Context
For the first time, researchers have made a super thin sheet of gold that is only one atom thick.
One-Atom Gold Sheet Created with ‘Murakami Method’
- This discovery means that gold can now be made into flat, two-dimensional sheets
- To get a free-standing, one-atom thick gold layer, scientists used “Murakami method” inspired by Japanese technique
- They used a special chemical called Murakami’s reagent, similar to how traditional Japanese swords are made.
What is Goldene?
Goldene is a special form of gold called a 2-dimensional allotrope. It shows that it’s a different arrangement of gold atoms.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Allotropes:
- It refers to the ability of a chemical element to exist in varying forms with different arrangements.
- Each form shows different physical properties while keeping chemical properties the same.
- Examples: Elements that show allotropes are Carbon, Phosphorus, and Sulphur.
|
- Thickness: It is 400 times thinner than gold leaf
- Structure: It has a unique quality where its structure is 9% smaller compared to regular gold.
- Properties: New gold form has unique traits like graphene.
 Gold is typically a metal, but a single-atom thick layer can transform it into a semiconductor.
Gold is typically a metal, but a single-atom thick layer can transform it into a semiconductor.- Just like how graphene behaves differently from regular carbon, this new gold behaves differently from standard gold.
-
Future Applications of Goldene:
- Carbon dioxide conversion
- Hydrogen-generating catalysis
- Selective production of value-added chemicals
- Hydrogen production
- Water purification
- Telecommunications
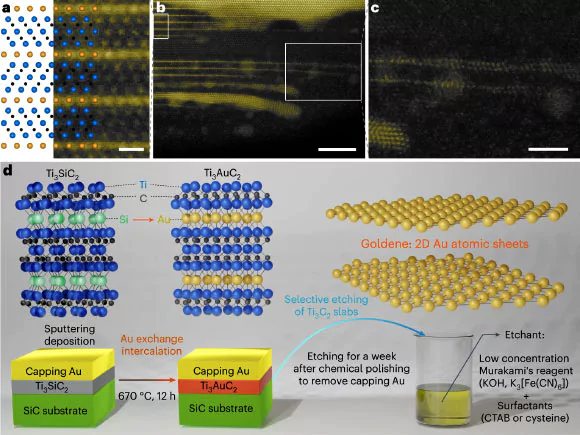
Process of Creating Goldene
- Initial Steps: Researchers started by layering a single sheet of silicon atoms between titanium carbide layers.
- Deposition of Gold: Gold was deposited on top of this structure.
- The gold atoms replaced the silicon atoms and formed a monolayer of gold atoms trapped within.
- Etching Process: The titanium carbide layers were then etched away using an age-old Japanese technique involving Murakami’s reagent.
Challenges in making Goldene
- Traditional obstacle: Gold tends to cluster together which makes it difficult to create single-atom sheets.
- Previous 2D Materials: Two-dimensional (2D) materials have been created since the discovery of graphene in 2004 but producing thin metallic sheets created difficulties due to metals’ tendency to form nanoparticles.
- Innovative Solution: Researchers from LiU used Murakami’s reagent.
- Murakami’s reagent is an ancient Japanese technique, to address this challenge.
- Murakami’s Reagent in Action
- Process Complexity: Precision in the etching process was crucial to ensure the successful creation of Goldene.
- Absence of light: Operations had to be conducted in the absence of light.
- It added another layer of complexity to the process.
About Gold (Au)
Gold (Au) is a chemical element. It is renowned for its dense, lustrous, and yellow appearance. It Belongs to Group 11 (Ib) and Period 6 of the periodic table.
Physical Properties of Gold (Au):
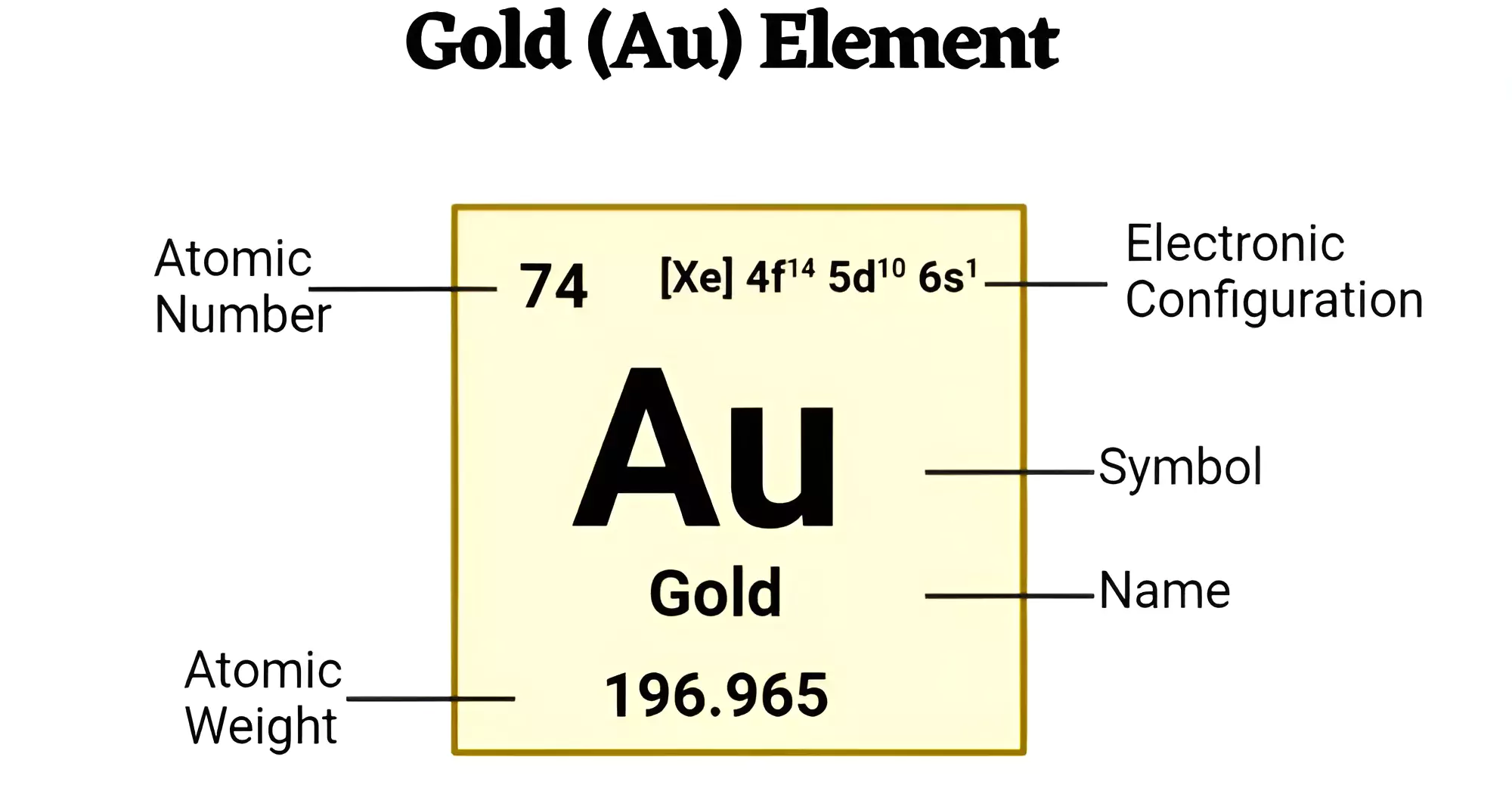
Here are the physical properties of gold are as follows;
- Appearance: Soft yellow metal.
- Ductility and Malleability: Highest among metals.
- Crystal Structure: Cubic system.
- Conductivity: High thermal and electrical.
- Isotopes: 197Au natural; 19 artificial (185Au to 203Au).
- Radioactivity: Artificial isotopes have half-lives from seconds to 199 days.
- Magnetism: Pure gold and most alloys are nonmagnetic.
- Gold Alloys: Commonly with silver and copper.
- Carat Golds: Expresses gold content (e.g., 24 carats is pure gold).
- Alloying Metals: Forms alloys with many metals like silver and copper.
- Mercury and Gold: Mercury forms amalgams with gold, useful for extraction.
Chemical Properties of Gold (Au):
Here is a summary of the chemical properties of gold:
| Group |
11 |
Melting point |
1,063 °C (1,945 °F) |
| Period |
6 |
Boiling point |
2,966 °C (5,371 °F) |
| Block |
d |
Density (g cm−3) |
19,300 kg per cubic metre. |
| Atomic number |
79 |
Atomic weight |
196.96657 |
| State at 20°C |
Solid |
Key isotopes |
197Au |
| Electron configuration |
[Xe] 4f145d106s1 |
CAS number |
7440-57-5 |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 6 May 2024
6 May 2024

 Gold is typically a metal, but a single-atom thick layer can transform it into a semiconductor.
Gold is typically a metal, but a single-atom thick layer can transform it into a semiconductor.