The Union Minister of Cooperation inaugurated ‘Co-Op Kumbh 2025’, an international conference on the future of India’s urban cooperative banking sector, and adopted the Delhi Declaration 2025.
About Cooperative Kumbh 2025
- It is an international conference on the urban cooperative credit sector that focuses on collaboration, innovation, and policy advancement.
About Delhi Declaration 2025
- A policy document adopted at Co-Op Kumbh 2025, titled the “Delhi Declaration 2025 – Roadmap to 2030”.
- It is intended as a strategic blueprint for the urban cooperative credit ecosystem (UCBs + credit societies) over the coming years (to 2030).
|
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Cooperation
- Host organisation: National Federation of Urban Co‑operative Banks and Credit Societies (NAFCUB)
- NAFCUB: It is an Apex Level promotional body for Urban Cooperative Banks and Credit Societies, registered as a Multi-State Cooperative Society in February 1977.
- Theme: “Digitalising Dreams – Empowering Communities”.
- The conference aligns with the International Year of Cooperatives 2025 as declared by the United Nations.
- Digital Initiatives: Launch of Sahkar Digi-Pay and Sahkar Digi-Loan apps to enable even the smallest UCBs to offer digital payment and loan facilities.
- Expansion Goal: A target to establish one UCB in every city with a population of over 2 lakhs within 5 years.
About Cooperative Banks
- They are financial institutions that are owned and controlled by their members, who are also customers of the bank.
- It is an institution established cooperatively to deal with the ordinary banking business.
- They are founded by collecting funds through shares, accepting deposits, and granting loans.
- Registered Under: Cooperative Societies Act of the State concerned or the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, of 2002.
- They are governed under:
- Banking Regulations Act, 1949: They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
- Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955: It has given RBI more control over UCBs, allowing it to intervene in their management and governance.
- Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS): State governments/Central government control administrative functions through the RCS.
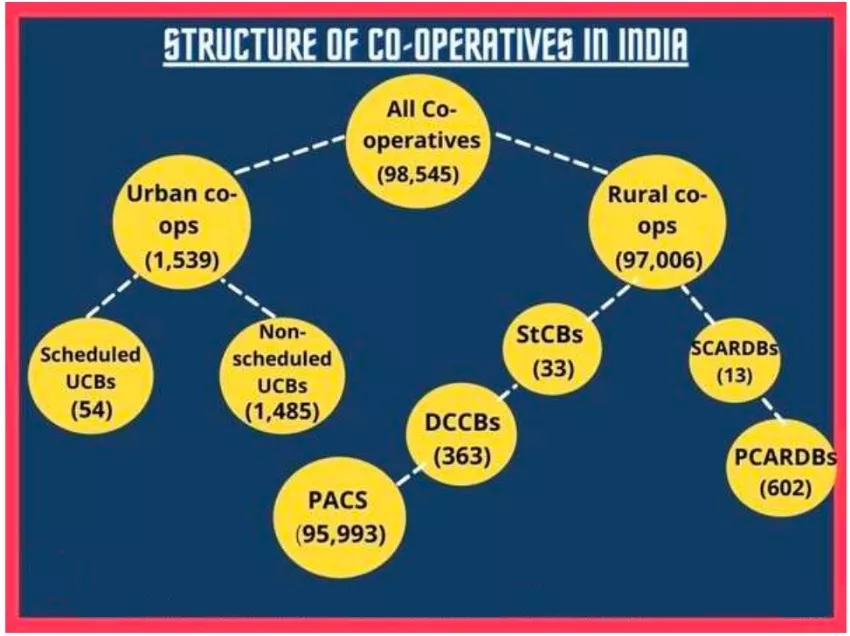
- They are broadly divided into Urban and Rural cooperative banks (Refer Image)
Characteristics of Cooperative Banks
- Ownership: Cooperative banks are owned by their members, who are also the shareholders of the bank.
- Control: Cooperative banks are controlled by their members, who elect the board of directors and participate in the decision-making process of the bank.
- Profits: The profits of cooperative banks are distributed among the members in the form of dividends.
- Services: Cooperative banks offer a range of banking and financial services to their members, including savings accounts, loans, and insurance.
- Community focus: Cooperative banks often strongly focus on serving their local communities’ needs and promoting economic development.
- Ethical values: Cooperative banks are guided by the cooperative principles of democracy, equality, and solidarity, and they aim to operate ethically and sustainably.
|
Urban Cooperative Banks (UCB)
- They are financial institutions that are organized and operated cooperatively in urban and semi-urban areas.
- In 2021, RBI appointed a committee(N S Vishwanathan Committee) that suggested a 4-tier structure for the UCBs.
- Tier 1 with deposits up to Rs 100 crore.
- Tier 2 deposits between Rs 100 crore and Rs 1,000 crore,
- Tier 3 with deposits between Rs 1,000 crore and Rs 10,000 crore, and
- Tier 4 with deposits more than Rs 10,000 crore.
- Status of UCB:
- Number and Presence: As per RBI and NABARD, there are 1,457 Urban Cooperative Banks, 34 State Co- operative Banks (StCBs), 351 District Central Co-operative Banks (DCCBs) and one Industrial Co- operative Bank
- Credit to Agriculture Contribution: Contributing 11% of the total credit to the sector.
- Deposit Base: The total deposit base of UCBs is at ₹5.26 trillion.
- Sector Share: As of March 31, 2020, an estimated 94% of entities in the banking sector were UCBs, showcasing their prevalence.
- Share in Banking Sector: 3.24% of deposits and 2.69% of advances.
- Financial Inclusion Impact: UCBs cater to the financial needs of approximately 85.2 million depositors and 6.7 million borrowers.
N S Vishwanathan Committee Suggestions
In February 2021, the RBI constituted an Expert Committee on Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks chaired by N S Vishwanathan, former RBI Deputy Governor.
- Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) Variation: Suggested a flexible CRAR ranging from 9% to 15% for UCBs, with Basel III norms for Tier-4 UCBs.
- Separate Ceilings for Loans: Prescribed separate ceilings for home loans, loans against gold ornaments, and unsecured loans for different UCB categories.
- Consolidation Approach: Recommended that RBI should take a largely neutral stance to voluntary consolidation but suggested mandatory mergers for UCBs not meeting prudential requirements.
- Resolution of UCBs: Suggested that the RBI, under the Banking Regulation (BR) Act, can prepare schemes for compulsory amalgamation or reconstruction of UCBs when voluntary actions are insufficient.
- Supervisory Action Framework (SAF): Proposed a twin-indicator approach for the SAF, considering only asset quality and capital (measured through NNPA and CRAR) instead of the current triple-indicator approach.
- Umbrella Organization (UO) Role: Highlighted the crucial role of the Umbrella Organization (UO) in strengthening the sector, suggesting it should be financially strong with a minimum capital of Rs 300 crore.
|
Significance of Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs)
- Financial Inclusion: Primarily serve small borrowers and lower-income groups excluded from large commercial banks.
- Promote savings habits and provide affordable credit to urban poor, MSMEs, and self-employed workers.
- Local Focus: Operate within specific communities or regions, ensuring close understanding of local needs. Offer personalized, relationship-based banking and faster decision-making.
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL): Mandated to allocate at least 60% of total lending to priority sectors like small business, housing, education, and weaker sections.
- Strengthens inclusive credit flow and supports government development goals.
- Economic Empowerment: Channel local savings into local investments, stimulating small-scale enterprise and job creation. Reduce dependence on informal moneylenders.
- Cooperative Ownership: Function on mutual-benefit principles with members are both owners and beneficiaries.
- Reinforce community trust, accountability, and democratic decision-making.
![]() 13 Nov 2025
13 Nov 2025

