Context:
According to a report by Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), Delhi recharged more groundwater than it extracted in FY 2021-22.
- This is the first time since at least 2009-2010 that Delhi’s recharge is more than its extraction.
- Compared to 2020-21, the number of “safe” tehsils in Delhi has gone up from three to four, while the number of “overexploited” tehsils has dropped from 17 to 15.
- However, Delhi is still “critical” in terms of groundwater extraction.
About Groundwater:
- Groundwater is the water that is present beneath the Earth’s surface within the spaces and fractures of rocks and soil.
- It is a vital component of the Earth’s water cycle and plays a crucial role in supporting ecosystems.
Groundwater Exploitation
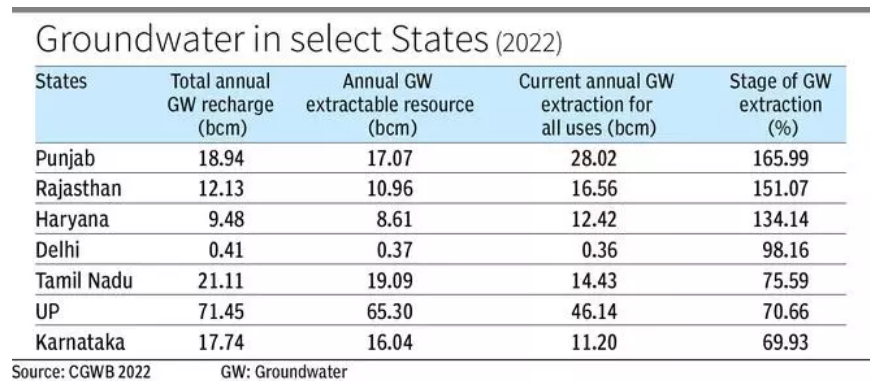
- States such as Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana are exploiting groundwater more than the quantity of its recharge.
- This overexploitation of groundwater is likely to be the source of geogenic contaminants such as arsenic and fluoride.
|
India’s Groundwater
- India has 4 per cent of global water resources for its use in spite of having 17 percent of the world population.
- There are wide spatial and temporal variations in the distribution of water.
- Groundwater is the backbone of India’s agriculture and drinking water security.
- Contribution of groundwater in agriculture is about 62 per cent, 85 per cent in rural water supply and 50 per cent in urban water supply, respectively.
- Main Source: The main source of groundwater resources is rainfall which contributes to nearly 61 per cent of total annual groundwater recharge according to a Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) report ‘National Compilation on Dynamic Groundwater Resources of India, 2022’
- India’s per capita availability of water has touched the water stressed benchmark, and is likely to reach a water scarce scenario by 2050.
- Recharge of groundwater: Recharge of groundwater depends on the type of rock formation in a place.
- For example, porous formations (such as alluvial formation) in the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra basin have high specific yields and are good repositories of groundwater.
Ways to Improve Groundwater level:
- The groundwater level can be increased by two means — artificial recharges and rainwater harvesting.
- Artificial recharge: It is a process that increases infiltration either through faster rates or due to availability of source water in a longer time duration.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collect and store rainwater for direct use or recharge purposes, reducing the reliance on groundwater for certain applications.
News Source: The Hindubusinessline
![]() 29 Aug 2023
29 Aug 2023
