Recently, the Tamil Nadu government has officially declared heatwaves a State-specific disaster and announced ex-gratia payments of ₹4 lakh for families of individuals who die of heat-related causes.
Heatwaves
- Definition: Period of unusually high temperatures compared to what is normally expected in a region.
- Criteria for Declaring a Heat Wave in India:
- Plains: Maximum temperature reaches at least 40°C.
 Coastal Stations: Maximum temperature reaches at least 37°C.
Coastal Stations: Maximum temperature reaches at least 37°C.- Hilly Regions: Maximum temperature reaches at least 30°C.
- Classification of Heat Waves:
- Based on Departure from Normal:
- Heat Wave: Departure from normal is 4.5°C to 6.4°C.
- Severe Heat Wave: Departure from normal exceeds 6.4°C.
- Based on Actual Maximum Temperature (Plains Only):
- Heat Wave: Actual maximum temperature reaches 45°C.
- Severe Heat Wave: Actual maximum temperature reaches 47°C.
- Declaration Criteria:
- Conditions must be met in at least two stations within a Meteorological sub-division.
- Conditions must persist for at least two consecutive days.
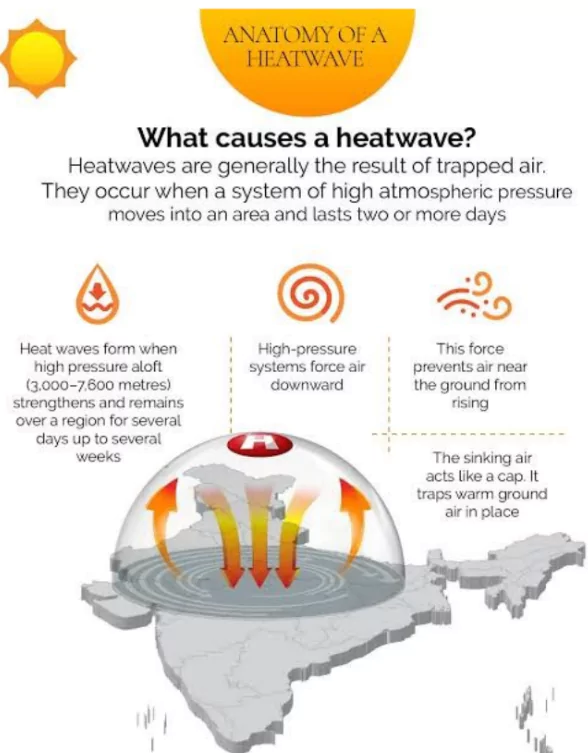
- Favourable Conditions for Heat Waves:
- Hot and Dry Air: Acts as a reservoir of heat, transported by prevailing winds.
- Low Humidity Levels: Allows heat accumulation and limits nighttime cooling.
- Clear Skies: Enables uninterrupted sunlight, raising ground and air temperatures.
- Large Amplitude Anticyclonic Flow: Sinking air compresses and warms adiabatically.
- Geographical Considerations: More frequent in arid/semi-arid regions, like Northwest India.
- Climate Change: Increased baseline temperatures enhance the likelihood and intensity of heatwaves.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
State-Specific Disasters
- Definition: Disasters that are local to a state and not listed by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Announcement: Declared by the State Government.
- Funding Mechanism: Utilises up to 10% of the funds from the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) for immediate relief.
- Responsible Authority: State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA), established under the Disaster Management Act of 2005.
- SDMA Composition: Chaired by the Chief Minister and includes no more than eight members appointed by the Chief Minister.
- Role of SDMA: Prepares and implements the state disaster management plan in line with the National Disaster Management Plan.
Notified Disasters
- Definition: it is a catastrophic event arising from natural or human-made causes, officially recognized by the government.
- Legal Framework:
- Defined under the Disaster Management Act of 2005.
- Current Categories of Notified Disasters (13 categories):
- Cyclones, Drought, Earthquakes, Fire, Flood, Tsunami, Hailstorm, Landslide, Avalanche, Cloudburst, Pest Attack, Frost and Cold Waves, COVID-19.
- Financial Assistance:
- Provided from two funds established under the DM Act:
- National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) at the national level.
- State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) at the state level.
|
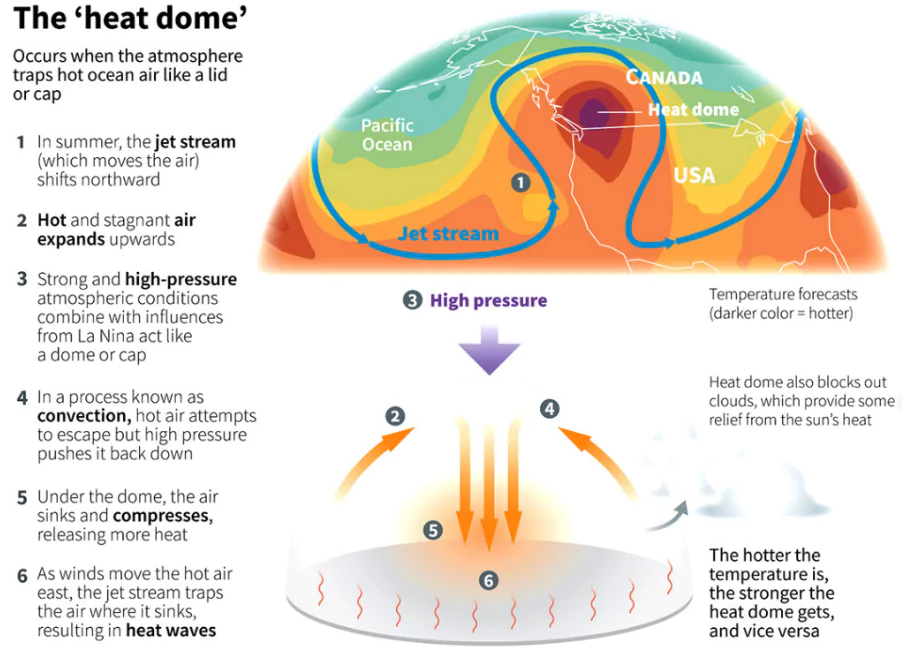
Heat Dome
- Definition: it is a weather phenomenon where a high-pressure system traps warm air, acting like a lid on a pot.
- Characteristics:
- Warm air cannot rise, resulting in clear skies.
- The high-pressure system allows more sunlight to reach the earth, leading to increased warming and soil drying.
- Reduced evaporation limits rain cloud formation.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
![]() 29 Oct 2024
29 Oct 2024

 Coastal Stations: Maximum temperature reaches at least 37°C.
Coastal Stations: Maximum temperature reaches at least 37°C.