Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Flash floods, National Disaster Management Authority, India Meteorological Department (IMD) , Cloud Burst, Lhonak Lake, and Teesta River.
Relevancy for Mains: Glacial Lake Outburst Flood, Causes of flash floods, Climate Change, Disaster Management And Technology, etc. |
More on News about Flash flood
- The northern part of West Bengal shares a border with Sikkim, which witnessed a flash flood in the Teesta River, causing human casulaties.
- A report compiled by the Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority (SSDMA) in 2019 reported that the Lhonak Lake, at the height of 5,245 meters above sea level, was “highly vulnerable” to a GLOF event, which could cause extensive damage to life and property in downstream areas.

About Flash Floods
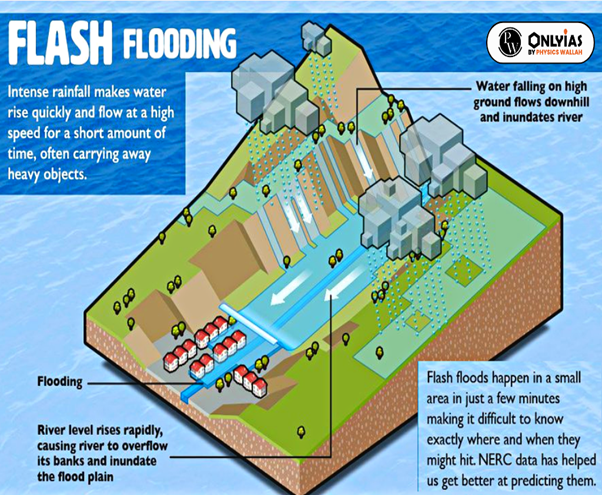
- Flash floods refer to a flood situation that occurs in a much shorter period i.e. six hours.
- Flash floods are the most dangerous because they combine a flood’s destructive power with incredible speed.
- Flash floods occur when heavy rainfall exceeds the ability of the ground to absorb it.
- They can happen within minutes of the causative rainfall, limiting the time available to warn and protect the public.
Causes of Flash Floods
- Exceeds Dam Capacity: Flash floods can be caused by factors other than rainfall. For example, when water exceeds the capacity of a dam, it can lead to flash floods.
- The release of water from the Chungthang dam led to a sudden increase in water levels up to 15-20 feet high in the Teesta River, causing Flash floods downstream.
- Cloud Bursts: In India, flash floods are often associated with cloud bursts, which are sudden, intense rainfall events that occur within a short duration.
- At least 13 were killed as flash floods hit Amarnath Yatra camp (in July 2022)
- Melting Glaciers: Himalayan states face the challenge of overflowing glacial lakes, formed due to the melting of glaciers.
- Cloud burst and GLOF in Kedarnath in 2013
- Landslide: Flash floods are accompanied by landslides, which are sudden movements of rock, boulders, earth or debris down a slope.
- In February 2021, flash floods killed nearly 200 people and washed away houses in Uttarakhand.
- Urbanization and Poor Drainage Systems: Urban areas with extensive concrete surfaces and inadequate drainage systems are prone to flash floods. Impervious surfaces prevent water from infiltrating the ground, resulting in rapid runoff and increased flood risk.
- Recent example of New Delhi Floods (2023).
- Deforestation and Soil Erosion: Removal of vegetation, such as forests or grasslands, can disrupt the natural water absorption capacity of the soil.
- Climate Change: Climate change is caused by human activities, resulting in erratic weather patterns and extreme weather events like hurricanes, etc., increasing flash floods.
ALSO READ: DISASTER MANAGEMENT IN INDIA
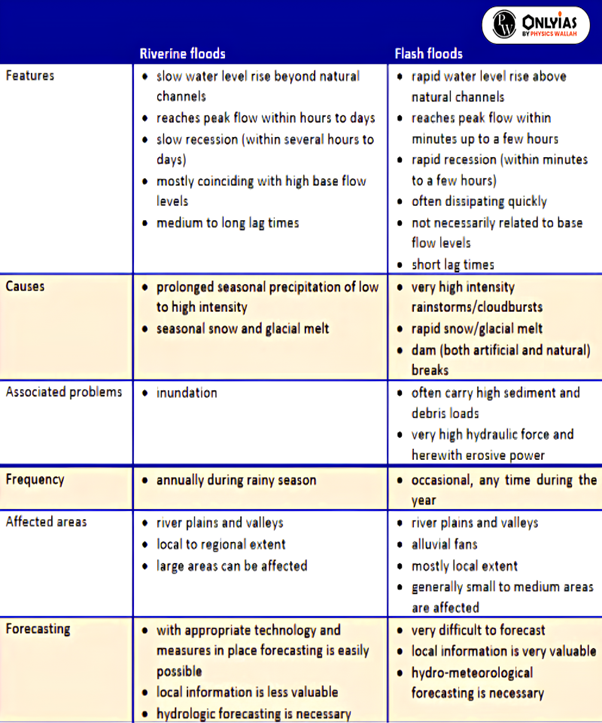
How are the Flash floods different from Riverine floods?
Impacts of Flash Floods
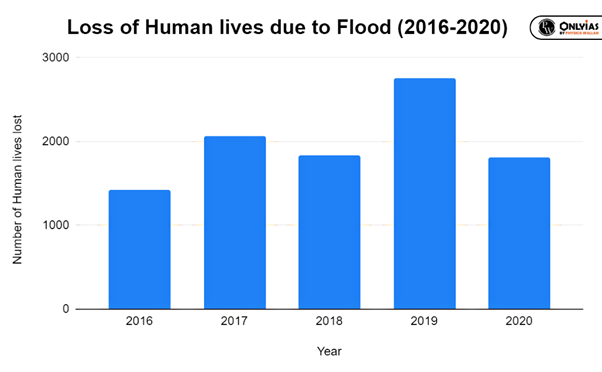
- Loss of life and injuries: Floodwaters’ sudden and rapid rise can catch people off guard, leading to drowning, injuries, and even fatalities (Refer Graph).
- Property damage: Flash floods can cause extensive damage to buildings, infrastructure, and personal property.
- Displacement and homelessness: When flash floods occur, people may be forced to evacuate their homes, leading to temporary or long-term displacement.
- 2.5 million internal displacements in India in 2022 (Displacement monitoring center-Geneva).
- Environmental impact: They can erode soil, wash away vegetation, and contaminate water sources. The sudden rush of water can disrupt ecosystems, endangering plant and animal life.
- Floods can threaten the survival of endangered species such as the Gangetic dolphin and the gharial in the Yamuna River.
- Infrastructure disruption: Flash floods can disrupt critical infrastructure systems such as power supply, water and sanitation facilities, transportation networks, and communication systems.
Initiatives taken in this direction
- IMD’s Flash Flood Guidance Services for South Asia:
- The Flash Flood Guidance is a robust system designed to provide real-time products, supporting the development of warnings for flash floods about 6-12 hours in advance.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has been using Doppler radars, flash flood forecasting and warning systems to predict the occurrence of flash floods.
- ISRO’s Landslide Atlas of India: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released the Landslide Atlas of India, a detailed guide identifying Landslide Hotspots in the country.
|
Way Forward
Flash floods are, by their characteristics, difficult to manage by traditional flood management approaches. Reducing the hazard requires the best mix of structural measures and non-structural measures to reduce impacts due to flash floods.
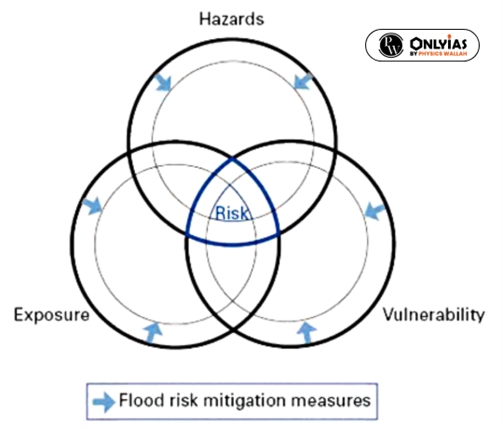
- Flash Flood Management:
- Before planning a flash flood management program, it is essential to identify risks caused by flash floods. The risks are composed of three elements – hazard, exposure, and vulnerability.
- Flash flood forecasting and warning: It play an essential role in the management of flash floods. However, it is still a challenge at times to give accurate and timely forecast and warning information to users.
- Geospatial Technologies: Appropriate spatial planning can help to reduce exposures and lessen the magnitude of flash flood hazards.
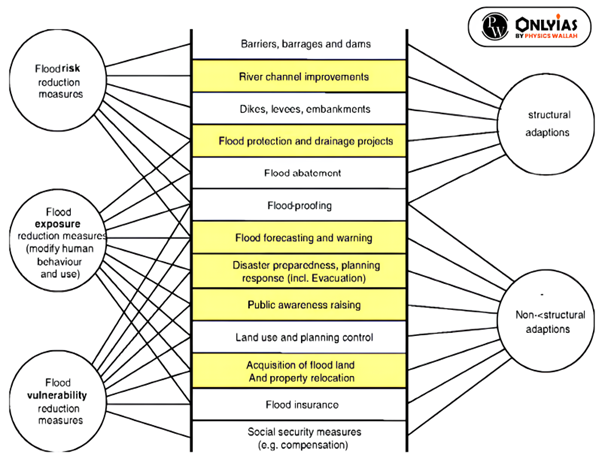
- Participation of All Stakeholders: Participatory approaches enable local communities to be aware of flash flood risks and this increases the efficiency of flash flood management.
- Legal and institutional framework: Especially when dealing with flash floods, the role of District/ Local disaster management organization is most important. This means local disaster management organizations should be given appropriate powers and responsibilities both legally and institutionally.
- Sustainable Land Management: Encouraging responsible land management practices, such as avoiding excessive excavation and deforestation, can help preserve the natural landscape and prevent soil erosion.
- State governments should prohibit the reclamation of the existing wetlands/ natural depressions.
Conclusion
The tragic cloud burst over Lhonak Lake in Sikkim, leading to devastating flash floods, underscores the urgent need for comprehensive disaster management strategies.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
Why are dewdrops not formed on a cloudy night? (2020)
- Clouds absorb the radiation released from the Earth’s surface.
- Clouds reflect back the Earth’s radiation.
- The Earth’s surface would have a low temperature on cloudy nights.
- Clouds deflect the blowing wind to ground level.
Ans: B |
![]() 5 Oct 2023
5 Oct 2023






