The Union Shipping Ministry has proposed new infrastructure additions to the ₹72,000 crore mega-project in Great Nicobar.
About Great Nicobar Island Development Project
- Launched in 2021, the Great Nicobar Island (GNI) project is a Rs. 72,000 crore mega project under the Holistic Development of Islands program.
- Aimed at transforming the GNI into a hub of trade, tourism, and strategic military presence.
- Implementation under the aegis of NITI Aayog along with collaborations with global firms and institutions for technology and expertise.
- It was cleared by the Ministry of Environment in November 2022 and is part of a broader strategy to enhance India’s strategic presence and infrastructure in the region.
- The project is expected to be developed over 30 years in a phased manner.
- Major Components:
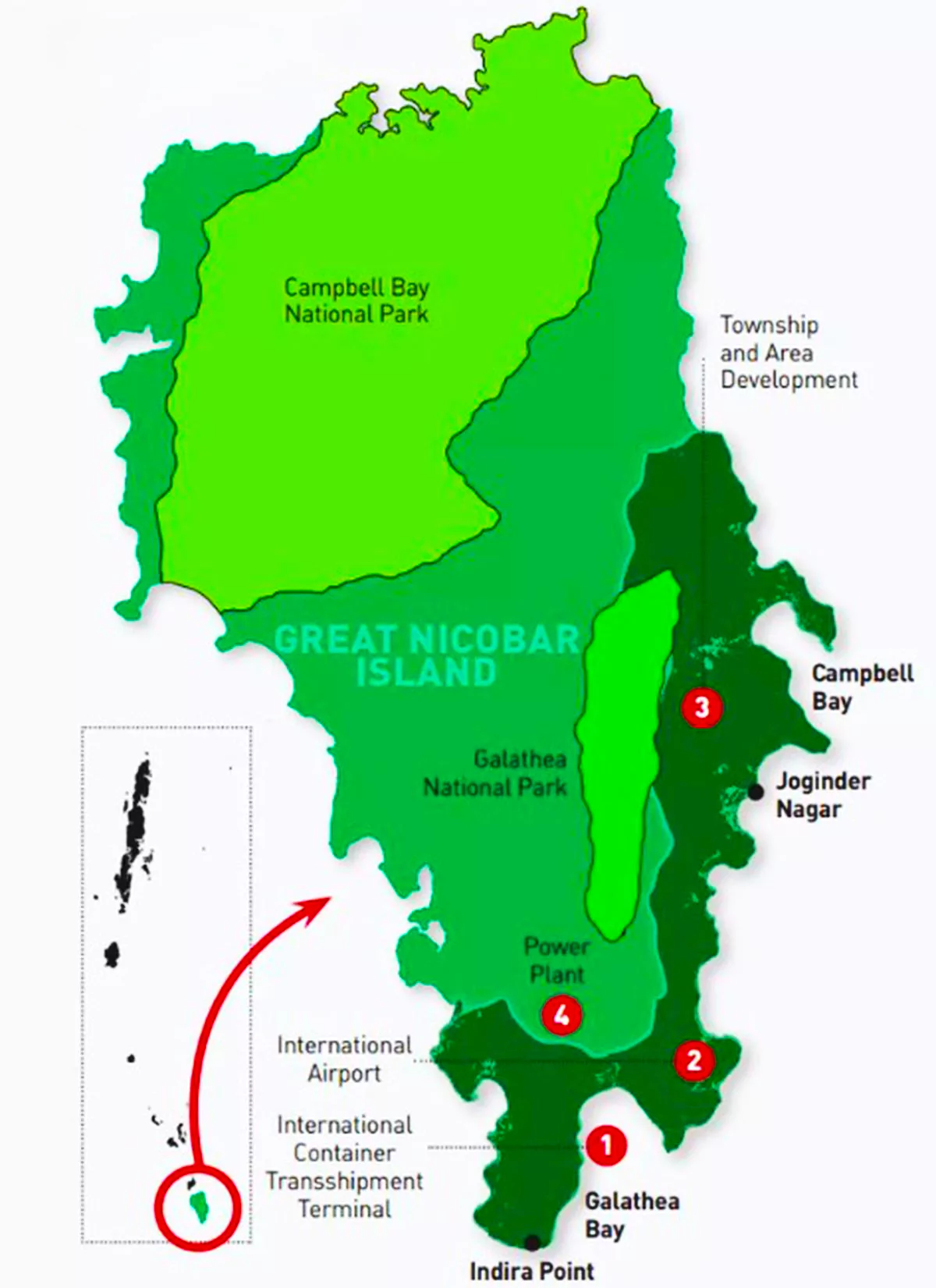
- International Transshipment Port (ITP): A deep-sea port at Campbell Bay to serve as a major hub for global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: Development of a modern airport to boost connectivity and support tourism.
- Integrated Township: Housing and social infrastructure for residents and workforce, including educational and healthcare facilities.
- Dual-use Military-Civilian Infrastructure: Strengthening India’s defense posture in the region while supporting civilian use.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
New Addition to the Project
- Cruise Terminal: For international and domestic high-end tourism.
- Ship-Building and Repair Facilities: Seeking 100 acres of seafront land.
- Exim Port: For construction material imports and exports.
Existing Components of the Mega Project
- International container transshipment port at Galathea Bay.
- Military-civil airport under Navy control.
- Power plant and greenfield township over 130 sq km of tropical forest.
About Great Nicobar Island (GNI)
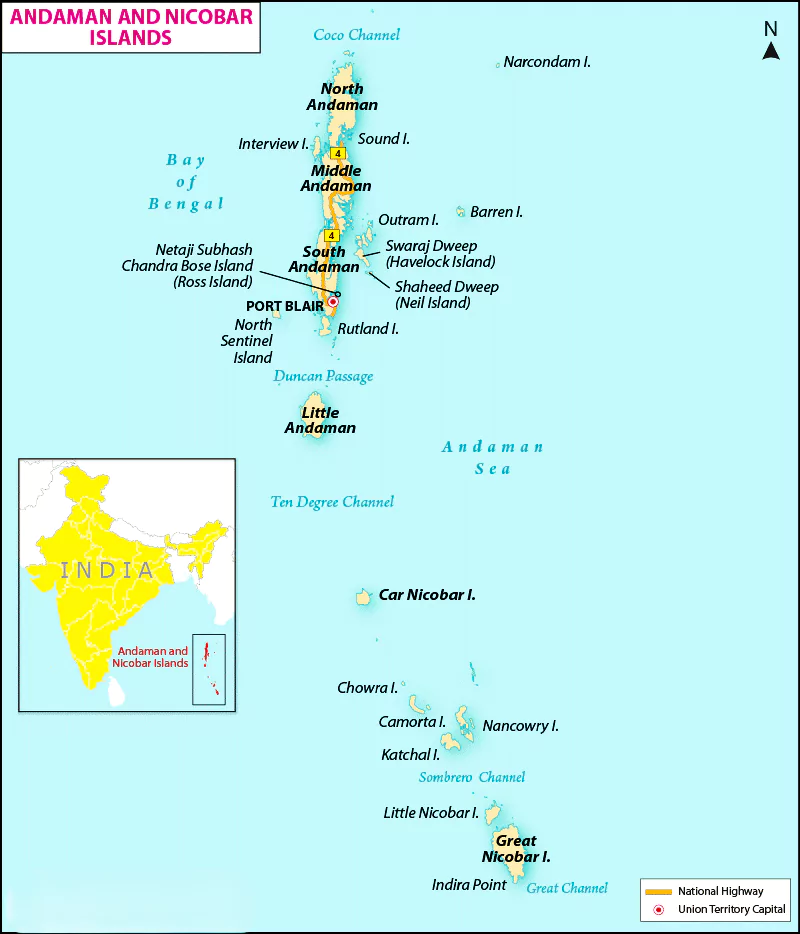
- Location: Southernmost island of the Andaman and Nicobar group of islands in the Bay of Bengal.
- Geography: Largest of the Nicobar Islands, mountainous terrain with tropical evergreen forests.
- It has a group of 836 islands.
- India’s Southern most Indira point is at the tip of GNI.
- Protected Sites:
- Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve
- Campbell Bay National Park
- Galathea National Park
- Ecological Significance:
- High biodiversity with unique flora and fauna, including endangered species.
- Important for marine life and coral reefs.
- Plays a crucial role in climate regulation.
- Designated a World Network of Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2013.
Strategic and Environmental Concerns
- Secrecy and Security: Information about the project denied under RTI citing sovereignty and security concerns.
- Environmental Impact: Coral reefs, forest clearances, and CRZ restrictions raise ecological issues.
- Contradictions in Vision: Proposed tourism and ship-breaking activities potentially conflict with strategic purposes cited by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Challenges in Implementation
- Policy Shift: Opens up Great Nicobar to foreign vessels and tourists, reversing isolationist policies.
- Stakeholder Dissonance: Resistance from local administration and Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Limited (ANIIDCO) over feasibility and compatibility of new proposals.
- Transparency Issues: Limited public access to information, raising accountability concerns.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Way Forward
- Environmental Sustainability: Conduct independent environmental impact assessments to align development with conservation priorities.
- Strategic Clarity: Ensure alignment between development objectives and strategic security concerns.
- Public Accountability: Increase transparency in decision-making processes and public access to project details.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Consult local stakeholders and experts to address feasibility and socio-environmental impacts.
![]() 6 Jan 2025
6 Jan 2025


