Context:
Recently, the United Nations’ International Labour Organization (ILO) released a report on the impact of Generative AI and other platforms on jobs quantity and quality.
Findings of Report:
- Job Augmentation: Most jobs and industries are only partially exposed to automation and are more likely to be complemented rather than substituted by AI.
- Generative AI systems similar to GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) are more likely to become productivity tools, supporting and speeding up the execution of some tasks within certain occupations.
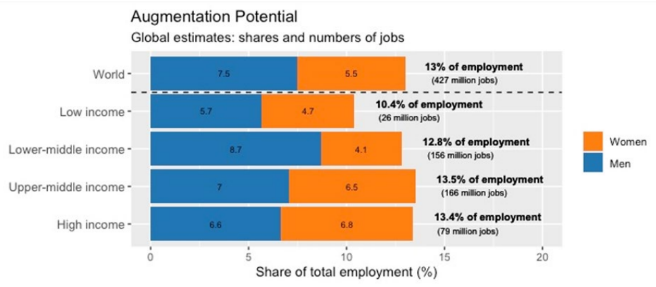
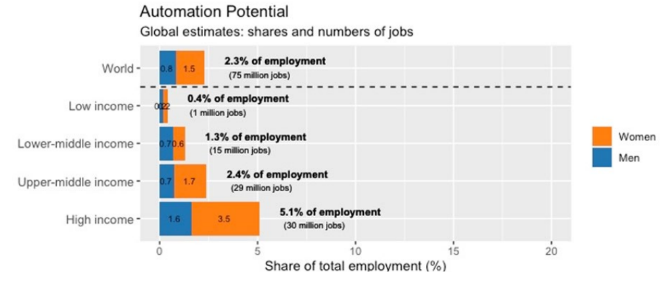
- Fears Over Job Destruction: The surge in generative AI and its chatbot applications has sparked concerns about job destruction, akin to the concerns surrounding the introduction of the moving assembly line in the 1950s.
- Technology can enhance job quality in the workplace by automating routine tasks, allowing more engaging work, but also limiting worker agency or increasing work intensity.
- Impact on Countries: Recent progress in machine learning, in particular developments around Large Language Mode (LLMs), is likely to have disruptive effects on labour markets, with larger effects in high-income countries and specific occupational groups.
- 5.5 percent of total employment in high-income countries was potentially exposed to the automating effects of generative AI, whereas only 0.4 percent of employment in low-income countries.
- Professional Variation: Clerical support workers face the greatest risk of being affected by AI.
- About 25% of clerical workers’ tasks face a high exposure to generative AI, and 58% of their tasks face a medium exposure to the technology.
- Example: Jobs such as typists, travel consultants, scribes, contact center information clerks, bank tellers, and survey and market research interviewers that could eventually be automated.
- Only 4% of service and sales workers’ tasks face high exposure to generative AI, and 18% of their tasks face medium exposure.
- Thus impact is not likely to be jobs reduction but rather the potential changes to the quality of jobs, notably work intensity and autonomy.
- Gendered Impact: Effects of automation are “highly gendered”, with more than double the share of women potentially affected by automation, due to their overrepresentation in clerical work, especially in high- and middle-income countries.
- In high-income countries, 7.8% of jobs held by women ( around 21 million jobs) have the potential to be automated.
- In contrast, only 2.9% of jobs in high-income countries held by men (around 9 million jobs) face the potential of being automated.
- The recent increase in women’s labor market participation may be threatened by concentrated job losses in female-dominated occupations.
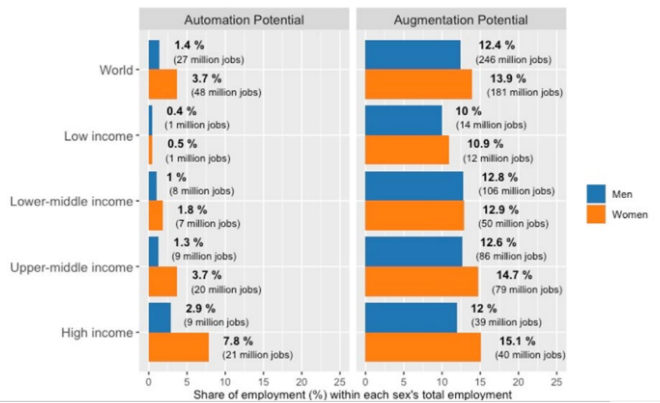
- Digital Divide: Generative AI technology is dependent on access and cost of broadband connectivity, as well as electricity.
- In 2022, one-third of the global population (around 2.7 billion people), still did not have access to the internet.
- Access to Electricity: According to the World Bank Enterprise Survey, 49% of registered firms in developing countries experienced electrical outages, averaging 4.5 days per month.
- Without proper policies in place, there is a risk that only some of the well-positioned countries and market participants will be able to harness the benefits of the transition, while the costs to affected workers could be brutal.
About Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- It is a type of AI technology that can produce various types of content, including text, imagery, audio and synthetic data.
- It utilizes deep learning, neural networks, and machine learning techniques to enable computers to produce content that closely resembles human-created output autonomously.
- Example: ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Bard.
| Pros of Generative AI: |
Cons of Generative AI: |
- Creativity and Novelty: It enables the creation of new and unique content, whether it’s images, music, or text.
- Automation and Efficiency: It automates the process of content creation, saving time and resources.
- Personalization and Customization: Generative models can be trained on specific data or preferences, allowing for personalized recommendations, tailored content, and customized user experiences.
- Exploration and Inspiration: Generative AI can provide inspiration to artists, designers, and writers by generating diverse variations, exploring creative possibilities, and serving as a starting point for further creative exploration.
|
- Ethical Concerns: Generative AI raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding the misuse of synthetic media, deepfakes, and potential infringement of intellectual property rights.
- Ex: in July, 2023, Kerala man loses ₹40k to AI-enabled deep-fake fraud.
- Lack of Control: Generative models can produce outputs that are difficult to control or fine-tune to specific requirements.
- Dataset Bias and Generalization: Generative models heavily rely on the training data they are exposed to.
- Computational Resources and Complexity: Training and deploying generative models can be computationally intensive and require significant resources, including high-performance hardware and substantial training times.
- Implementing and maintaining these models can be complex and resource-demanding.
- Quality and Coherence: While generative models have made significant progress, they may still struggle with producing outputs that consistently exhibit high quality, coherence, and contextual relevance.
|
Report Recommendations:
- All Stakeholder Approach: Consultation and negotiation between employers and workers is critical for managing the transition process as it encourages redeployment and training over job loss.
- Adhering to The ILO’s Employment Protection Convention (No. 158, 1982): To reduce negative externalities from dismissal and support an orderly process that balances workers’, employers’, and societies’ needs.
- It includes provisions on the termination of employment for technological reasons.
- Investing in the Care Economy: Improving job quality for care economy workers can provide decent employment and meet society’s care needs to offset the negative externalities of Generative AI in the long term.
- It requires increased investment, training, and income support during the transition.
- Potential: According to the ILO, achieving the SDG targets would require more than double employment in care economy sectors from 206 million in 2015 to 475 million in 2030.
- Quality Adherence: Ensure quality of the new jobs created as a result of technological change.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
- It was founded in 1919 under the League of Nations and incorporated into the U.N. as a specialized agency in 1946.
- HQ: Geneva.
- The ILO is the first and oldest specialized agency of the United Nations (U.N.).
- Goal: To advance social and economic justice by setting international labor standards.
- Conventions and protocols of ILO are a major contributor to international labor law.
- ILO was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
(For more information about Large language Model, kindly refer to PWONLYIAS July Current Affairs Magazine) |
News Source: Economic Times
![]() 24 Aug 2023
24 Aug 2023


