Irradiation technology has been widely adopted, especially in countries with advanced safety standards, to ensure food safety and reduce waste.
Importance of Food
Food is essential to human life, health, culture, and the economy. Its importance spans across several key dimensions:
- Nutritional Value: Food provides the energy and nutrients required for the body to function properly.
- Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals are vital for growth, development, and maintaining overall health.
- Economic Impact: The food industry, including agriculture, food processing, and distribution, is a major source of employment.
- Religious and Cultural Significance: Traditional foods and culinary practices are often central to cultural expressions and community gatherings.
- The earliest Pagan and Hindu gods were directly responsible for the production of food, like the Earth, the river, the rain.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Crucial Insights on Food Safety and Wastage
As India moves towards the vision of Viksit Bharat in its 78th year of Independence, advancing food safety and security is crucial.
- Food Safety and Security: This entails ensuring that the food reaching consumers is safe, as well as minimising loss and waste to guarantee that sufficient, nutritious food is available to all.
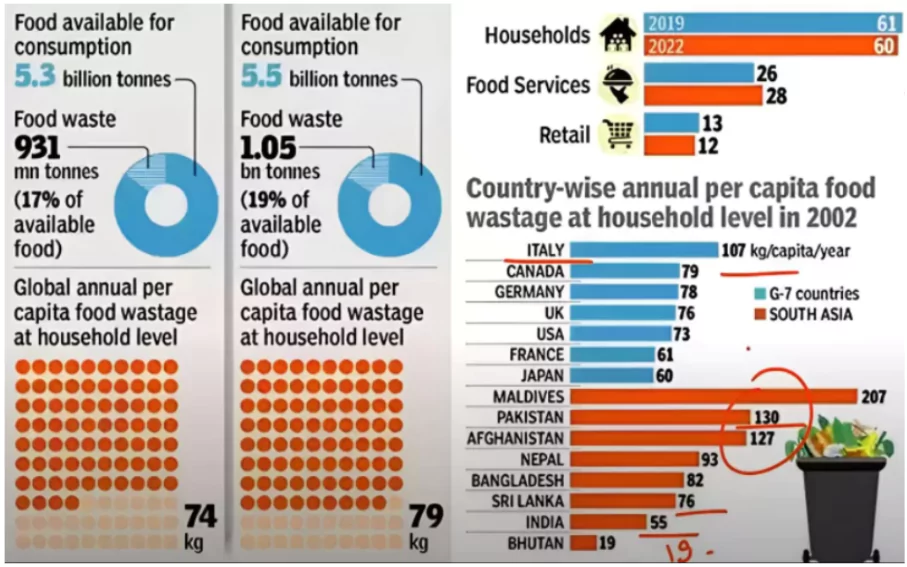
- Food Wastage: According to the Food Waste Index Report 2024, in 2022, the world wasted 1.05 billion tonnes of food.
- It amounts to around 1/5th of food available to consumers being wasted, at the retail, food service, and household level.
- Food Irradiation Units: In line with India’s commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals 2 (Zero Hunger), the Union budget for 2024-25 has allocated funds to set up 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector.
About Food Safety and Security
- Food Safety: refers to the handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure that food is safe to eat.
- Food Security: Based on the 1996 World Food Summit, food security is defined when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
- Key Aspects of Food Safety:
- Contamination:
- Biological: Pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and parasites can contaminate food, leading to foodborne diseases. For example, Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
- Chemical: Residues from pesticides, heavy metals, and other chemicals can contaminate food, posing health risks.
- Physical: Foreign objects like glass, metal fragments, or plastic can be present in food, leading to injuries or other health issues.
- Food Adulteration: The intentional addition of inferior or harmful substances to food to increase quantity or improve appearance.
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Lack of proper hygiene practices including washing hands, sanitizing surfaces, and proper cooking and storage of food exacerbates food safety concerns.
- Food Safety Regulations: Overly strict guidelines or lack of flexibility in regulations can lead to edible food being discarded or composing.
- In India, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is the key regulatory body which ensures that food products meet safety and quality standards.
- Four main dimensions of food security:
- Physical Availability Of Food: Food availability addresses the “supply side” of food security and is determined by the level of food production, stock levels and net trade.
- Economic and Physical Access to Food: Concerns about insufficient food access have resulted in a greater policy focus on incomes, expenditure, markets and prices in achieving food security objectives.
- Food Utilization: Utilization is commonly understood as the way the body makes the most of various nutrients in the food.
- Stability Of The Other Three Dimensions Over Time: You are considered to be food insecure if you have inadequate access to food on a periodic basis, risking a deterioration of your nutritional status.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Major Reasons Leading to Food Wastage
Food wastage refers to the loss or discard of edible food throughout the supply chain, from production to consumption.
- Post-Harvest Losses: A significant portion of food is lost during harvesting, storage, and transportation due to inadequate infrastructure, poor storage facilities, and inefficient supply chains.
- India’s post-harvest losses amount to approximately ₹1,52,790 crore annually, according to a Ministry of Food Processing Industries 2022 study.
- Retail and Consumer Waste:
- At the retail level, food waste occurs due to overstocking, damage, or expiration of products.
- At the consumer level, food is often wasted due to over-purchasing, improper storage, and food spoilage.
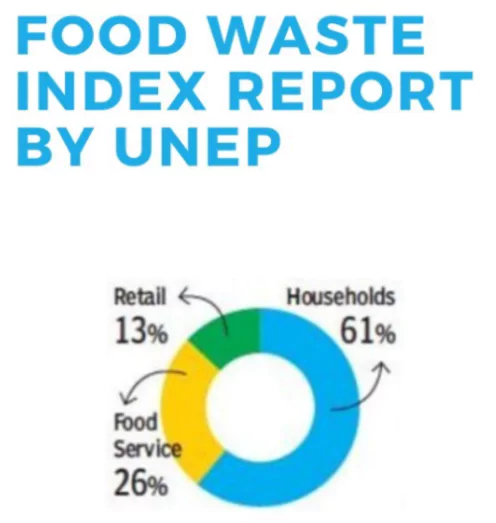
- According to the UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2024, the majority of food waste, accounting for 60%, happened within households, while food services contributed to 28%, and retail accounted for 12%.
About Food Irradiation Technology
Food irradiation is a technology used to improve food safety and extend the shelf life of food by reducing or eliminating microorganisms and insects that can cause foodborne illness and spoilage.
Irradiation Process:
- Ionizing Radiation: Food is exposed to ionizing radiation, which is energy in the form of waves or particles. The types of ionizing radiation used in food irradiation include:
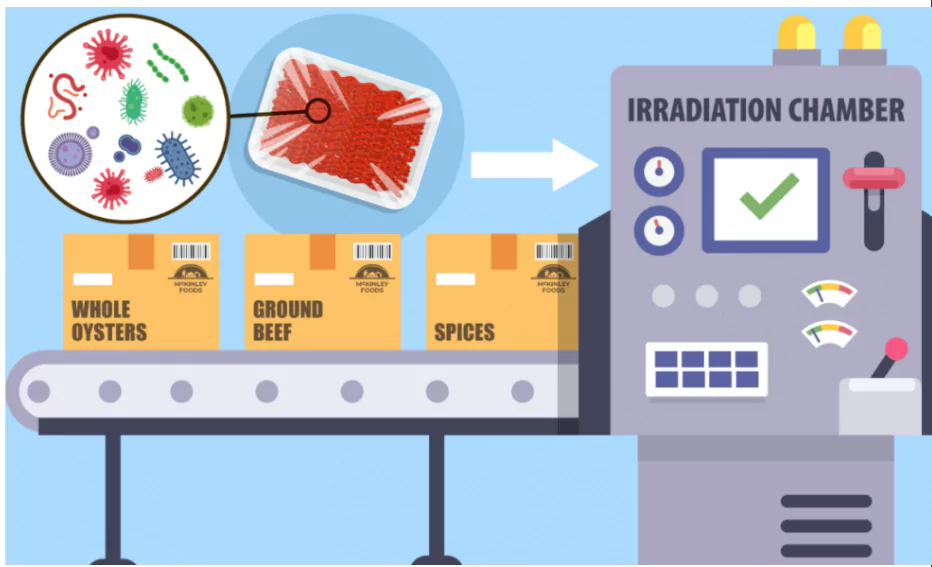 Gamma rays (emitted by radioactive isotopes like Cobalt-60 or Cesium-137). Gamma rays (emitted by radioactive isotopes like Cobalt-60 or Cesium-137).- X-rays.
- Electron beams.
- Effect on Microorganisms: The ionizing radiation disrupts the DNA of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, rendering them inactive or killing them.
- This helps prevent foodborne illnesses and reduces spoilage.
- Impact on Food: The irradiation process does not significantly raise the temperature of the food, so it does not “cook” the food.
- The nutritional value, taste, texture, and appearance of most foods remain largely unaffected, although very high doses can cause changes in some foods.
- Applications of Food Irradiation Technology to Reduce Food Wastage: Reducing or eliminating pathogens (like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria) , disinfestation, shelf life extension, quarantine treatment (to control pests), etc.
|
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Measures to Reduce Food Wastage
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: Implement better inventory management systems in grocery stores and restaurants, improve transportation logistics to reduce food spoilage during transit, etc.
- Government Policies and Regulations: Clarify and standardize food expiration labels like “best before” and “use by” to prevent unnecessary disposal of edible food.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Smart Packaging: Invest in packaging technology that extends the shelf life of products.
- Food Waste Apps: Promote apps that help track food at risk of being wasted and connect excess food with those who need it.
- Restaurant and Hospitality Industry Initiatives:
- Portion Control: Offer flexible portion sizes in restaurants to match customers’ appetites.
- Doggy Bags: Encourage customers to take leftovers home.
- Buffet Waste Reduction: Implement policies to reduce food waste in buffets, such as smaller trays and frequent refills.
|
Major Initiatives Undertaken To Improve Food Safety And Security
India has undertaken several major initiatives to improve food safety and security:
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI): To regulate and oversee food safety standards in India.
- FSSAI sets science-based standards for food products and regulates their manufacture, storage, distribution, sale, and import to ensure the availability of safe and wholesome food.
- Public Distribution System (PDS) Reforms: To streamline the distribution of food grains to ensure efficiency and reduce leakages.
- Implementation of end-to-end computerization of the PDS, use of Aadhar-linked ration cards, and introduction of e-POS devices at ration shops to increase transparency.
- Safe and Nutritious Food (SNF) Initiative: To promote safe and nutritious food at various touchpoints such as homes, schools, workplaces, and eateries.
- Surveillance and Monitoring Programs: To regularly monitor and test food products for contamination and adulteration.
- National Food Laboratory Network: Establishes food testing laboratories across the country to ensure food safety.
- Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF): A mechanism for quick detection and response to food safety risks.
- Food Recall Protocol: To protect consumers from unsafe food products by facilitating the removal of such products from the market.
- International Collaborations: Collaborations with international bodies like the World Health Organization (WHO) and Codex Alimentarius for setting and implementing food safety standards.
Way Forward
As India progresses toward the vision of “Viksit Bharat” by its 78th year of Independence, enhancing food safety and security will be pivotal to realizing this goal.
- Expanding the Reach of Food Irradiation Technology: The allocation of funds in the Union budget for 2024-25 is a significant step. To maximize the impact of this initiative:
- Capacity Building: There should be a focus on training and educating stakeholders on the benefits and operation of irradiation technology.
- Scaling Up: Based on the success of the initial 50 units, the program could be scaled up across the country.
- Strengthening Food Safety Standards: Increasing the capacity of the FSSAI to regulate and monitor food products effectively.
- Strengthening enforcement of food safety regulations to minimize food adulteration and contamination.
- Minimizing Food Loss: It is an important avenue to improve national/global food security to meet the United Nations (UN) 2030 goal to halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels, and reduce food losses along production and supply chains.
- Promoting Circular Economy: Diverting food loss and waste towards livestock and poultry feed could emerge as a rational solution to reduce food wastage.
- Policy Support and Governance: Provide incentives for MSMEs to adopt food irradiation and other food safety technologies.
- Ensure that food safety and security policies are integrated with broader health, agriculture, and environmental policies to create a cohesive and effective approach.
- Setting of Reduction Targets: Prioritize the problem of food wastage and set clear reduction targets at national and global levels.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Promote sustainable food production and consumption through education and awareness campaigns.
- Innovative Food Conservation Model: For example, Adrish is a zero-waste lifestyle startup that has helped save 2,95,810 kg of packaging waste from landfill and refrained from using 1,47,90,500 plastic bags.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
By focusing on these strategic areas, India can significantly advance its food safety and security landscape, contributing to the overall health and well-being of its population while reducing food wastage and achieving sustainable development goals.
![]() 4 Sep 2024
4 Sep 2024

