Prime Minister Inaugurated the First Bodo Mahotsav in New Delhi to celebrate the language, literature, and culture of the Bodo community.
Prime Minister’s Remarks at the Festival
- He declared the North East, including Bodoland, as India’s Ashtalakshmi, a region of prosperity.
- He also emphasised mutual trust and efforts to integrate former conflict zones into the mainstream
- He also highlighted advancements in healthcare, including new medical colleges and hospitals in Assam.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Bodoland Festival
- The Bodoland Mahotsav is a cultural festival celebrating the language, literature, and culture of the Bodo community.
- Objective of the Festival: To strengthen peace and unity within the Bodo community building a vibrant Bodo society.
- Theme: “Peace and Harmony for Prosperous Bharat.”
- It marks the first festival of unity post the 2020 Bodo Peace Accord, which ended 50 years of conflict.
- Cultural Contributions: GI-tagged products like Dokhona, Gamsa, and Karai-Dakhini showcased.
- It will also help in promoting weaving and sericulture through the Bodoland Sericulture Mission.
- Tourism Boost: Focus on Manas National Park and other natural attractions for creating employment.
- Sessions & Themes to be discussed at the Festival:
- “The Rich Bodo Culture, Tradition, and Literature Contributing Towards Indian Heritage.”
- “Challenges and Opportunities of Mother Tongue Medium-of-Instruction Under NEP 2020.”
- Discussions on cultural tourism and building a “Vibrant Bodoland.”
- Attendees: Over 5,000 cultural and linguistic enthusiasts from India, Nepal, Bhutan, and other nations.
About the Bodo Tribe
- Origin: The Bodos (or Boros) are an ethnolinguistic group from Assam.
- Geographical Spread: Primarily reside in the Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR) of Assam.
- Also found in Bangladesh, Nepal, and other North-East Indian states.
- Scheduled Tribe (ST) Status: Recognized as “Boro” and “Borokachari” under The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
- Language: Bodo language belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family. It is included in the 8th Schedule of the Indian Constitution, granting it official recognition.
- Governance in BTR: Administered by the Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC), established under the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- Bodo Peace Accord (2020): A landmark agreement between the Central Government, the Assam State Government, and various Bodo groups.
- It ended decades of violence and conflict.
- It also established a framework for peace, development, and integration of the region.
- Achievements in Bodoland (Post-Accord):
- Development of infrastructure for education, health, and culture.
- Rehabilitation of over 4,000 former cadres of the National Democratic Front of Bodoland.Over ₹700 crore spent on development projects, with ₹1500 crore special packages from the Central Government.
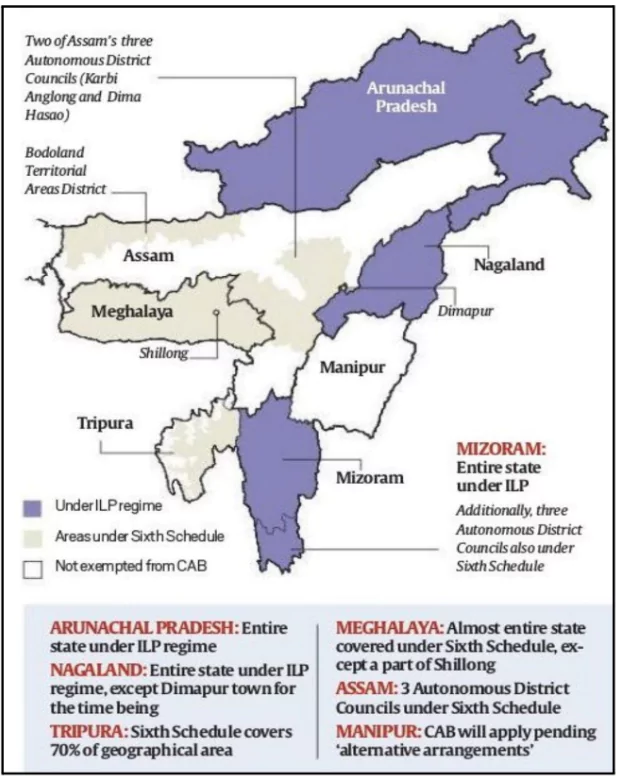
Sixth Schedule of Indian Constitution
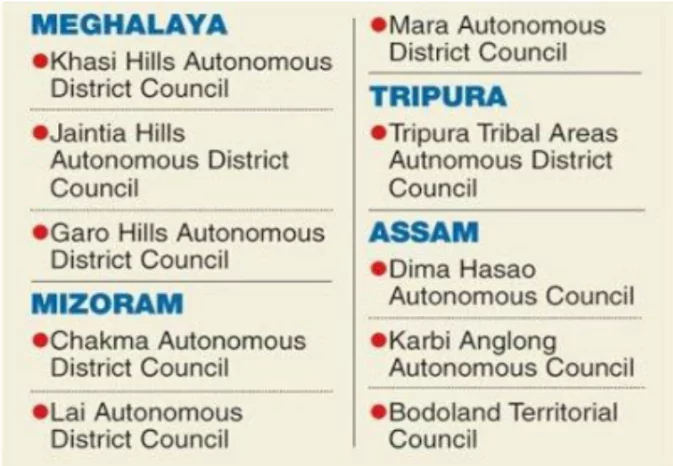
- The Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution provides for the establishment of Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) in certain tribal areas.
- Article 244A: outlines the establishment of autonomous districts and councils within the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- Article 244B: It defines the powers, functions, and composition of the ADC.
- Article 244C: It discusses the administrative, judicial, and financial powers of the ADC.
- It empowers tribal communities to govern themselves and protect their unique cultural identity.
- These ADCs are designed to safeguard the rights and cultural identity of tribal communities.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Key Functions of ADCs
- Legislative Powers: ADCs have the authority to make laws on various matters such as land, forest, water resources, agriculture, and social customs.
 Executive Powers: They execute development schemes, welfare programs, and administer local governance.
Executive Powers: They execute development schemes, welfare programs, and administer local governance.- Judicial Powers: ADCs can establish local courts to resolve disputes based on customary laws and usages.
- Financial Powers: ADCs have financial autonomy, enabling them to collect taxes and manage their own finances.
- Cultural Preservation: They promote and preserve the cultural heritage of tribal communities.
- Development: ADCs play a crucial role in the socio-economic development of their respective regions.
![]() 16 Nov 2024
16 Nov 2024


 Executive Powers: They execute development schemes, welfare programs, and administer local governance.
Executive Powers: They execute development schemes, welfare programs, and administer local governance.