The Union Cabinet has extended the universal supply of fortified rice in all central government schemes under the National Food Security Act, 2021 until December 2028.
Rice Fortification Initiative to Combat Anaemia with 100% Central Funding
- Rice fortification initiative would continue as a central sector initiative with 100% funding
- The initiative aims to address anaemia and micronutrient deficiencies in the population.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Micronutrients
- Micronutrients consist of vitamins and minerals and are measured in either milligrams (mg), micrograms (mcg) or International Units (IU).
- For Example:
-
- Vitamin B1: Also known as thiamine, vitamin B1 aids in converting nutrients into energy. They are found in Foods including white rice, fortified breakfast cereals and black beans.
- Vitamin B2: Also known as riboflavin, this vitamin is good for energy production, cell function and fat metabolism. They are found in foods including instant oats, fat-free yogurt and milk.
Macronutrients
- Macronutrients are a group of nutrients that provide your body with energy and the components it needs to maintain its structure and functions. They’re needed in relatively larger amounts than other nutrients, hence the term “macro”.
- For Example:
- Carbohydrates, protein, and fat.
|
What is Food Fortification?
Food fortification involves deliberately increasing the content of essential micronutrients in food to improve its nutritional quality and provide public health benefits with minimal health risks.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) defines this process and oversees its implementation.
Fortification of Rice
- Rice is fortified using various technologies such as coating, dusting, and extrusion.
- The extrusion process produces fortified rice kernels (FRKs) by mixing dry rice flour with a premix of micronutrients, which is then processed through an extruder to create kernels resembling regular rice.
- Fortified rice is blended with regular rice, ensuring 10 grams of FRK is combined with 1 kilogram of regular rice.
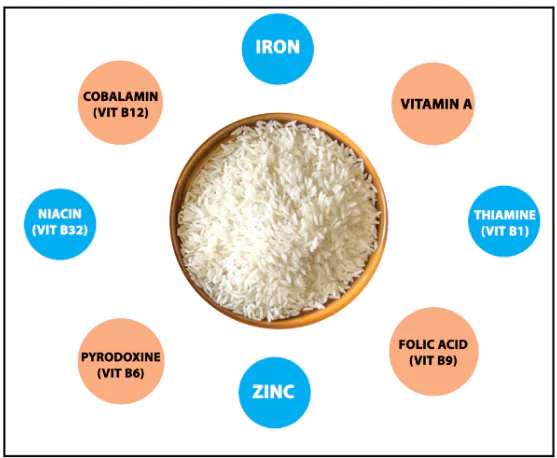
- Fortified rice is enriched with essential micronutrients, including:
-
- Iron: 28 mg – 42.5 mg
- Folic Acid: 75 – 125 micrograms
- Vitamin B-12: 0.75 – 1.25 micrograms
- Additional nutrients may include zinc, vitamin A, and various B vitamins.
Progress of the Fortification Initiative
- The rice fortification initiative was announced in 2015, with a goal for implementation across various central government schemes by 2024.
- The initiative has been rolled out in three phases:
- Phase 1: Covered programs like Integrated Child Development Services and PM POSHAN by March 2022.
- Phase 2: Extended to Public Distribution System (PDS) in 112 Aspirational Districts and 291 high stunting burden districts by March 2023.
- Phase 3: Aims for full coverage across remaining districts by March 2024.
- Annual cost: Approximately Rs 2,700 crore, accounting for less than 2% of India’s total food subsidy bill.
- Distribution so far: By March 2024, about 406 lakh metric tonnes of fortified rice are expected to be distributed through the PDS.
- Facility for Fortification: The Centre has invested Rs 11,000 crore to develop the fortified rice supply chain in India, with 925 manufacturers producing fortified rice.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Benefits of Fortified Rice
- Fortified rice retains the same cooking and eating properties as regular rice, making it easy to integrate into daily diets.
- It is packaged in jute bags labelled with the logo (‘+F’) and the statement “Fortified with Iron, Folic Acid, and Vitamin B12”.
Need of Fortified Rice
- India faces significant malnutrition challenges with one in two women is anaemic and one in three children is stunted.
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) shows that anaemia affects diverse demographics across age and income levels, with deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid being prevalent.
- Fortifying rice, a staple food for two-thirds of the Indian population, provides a strategic approach to supplement the diets of economically vulnerable groups.
![]() 10 Oct 2024
10 Oct 2024
