![]() 3 Mar 2025
3 Mar 2025
English
हिन्दी

UNESCO has released a report titled ‘Languages matter: Global guidance on multilingual education’ recently.
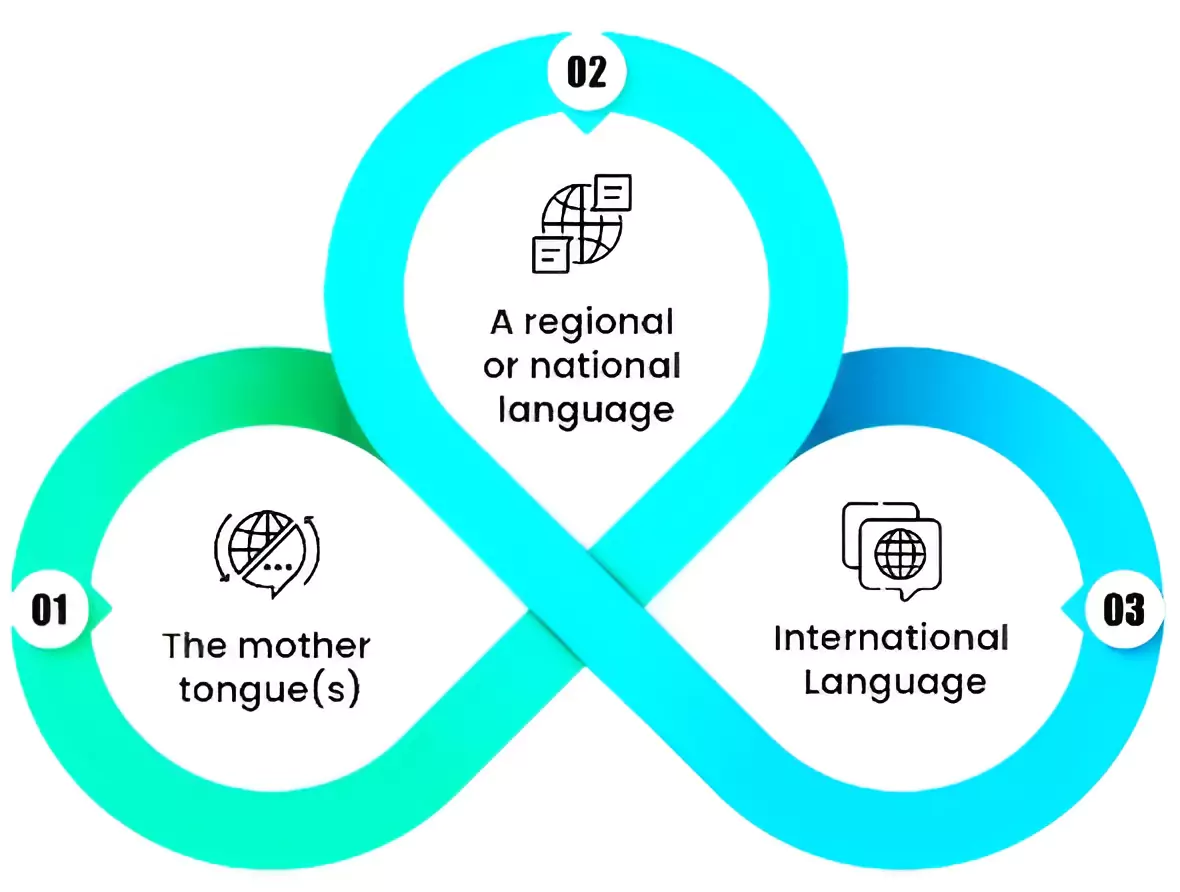
Examples of Multilingual Education
|
|---|
Multilingualism in Indian Education
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>