Researchers at IIT Bombay, developed a new graphene-based Dual-Sided Superhydrophobic Laser-Induced Graphene (DSLIG) evaporator.
- This innovation offers a consistent, efficient, and scalable desalination solution by mimicking the lotus leaf effect, and integrating dual-mode heating (solar + electric).
Interfacial Solar Evaporation
- A method where only the surface layer of water is heated using a floating evaporator that absorbs sunlight. This avoids heating the full water volume, saving energy.
Advantage
- Localized heating: Ideal for off-grid desalination
- Higher thermal efficiency: Minimizes energy loss
PWOnlyIASExtaEdge
Lotus Leaf Effect
- The Lotus Leaf Effect refers to the natural superhydrophobicity (extreme water-repellent property) observed on the surface of lotus leaves.
- It plays a crucial role in self-cleaning and anti-wetting behavior in nature and is now being replicated in advanced materials and technologies.
Joule Heating
- It (also called resistive heating or Ohmic heating) is the process by which electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current passes through a conductor or resistive material.
|
Challenges with Solar Desalination Techniques
- Fluctuating Sunlight: Cloud cover and time-of-day variation cause unstable heating, lowering evaporation efficiency
- Low Absorption Efficiency: Reduced light absorption on some materials limits thermal performance
- Salt Deposition: Salt crystals accumulate on the evaporator surface, blocking water contact and reducing effectiveness.
About the DSLIG Evaporator Technology
- DSLIG = Dual-Sided Superhydrophobic Laser-Induced Graphene evaporator.
- Designed for interfacial solar desalination, enhanced with Joule heating backup.
Key Components
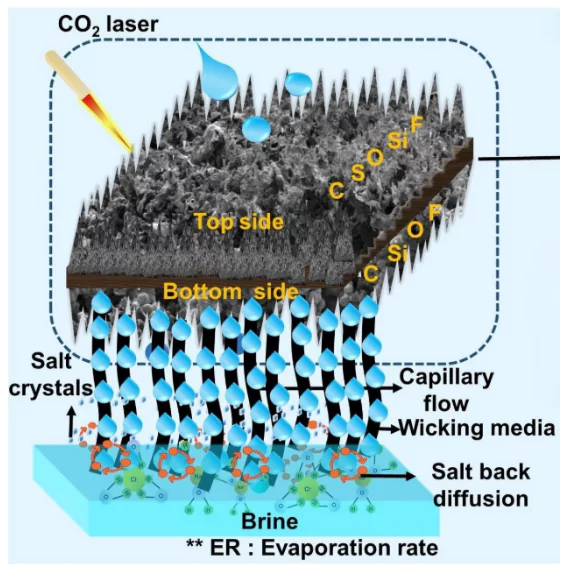
- PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride): Provides superhydrophobicity (lotus-effect) on both sides.
- PES (Polyether Sulfone): Provides mechanical strength and flexibility.
- Laser-Induced Graphene (LIG): Engraved using laser to form graphene layer on PVDF for light absorption and heat conversion
Working Mechanism
- Solar heating: Heats a thin water layer at the surface for evaporation (localized heating).
- Electric heating: Joule heating compensates during cloudy conditions or low sunlight.
- Superhydrophobicity: Repels salt and water to prevent salt deposition on the surface.
Benefits of DSLIG Technology
| Feature |
Advantage |
| Dual Heating |
Combines solar and electric heating for all-weather operation |
| Superhydrophobic |
Repels salt and water, increases longevity and efficiency |
| Eco-Friendly |
Low carbon footprint and material toxicity |
| Versatile |
Treats highly concentrated brine and industrial waste |
| Scalable Design |
Multiple DSLIG units can be stacked to enhance output |
| Cost-Effective |
Uses inexpensive, durable polymers (PVDF + PES) |
Other Desalination Technologies
Desalination technologies are mainly categorized into two types based on the working principle:
A. Thermal Desalination Techniques
Definition: In thermal methods, saline water is heated and the resulting water vapor is condensed to produce freshwater.
- These techniques mimic the natural water cycle and are best suited for seawater desalination, especially in regions with abundant thermal energy.
| Method |
Description |
Use Case / Advantage |
| Multi-Stage Flash Distillation (MSF) |
Seawater is heated and rapidly evaporated in multiple stages under decreasing pressure. |
Widely used in the Middle East due to oil surplus for energy needs. |
| Multiple Effect Distillation (MED) |
Seawater is evaporated in a series of vessels (effects) using steam from the previous stage. |
More energy-efficient than MSF; lower temperature operation. |
| Vapour Compression (VC) |
Uses mechanical or thermal compressors to recycle vapor for heating the incoming feedwater. |
Compact design, ideal for small-scale or portable setups. |
B. Membrane-Based Desalination Techniques
Definition: These methods use semi-permeable membranes to filter out dissolved salts and impurities from saline or brackish water by applying pressure or electric potential.
- Preferred where electricity is available and chemical contamination is minimal.
| Method |
Description |
Advantages / Suitability |
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) |
Feedwater is pushed through a membrane under high pressure, allowing only water molecules to pass. |
Most commonly used worldwide; highly energy-efficient . |
| Electrodialysis (ED) |
An electric field is applied to move ions through ion-selective membranes, separating salts from water. |
Best suited for brackish water with moderate salinity. |
| Nanofiltration (NF) |
Similar to RO, but uses larger pore membranes; removes divalent salts and organic compounds. |
Lower energy cost, less waste, suitable for softening hard water. |
![]() 18 Apr 2025
18 Apr 2025


