On September 20, 1924, John Marshall, then-Director General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), announced the discovery of the “Indus Valley Civilisation” through an article in The Illustrated London News.
More about the discovery
- This 100 year old announcement came after significant discoveries at the Harappa and Mohenjo-daro sites.
- It marked a monumental moment in the study of South Asian history.
- The Harappan civilisation flourished around 2,500 BC (Bronze Age) in western part of South Asia, in contemporary Pakistan and Western India.
- It continues to intrigue scholars for its advanced urban planning, metallurgy, ceramics, water management, and undeciphered script.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Key Sites and Discoveries
- Harappa (Pakistan) was first excavated in 1921-22 by Daya Ram Sahni.
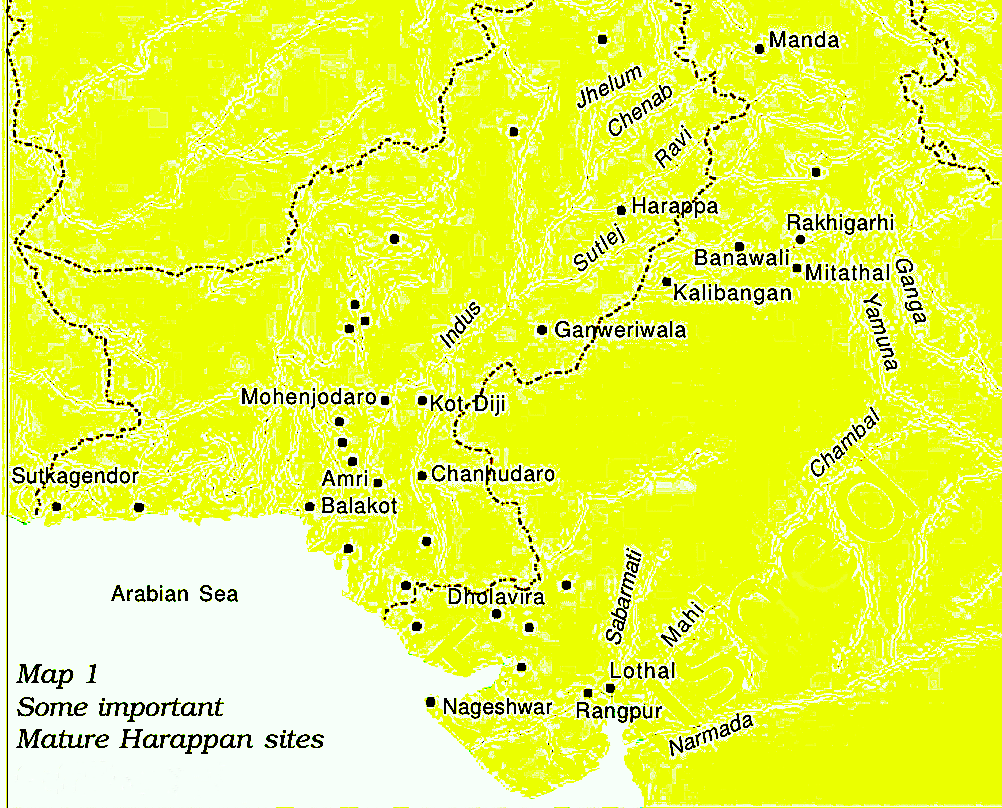 Mohenjo-daro was uncovered by Rakhal Das Banerji in 1922.
Mohenjo-daro was uncovered by Rakhal Das Banerji in 1922. - Both archaeologists unearthed seals, pottery, and metal artifacts, leading to Marshall’s recognition of a civilisation spread across vast distances, including areas now in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
- With about 2,000 known sites, the civilisation’s major centers include Harappa, Mohenjo-daro, Ganweriwala, Rakhigarhi (India), Surkotada (India), Lothal (India) and Dholavira (India).
- Geographical Extent:
- Westernmost:Sutkagendor (in Balochistan, Pakistan)
- Easternmost: Alamgirpur (Western UP)
- Northernmost: Mandu (Jammu)
- Southernmost: Daimabad (Ahmednagar, Maharashtra)
Harappan Achievements
- Urban Planning: Grid-pattern streets, water reservoirs, drainage systems, and standardised brick construction.
- Craftsmanship: Bronze and copper artifacts, beads, seals with inscriptions, and intricate terracotta products.
- Advanced Civilization: Standardised weights and measures, use of a script, and maritime contacts with West Asia.
| Harappan Site |
Location |
Important Features & Findings |
| Sutkagendor |
Pakistan-Iran border |
- Coastal site.
- Evidence of trade with Mesopotamia and Oman
- Possibly a trading outpost on the Makran coast.
|
| Chanhudaro |
Sindh, Pakistan |
- Known for bead-making, shell-working, and metal crafts
- No fortified walls, indicating it was an industrial hub.
|
| Kalibangan |
Rajasthan, India |
- Early use of plowed fields
- fire altars, evidence of ritual practices
- brick-lined drains.
|
| Lothal |
Gujarat, India |
- Dockyard for maritime trade
- Evidence of the bead industry, rice cultivation and terracotta figurines.
|
| Dholavira |
Gujarat, India |
- Sophisticated water conservation system
- large city layout with distinct zones
- signboard with Indus script.
|
| Rakhigarhi |
Haryana, India |
- One of the largest Harappan sites.
- Evidence of planned settlements
- Human burials with grave goods.
|
| Mohenjo-daro |
Sindh, Pakistan |
- Great Bath, granary
- Advanced drainage system
- large urban center with well-planned streets and houses.
|
| Harappa |
Punjab, Pakistan |
- Granaries
- Evidence of urban planning
- Cemetery with burial practices
- Advanced metallurgy.
|
Challenges and Continuing Mysteries
- Undeciphered Script: The Harappan script remains a mystery.
- Reasons for Decline: The reasons behind the decline of the Harappan civilization are unclear.
- Pre-Aryan Origins: Scholars have made significant contributions to understanding the civilization’s pre-Aryan origins.
- Connections to Earlier Cultures: The Harappan civilization’s connections to earlier cultures like Mehrgarh are being explored.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Decline of Indus Valley Civilisation
- No consensus on causes: The decline of the Indus Valley Civilization remains debated, with multiple theories proposed.
- Environmental change: Gradual climatic shifts may have led to agricultural collapse due to overpopulation and resource exploitation.
- Sudden environmental events: Tectonic activity could have caused floods, dried rivers (like the Sarasvati), or other natural disasters.
- Human intervention: Invasions by hill tribes or Indo-Aryans possibly disrupted trade and weakened cities.
- Epidemic theory: Some suggest an epidemic or similar disaster may have contributed.
- Complex decline: Likely a combination of natural and human factors.
![]() 20 Sep 2024
20 Sep 2024
 Mohenjo-daro was uncovered by Rakhal Das Banerji in 1922.
Mohenjo-daro was uncovered by Rakhal Das Banerji in 1922. 