Fiscal deficit management is crucial in the current context of declining household financial savings.
Fiscal Deficit
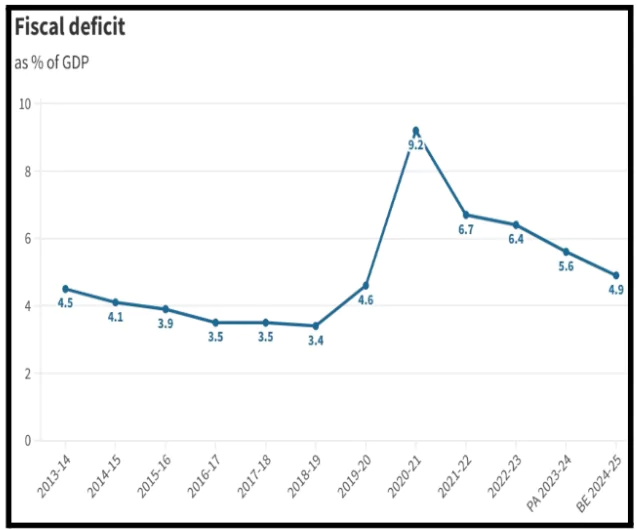
- About: Fiscal deficit is defined as excess of total expenditure over total receipts excluding borrowings during a fiscal year.
- It reflects the borrowing requirements of the government for financing the expenditure including interest payments.
- Formula:
- Fiscal deficit = Revenue expenditure + capital expenditure – Revenue receipts – capital Receipts excluding borrowings.
- Indicator of Future Liabilities: It is an indicator of the increase in future liabilities of the government on interest payment and loan repayment.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Fiscal Deficit Target in the Budget 2024-25
- Fiscal Deficit Reduction Goal: The government aims to reduce the fiscal deficit to 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, down from the budgeted 4.9% for 2024-25.
- This is part of a broader goal to reduce the debt-GDP ratio, which is projected to be 54% in 2025-26.
Debt-GDP Ratio
- About: The debt-GDP ratio measures the government’s total debt compared to the country’s economic output (GDP).
- Formula: Total debt/total GDP
- To lower the debt-GDP ratio, the government needs to reduce its fiscal deficit
- High Debt-GDP Ratio Impact: If the debt-GDP ratio is high, a large portion of the government’s revenue goes towards paying interest on the debt.
|
- Long-term Debt Management: From 2026-27 onwards, the government’s goal is to maintain a fiscal deficit that ensures the Central government’s debt follows a declining trend as a percentage of GDP.
- Future Goals: The government aims to keep reducing the debt-GDP ratio after 2025-26 but hasn’t set a specific target or timeline.
- This means it might not meet the previous target of 40% debt-GDP ratio set by the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act.
Issues with respect to Increasing Fiscal Deficit
Government expenditures exceeding revenue by a high margin can lead to a difficult situation.
- Impact on Inflation: A persistently high fiscal deficit can lead to higher inflation as the government may resort to printing new money to fund its deficit.
- Challenges in Public Debt Management: A high fiscal deficit can hinder the government’s ability to manage its overall public debt effectively.
- The fiscal imbalance results in a significant rise in public debt as the government borrows more to cover the shortfall.
- Risk of Balance of Payments Crisis: The combination of a large deficit and rising debt creates pressure on the country’s foreign reserves, leading to a balance of payments crisis.
- Example: In the 1980s, rising fiscal deficit accompanied by rising government debt led to a difficult balance of payments situation and a high ratio of interest payment to revenue receipts.
- Rising Interest Payments: The ratio of interest payments to revenue receipts surges, limiting the government’s ability to fund other priorities.
- International Comparison: Between 2015-19, the interest payment to revenue receipts ratio averaged 5.5% for Japan, 6.6% for the UK, and 8.5% for the US.
- In contrast, India’s average ratio was much higher at 24% during 2015-16 to 2019-20.
- Increased Borrowing for Development Expenditures: To meet essential developmental expenditures, the government is forced to borrow progressively more, further deepening the fiscal strain.
- Crowding Out of Private Investment: A high fiscal deficit can lead to higher interest rates as the government competes with the private sector for borrowed funds.
- This “crowding out” effect can make borrowing more expensive for businesses, reducing private investment. Lower private investment can stifle economic growth and innovation, ultimately impacting job creation and productivity.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Government Initiative Related to Fiscal Deficit Management
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003:
- About: FRBM Act establishes financial discipline to reduce fiscal deficit. It aims to manage fiscal deficit, and maintain macroeconomic stability.
- Key features of the FRBM Act
- Medium Term Fiscal Policy Statement: It lays down the limits on the size of the budget deficits for three years and target for tax and non-tax receipts.
- It sets a target for the Centre’s annual fiscal deficit ratio (FDR) at 3% of gross domestic product (GDP).
- The states had to legislate their own FRBM Acts, limiting a state’s FD to 3% of its own GDP.
- FRBM Review Committee Report (Chairperson: N.K Singh)
- Debt as a Primary Target: The Committee suggested using debt as the primary target for fiscal policy.
- Debt to GDP Ratio: The FRBM Review Committee Report has recommended a debt to GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Governments.
- Borrowing from RBI: According to the suggestions of the committee, the government must not borrow from the RBI, except when:
- The Centre has to meet a temporary shortfall in receipts.
- RBI subscribes to government securities to finance any deviations.
- RBI purchases government securities from the secondary market.
- Fiscal Council: The Committee proposed to create an autonomous Fiscal Council with a Chairperson and two members appointed by the centre.
- Deviations: The Committee noted that under the FRBM Act, the government can deviate from the targets in case of a national calamity, national security or other exceptional circumstances notified by it.
|
Possible Solutions For Maintaining Fiscal Deficit
- Fiscal Consolidation: Implementing fiscal consolidation measures can help reduce the fiscal deficit and stabilize public debt through:
- Spending Cuts: Reducing government expenditures on non-essential programs and services.
- Revenue Increases: Raising taxes or improving the efficiency of tax collection.
- Debt Management: Refinancing or restructuring existing debt to manage interest payments and repayment schedules better.
- Maintaining a Fiscal Deficit of Around 3% of GDP: To support private investment and economic growth, it is important to maintain the fiscal deficit at around 3% of GDP. Exceeding this limit may lead to irresponsible borrowing and financial instability.
- Encouraging Household Savings and Investment: With household savings currently low (5.3% of GDP), efforts should focus on increasing household savings to free up funds for private investment.
- This would allow the government to manage its fiscal deficit without crowding out private investment.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Importance of Fiscal Consolidation
- Ensuring Sustainable Public Finances: Gradually reducing the fiscal deficit-to-GDP ratio helps maintain economic stability and ensures that public finances remain sustainable.
- It prevents excessive borrowing and debt accumulation, which could jeopardise future economic health.
- Implementing Prudent Fiscal Policies: Effective fiscal management involves expenditure rationalisation, revenue enhancement measures, and subsidy reforms.
- These actions help reduce reliance on borrowing and address fiscal imbalances, fostering a more balanced and sustainable budget.
- Promoting Investor Confidence: A disciplined approach to fiscal management enhances investor confidence.
- Lower fiscal deficits and stable debt levels signal a commitment to fiscal responsibility, making the country more attractive to both domestic and international investors.
|
![]() 7 Sep 2024
7 Sep 2024

