Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming India’s industry, economy and society.
- India is positioning itself as a major player in the global AI landscape, especially following its hosting of the G20 and Global Partnership on AI meetings in 2023.
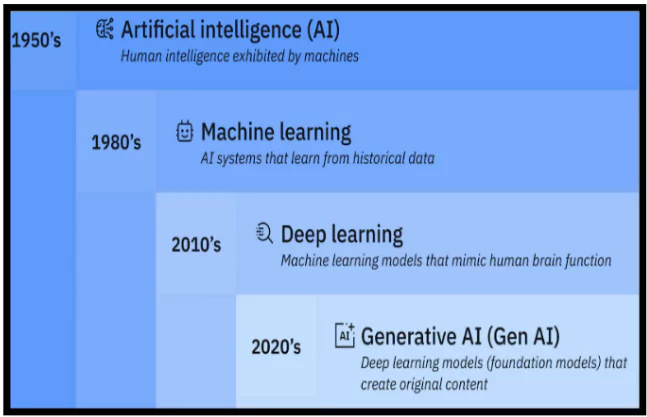
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Definition: Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are designed to think, learn, and solve problems autonomously.
- Coined by: The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined by American computer scientist John McCarthy in 1956.
Significance of AI for India
- Projected Growth of India’s AI Market: According to the Nasscom report, India’s AI market is expected to reach $17 billion by 2027, growing at an annual rate of 25-35%.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Evolution of AI in India
- Early Days (1960s-1980s): Institutes like IIT Kanpur and IISc Bangalore laid the groundwork for AI research.
- The Knowledge Based Computer Systems (KBCS) project, initiated in 1986, marked India’s first significant AI program.
- Foundations (1990s): The establishment of C-DAC in 1988 enhanced supercomputing, indirectly supporting AI research.
- Indian software companies began exploring AI for business automation.
- Growth Phase (2000s): IT giants such as TCS, Infosys, and Wipro invested in AI research, and academic institutions expanded AI and machine learning programs.
- Acceleration (2010s): The “Digital India” initiative (2014-15) emphasised emerging technologies, including AI.
- In 2018, NITI Aayog released the National Strategy for AI, focusing on economic growth and social inclusion, leading to a rise in AI startups.
- Current Era (2020s): AI is now a priority for both government and industry, with India aiming to become a global AI hub through initiatives like “AI for All,” integrating AI across sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and education
|
-
- By 2025, AI could contribute $450-500 billion to India’s GDP, accounting for around 10% of its goal to achieve a $5 trillion economy.
- Transformative Tool: For India, an economy with over 1.4 billion people, AI can act as a tool in addressing challenges like poverty, healthcare access, and education while propelling its economy into new dimensions. Example:
- The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) uses AI to integrate Electronic Health Records (EHR), to make quality healthcare more accessible and affordable for the underprivileged.
- Pune’s Intelligent Traffic Management System (ITMS) uses artificial intelligence and data analytics to streamline vehicle flow and bolster road safety.
- Use of Smart Drones and Agribots for cropping, weeding, applying fertilisers and harvesting in agricultural farms.
- In Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, AI Sowing App provides farmers information on optimal sowing dates and depths.
Factors Contributing to India’s AI Potential
- Strong AI ecosystem: India has a strong AI ecosystem, featuring skilled engineers, data scientists, and researchers from top institutions like the IITs and IISc.
- Robust Digital Infrastructure: India’s Aadhaar and Unified Payments Interface (UPI) have significantly advanced its digital infrastructure, making it one of the world’s most digitally connected nations.
- This robust digital ecosystem generates a vast pool of data essential for training AI algorithms.
- Rising Adoption and Workforce Readiness: There has been a 117% increase in AI-related course enrollment among non-technical professionals in the past year, indicating a broadening scope of AI skill development beyond tech experts.
- In 2023, hiring of AI talent in India increased by 16.8 per cent,
- Many organisations are implementing internal training initiatives to address the skill gap.
- Start-up Culture and Innovation Hubs: India’s startup ecosystem is the third-largest in the world, with several AI-focused startups emerging across sectors such as healthcare (Niramai), agriculture (Intello Labs), and education(Jungroo Learning).
- Government Support: The Indian government’s proactive stance on AI is a critical factor.
- Example: National AI Strategy, AI for All, Centers of Excellence for AI.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Challenges Facing India on the Path to AI Leadership
- Data Related Challenges:
- Quality of Data: The effectiveness of AI models is hindered by inconsistent data availability and quality across various sectors in India.
- Additionally, the absence of standardised data formats complicates the development of robust AI models.
- Insufficient Data Center Infrastructure in India: Despite producing 20 percent of the world’s data, India is home to only 2 percent of global data centres.
- Data Privacy and Security: There are concerns over data privacy, cybersecurity, and the ethical use of AI are significant barriers.
- Language Barriers: The lack of structured data in local Indian languages contributes to issues of bias and underrepresentation in AI applications.
- Infrastructural Challenges:
- Digital Divide: Large sections of the population, especially in rural areas, remain digitally excluded.
- Limited Computing Infrastructure Capacity in India: Current computing infrastructure accounts for less than 2 percent of the world’s capacity.
- Skill Related Challenges: There is a shortage of specialised skills required for advanced AI research and development.
- Ethical and Governance Challenge: Ethical concerns in AI emerge from issues like algorithmic bias, lack of transparency in decision-making, and potential misuse for surveillance.
Government Initiatives for AI promotion in India
- Enhancing Computational Infrastructure: The central government is enhancing computational capabilities, with plans to procure 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) within the next 18 to 24 months.
- India’s National Semiconductor Mission: It was launched in 2021 under the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) with an aim to build a domestic chip industry, supported by over $10 billion in production-linked incentives.
- Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI): In 2020, India joined with 15 other countries to form the GPAI to establish frameworks for the responsible utilisation of emerging technologies.
- Delhi Declaration of the GPAI Summit: Acknowledges the need to harness new opportunities and mitigate the risks arising from the development, deployment, and use of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- INDIAai Portal: It is the National artificial intelligence Portal of India launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and the National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM).
- IndiaAI Mission: The Indian government has allocated Rs 10,372 crore for the next five years under which the government will allocate funds towards subsidising private companies looking to set up AI computing capacity in the country.
- ‘AI for All’: It is a self-learning online program designed to raise public awareness about Artificial Intelligence.
- Artificial Intelligence Appreciation Day: It is celebrated on July 16 every year to highlight AI’s transformative impact across industries and emphasises collaboration, ethical development, and innovation.
- Other Initiatives:
- Digital India, Make in India, and Smart Cities Mission, National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), BharatNet, GI Cloud (MeghRaj) and Global INDIAai Summit hosted by India are driving AI adoption across sectors.
Way Forward/Strategies for Global AI Leadership
- Investing in Education and Skill Development: There is a need to integrate AI education in universities and technical institutes to help bridge the skills gap.
- Inclusive AI: Promoting Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education, especially for women and marginalised communities, will foster inclusive participation in the AI economy.
- Enhancing Computational Infrastructure: There is a need to address the bottleneck of data centre capacity by increasing local data centre investments to meet growing demands.
- Investment in Research and Development: Indian businesses must prioritise R&D.
- Substantial investment in core compute capabilities and talent will be the cornerstones for developing a successful AI ecosystem in India.
| FutureSkills Prime is a digital skilling initiative by Nasscom & Meity, aimed at making India a Digital Talent Nation. |
-
-
- Building a Strong Regulatory Framework: There is a need for clearer data protection laws, robust guidelines on AI ethics, and a focus on developing transparent AI systems.
- Leveraging AI for Social Good: Example: AI applications like predictive analytics for crop yields, diagnostic tools, and personalised learning platforms can significantly enhance quality of life.
- Bridging the Skilling Gap: To enhance workforce AI capabilities, expanding initiatives like FutureSkills PRIME is essential. Furthermore, skilling rural youth is crucial to bridge the rural divide.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
India is at a crucial juncture, ready to leverage strong government support and industry collaboration to lead in the global AI landscape. By harnessing AI’s transformative power, the nation can drive significant economic prosperity and social growth.
![]() 10 Oct 2024
10 Oct 2024

