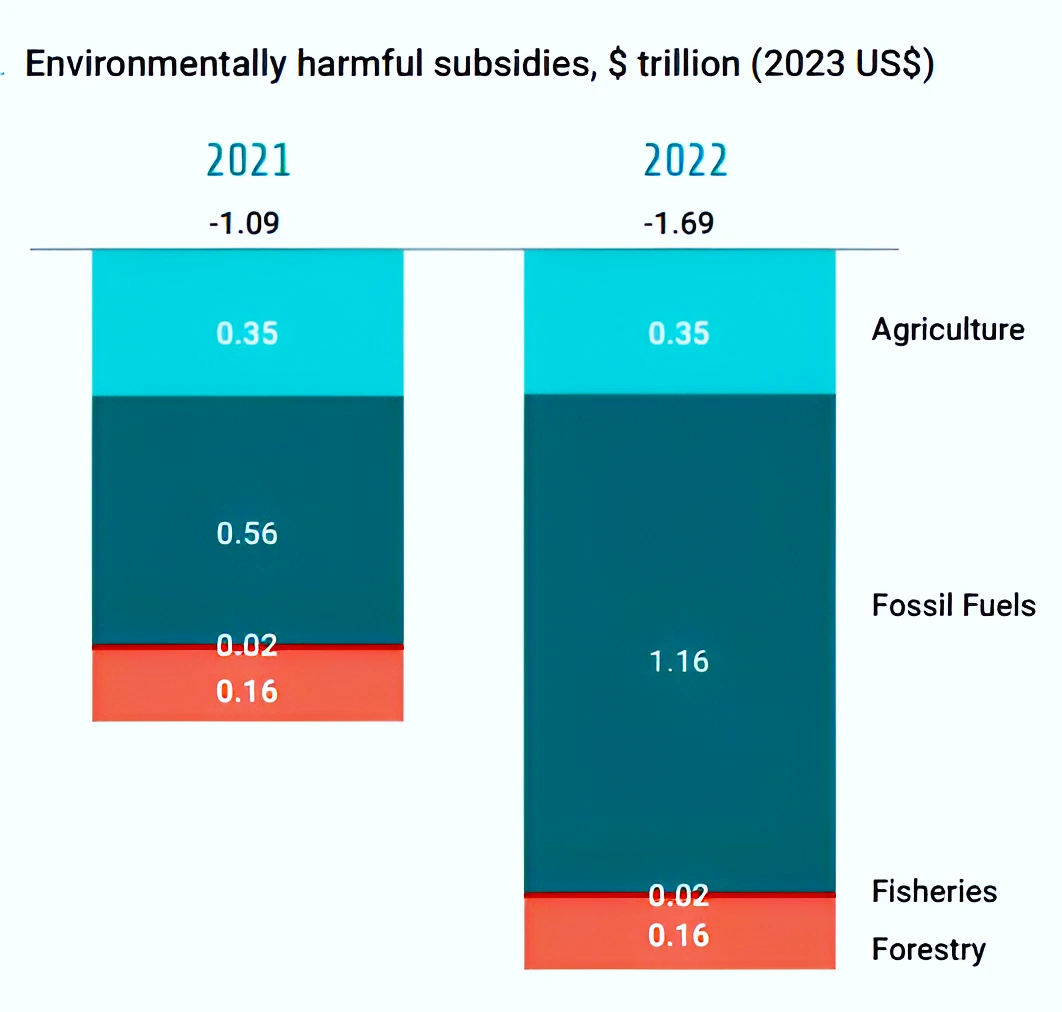
- Increase in Environmentally Harmful Subsidies: They have increased by 55 percent to US$1.7 trillion since the last report which is driven by fiscal support for fossil fuel consumption.
- Almost 90 percent of tracked negative public flows (EHS) are directed to fossil fuels (66 percent) and agriculture (20 percent).
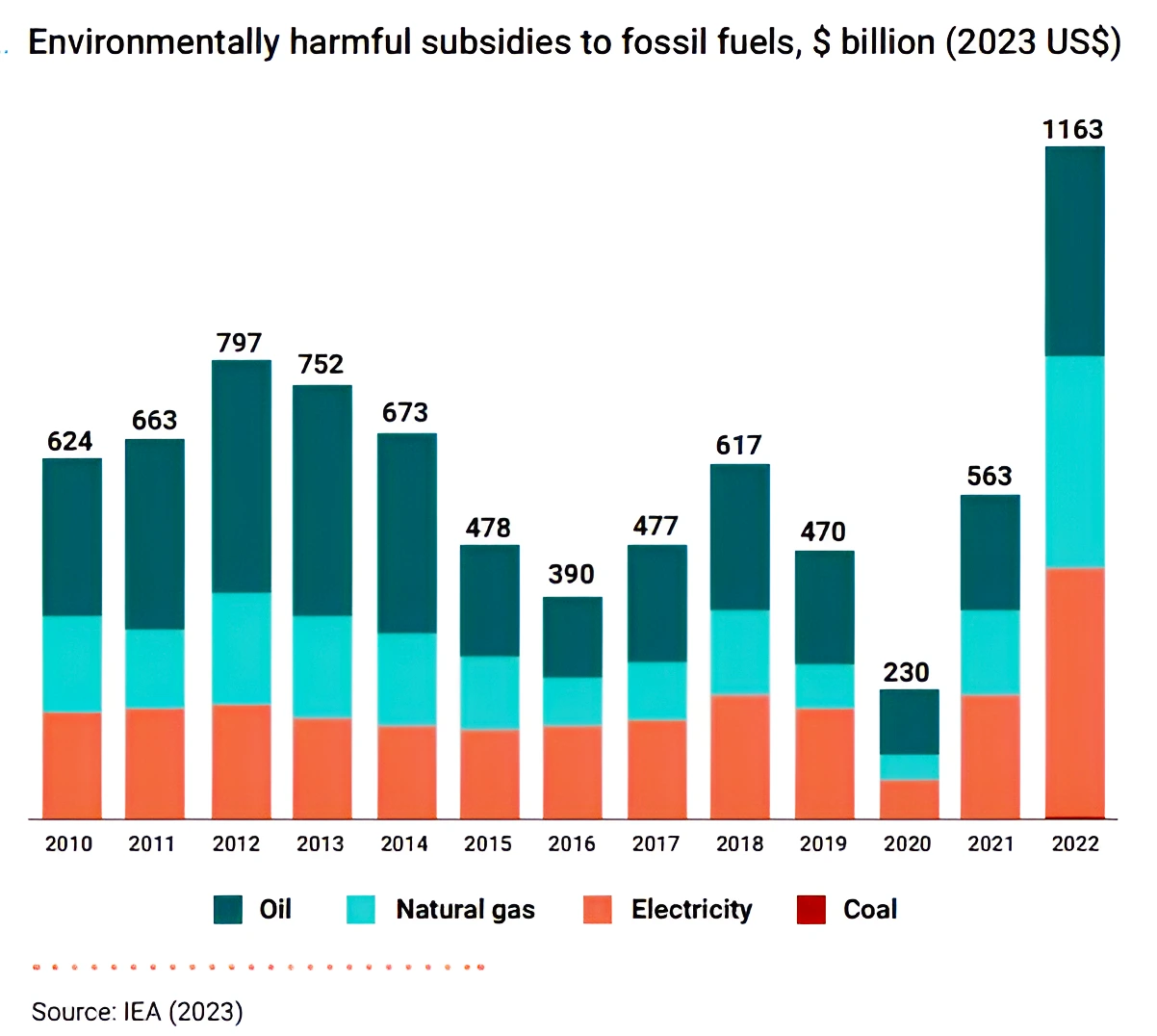
- Fossil fuel subsidies to consumers doubled from US$563 billion in 2021 to US$1,163 billion in 2022.
- Current finance flows to NbS:
- Underfunding of NbS: Current finance flows to NbS is around US$200 billion which is only a third of the levels needed to reach climate, biodiversity, and land degradation targets by 2030.
- Poor Growth in Financing: NbS financing has only increased by 11% since the 2022 edition.
- The combined impact of public and private negative finance flows undermines potential increases in finance for NbS.
- Source of NbS Funding: Currently, 82% of NbS’s funding comes from governments.
- Future investment needs and opportunities:
- Realignment of nature-negative finance flows: Due to their massive scale, realigning nature-negative finance flows is the most effective way to prevent and stop nature loss. Thus, more action is needed to repurpose harmful subsidies.
- As per the report, annual finance flow towards NbS should be doubled from $200 billion to $436 billion by 2025 and almost tripled to $542 billion by 2030 to help achieve climate, biodiversity, and land degradation targets.
- Regulating Mechanism: Governments need to put in place regulations and economic incentives to turn private finance flows away from nature-harming activities and toward nature and nature-based solutions.
Must Read: Loss And Damage Fund Approved At COP28 Summit
What are Nature-based Solutions (NbS)?
- Nature-based solutions (NbS) are defined as per the United Nations Environment Assembly 5 (UNEA5) as: “actions to protect, conserve, restore, sustainably use and manage natural or modified ecosystems.
- UNEA is the governing body of the UN Environment Program.
Nature-based Solutions (NbS): Significance
- Addressing Climate Change: NbS are effective instruments for addressing biodiversity loss and climate change while improving ecosystem resilience and human well-being.
- Certain NbS can benefit humans, ecosystems, biodiversity, and the climate all at once.
- For example: The improved management of peatlands has disproportionate benefits for climate change mitigation and adaptation while providing critical habitat for species and maintaining soil fertility and other critical ecosystem services that support human wellbeing.
- Peatlands contain up to one-third of the world’s soil carbon while covering only three to four percent of its land area.
- Cost Effective: They provide critical investment opportunities as they are cost-effective and provide multiple benefits.
State of Finance for Nature Report: Recommendations
- Boosting NbS Investments: Increase domestic expenditure on NbS, particularly on NbS providing public goods.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Investing in sustainable supply chains, prioritizing conservation and regenerative practices in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries.
- Develop Nature as an Asset: Develop nature as an asset class to create non-traditional revenue streams, for example, biodiversity and carbon credits.
News Source: State of Finance for Nature (SFN)
![]() 12 Dec 2023
12 Dec 2023

