Months after suspending the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar border, the Union Home Ministry (MHA) has introduced a new protocol to regulate the movement of people living within 10 kilometers on either side of the largely unfenced international border.
Key Facts About Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB)
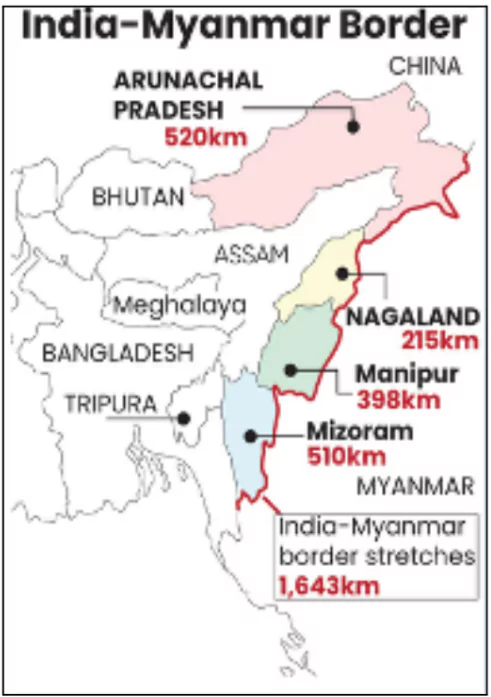
- Length and Coverage: Total length of 1,643 kilometers.
- It passes through Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Geographical Extent: Runs from the tripoint with China in the north to the tripoint with Bangladesh in the south.
- Security: Guarded by the Assam Rifles.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Free Movement Regime (FMR)
- FMR permits hill tribes from both India and Myanmar to travel freely within a specified range along the Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB).
- Border Crossing: Allowed with a border pass valid for one year, issued by a competent authority.
- Duration of Stay: Visitors can stay for up to two weeks per visit.
- Implementation: Initiated in 2018 as part of the Central Government’s Act East policy.
New Guidelines for Cross-Border Movement
- Border Pass: Issued by Assam Rifles for a stay of up to seven days in the neighboring country.
- Includes a photograph, QR code, and biometrics; must be returned upon completion of the visit.
- Entry Process: Individuals must report at designated points, complete documentation, and undergo security and health checks.
- Verification: Police will verify details on the border pass, and violations will lead to legal action.
- Implementation Phases: Initial activation of eight pilot entry points, followed by 14 more after biometric systems are installed, with the remainder dependent on infrastructure readiness.
Reasons for Tightening Guidelines
- Internal Security: Aimed at maintaining the demographic balance and preventing unregulated cross-border movement.
- Ethnic Violence in Manipur: Movement across the border has been linked to violence in Manipur, which has resulted in over 250 fatalities since May 2023.
- Political and Social Pressure: Influences from political and civil society groups prompted stricter measures rather than complete removal of the FMR.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Issues with Previous FMR Implementation
- Lack of Standardized Documentation: Absence of uniform border passes or recognition by both countries.
- Implementation Gaps: Border passes were managed by state officials instead of a unified protocol.
- Proposed Solutions: Plans include constructing a fence along the Indo-Myanmar border to enhance security and streamline movement.
![]() 26 Dec 2024
26 Dec 2024
