The Food Recovery to Avoid Methane Emissions (FRAME) shows that each food bank cuts greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions equal to removing 900 gasoline cars from the road for a year.
About FRAME
- It measures the emissions avoided by Work in Local Community Centers Redirecting food waste for human consumption.
- Developed by : The Global Food Banking Network (GFN), Global Methane Hub, and the Carbon Trust.
- The FRAME system was first tried in Mexico and Ecuador with six community-run food banks.
- The new FRAME tool allows food banks, recovery organizations, and private companies to measure and manage emissions from food recovery and redistribution.
What is a food bank?
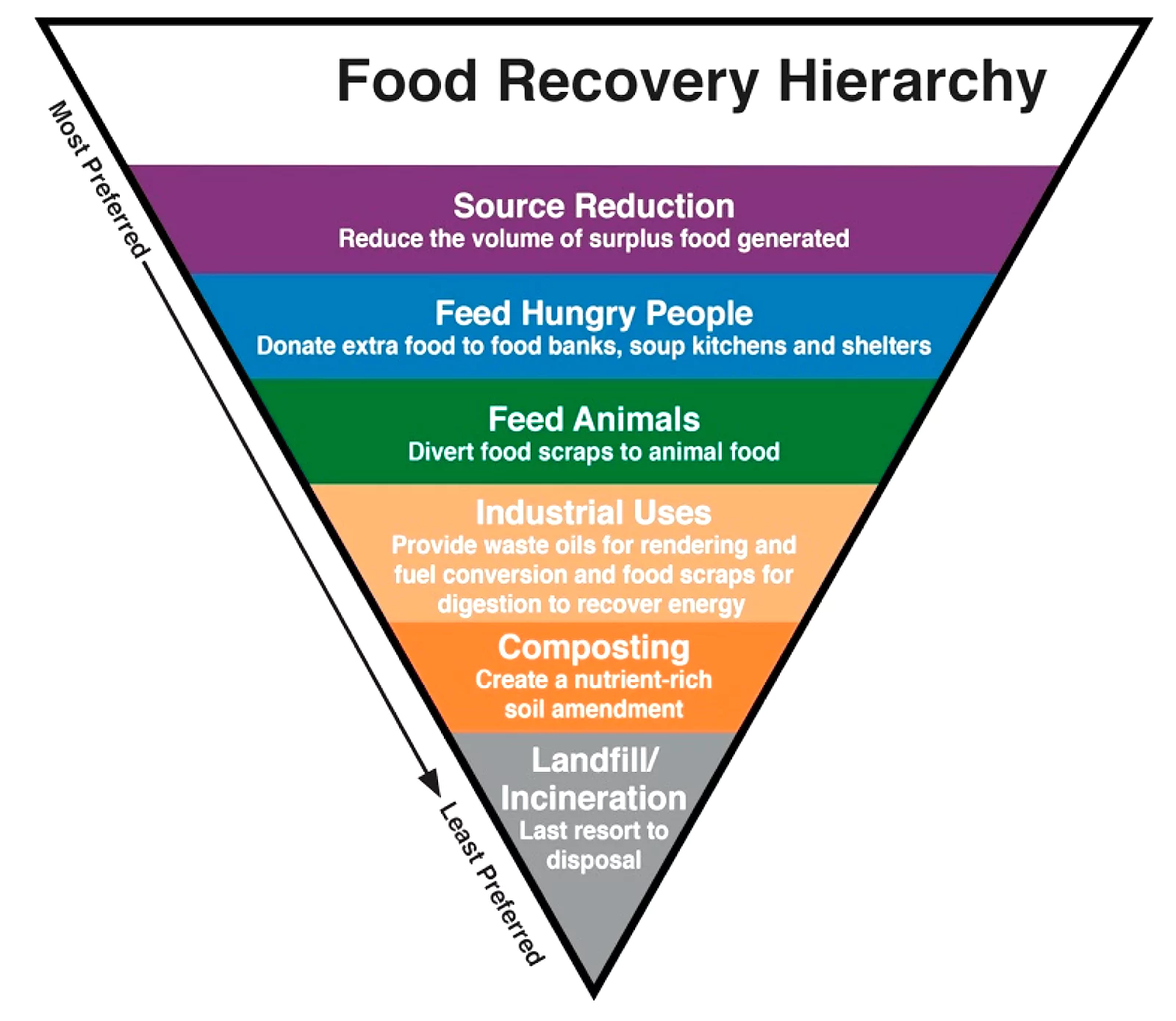
 A food bank is a non-profit organisation that provides food to people who struggle to afford enough food to avoid hunger.
A food bank is a non-profit organisation that provides food to people who struggle to afford enough food to avoid hunger.
- It usually works through other organisations like food pantries and soup kitchens, though some food banks directly distribute food themselves.
- Volunteer-driven Initiatives: Food banks recover surplus food from across the food supply chain and distribute it to people facing hunger through community organisations.
- Global Impact of Food Banks
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Food banks in india
In India, many operations are active for food distribution
- India FoodBanking Network (IFBN): This network aims to provide food assistance to vulnerable people.
- It unites all institutions and sectors such as non-profits, government, and academics together to work.
- Feeding India by Zomato: This initiative aims to distribute meal kits to economically impacted individuals.
- They also ensure that children get food through school lunch programs.
- No food waste: It is an organisation that aims to redistribute surplus food from weddings , parties, and events to the people in need of food.
|
-
- 2019 Results: Food banks globally avoided over 12 million tonnes of CO2 emissions in 2019, saved 75 million tonnes of surplus food from landfills, and served over 66 million people facing hunger.
- Contribution to UN’s Target 12.3
- Reducing Food Waste: Food banks help meet UN Target 12.3, which aims to halve food waste at retail and consumer levels and reduce losses in production and supply chains by 2030.
Food Loss and Waste (FLW) Statistics
- Global Food Loss: FAO estimates that 14% of food is lost post-harvest before reaching retailers.
- UNEP’s Food Waste Index Report shows an additional 17% is wasted at retail and consumer levels.
-
Methane from Food Waste
- Methane’s Role: Food waste in landfills produces methane, a gas that traps 80 times more heat than CO2 in the short term, increasing global warming.
-
FLW’s Contribution to Emissions
- 2017 FLW Emissions: In 2017, food loss and waste contributed 9.3 gigatonnes of CO2 emissions.
- Food systems account for a third of global GHG emissions, half of which come from FLW.
-
Global Hunger and Food Waste
-
- Hunger in 2023: Between 713 and 757 million people faced hunger in 2023.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Methane (CH4)
- Methane is a colorless, odorless, and flammable gas that makes up the majority of natural gas.
- Uses of Methane
- As a Fuel: Methane is commonly used to produce heat and light.
- In Manufacturing: It is also used in the creation of organic chemicals.
- Challenges
- Global warming: Methane contributes to global warming and affects the Earth’s climate.
- It is responsible for roughly one-third of current global warming.
- Storage Issues: Methane is difficult to capture and store because it remains in a gas form at standard temperature and pressure.
|
![]() 7 Sep 2024
7 Sep 2024

 A food bank is a non-profit organisation that provides food to people who struggle to afford enough food to avoid hunger.
A food bank is a non-profit organisation that provides food to people who struggle to afford enough food to avoid hunger. 