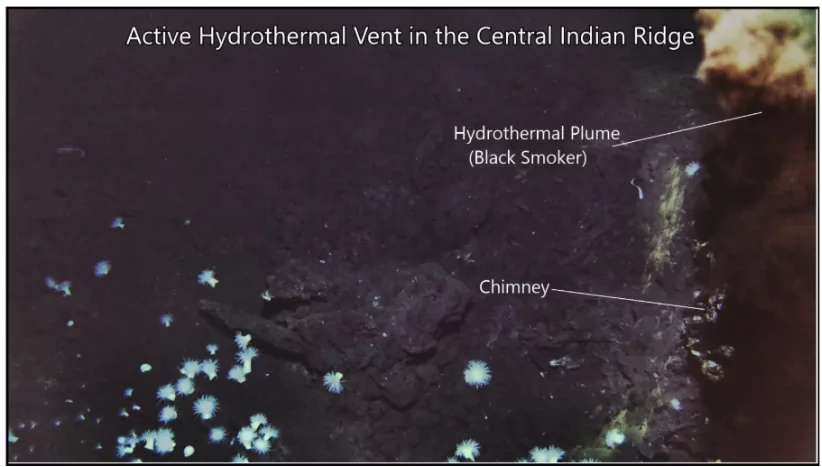
Indian oceanographers from National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) and National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) captured a historic image of an active hydrothermal vent in the Indian Ocean.
About Hydrothermal Vent
- Formation: Hydrothermal vents are underwater hot springs found in tectonically active regions, where cold seawater interacts with magma, becoming superheated (up to 370°C) and emerging as mineral-rich plumes through chimneys or vents.
- Recent Discovery in Indian Ocean: An active hydrothermal vent was discovered at a depth of 4,500 meters along the Central Indian Ridge.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Chemosynthetic Organisms
What is Chemosynthesis?
Chemosynthesis is a process where organisms use chemical energy to produce organic compounds. Unlike photosynthesis, which uses sunlight, chemosynthesis harnesses energy from the oxidation of inorganic molecules.
Chemosynthesis Process
- Chemosynthetic organisms, primarily bacteria and archaea, oxidize inorganic compounds like hydrogen sulfide, methane, or ammonia.
- This process releases energy, which is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic molecules, primarily carbohydrates.
Chemosynthetic Organisms
- Chemosynthetic organisms play a crucial role in deep-sea ecosystems, supporting diverse communities of life in the absence of sunlight
- Tube worms: These iconic creatures form dense colonies around hydrothermal vents. They house chemosynthetic bacteria within their tissues, providing a symbiotic relationship where the bacteria produce energy for both organisms.
- Clams and mussels: These bivalves also harbor chemosynthetic bacteria within their gills. The bacteria oxidize sulfide compounds, providing energy for the clams and mussels.
|
- Ecosystem and Lifeforms: These vents support unique ecosystems powered by chemosynthesis, where microbes act as primary producers, sustaining diverse organisms in extreme conditions.
- Key Features:
-
- Includes chimneys and black smokers emitting superhot mineral-rich plumes.
- Hosts rich deposits of copper, zinc, gold, silver, platinum, iron, cobalt, and nickel.
- Supports chemosynthetic organisms thriving in mineral-rich environments.
- This discovery highlights the potential for resource exploration and the study of extreme marine ecosystems.
Significance of Discovery for Deep Ocean Mission
- Mineral Resource Exploration: Deposits around vents contain valuable metals like copper, zinc, gold, silver, cobalt, and nickel, essential for economic growth.
- Biological Insights: Unique microbial life forms offer clues to extremophile ecosystems, with potential applications in biotechnology and medicine.
- Samudrayaan Mission: Enhances India’s capabilities in manned deep-sea exploration for both inactive and active vent systems.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
About Deep Ocean Mission (DOM)
- DOM aims to position India as a pioneer in ocean science and technology, contributing to global efforts in sustainable ocean resource management.
- Objective: To explore and harness the resources of the deep ocean.
- Implementing Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Approval: Union Cabinet in 2021 for Five years.
- Budget Allocation: Approximately ₹4,077 crore
- Key Focus Areas:
-
- Development of technologies for deep-sea mining
- Development of a manned submersible to reach 6,000 meters depth(Matsya 6000)
- Ocean climate change advisory services
- Exploration of deep-sea biodiversity
- Development of ocean technologies
|
Additional Reading: DOM
![]() 20 Dec 2024
20 Dec 2024


