The International Monetary Fund (IMF) maintained its June growth rate projection for India at 7% for FY25 in its latest released World Economic Outlook (WEO).
Key Highlights of the World Economic Outlook
- Global Growth Projections: Global growth is projected to be 3.2% for both 2024 and 2025.
- The global economy has shown resilience despite inflation and external challenges.
- Inflation Trends: The battle against inflation is nearly won. Inflation peaked at 9.4% in Q3 of 2022.
- It is expected to fall to 3.5% by the end of 2025, nearing central bank targets in most countries.
- Geopolitical and Economic Risks:
- Geopolitical conflicts (e.g., in the Middle East), which could disrupt commodity markets.
- Rising trade tensions and shifts toward protectionist policies.
- A potential reduction in migration to advanced economies, which could unwind some of the supply gains helping to ease inflation.
- These factors could reduce global output by 1.6% by 2026.
- Fiscal Challenges and Debt Management: Urgent need to stabilize debt dynamics and rebuild fiscal buffers, especially in the United States and China.
- Current fiscal plans are not sufficient to stabilize debt in several countries.
- Delayed action on debt reduction could lead to disorderly adjustments.
- Excessively abrupt fiscal tightening could harm economic activity.
- Warning on Market Pressures: High debt levels combined with high interest rates pose a risk.
- If fiscal policies are not credible, market pressures may force abrupt and uncontrolled adjustments.
- Countries must act proactively to avoid being at the mercy of market forces.
- Triple Policy Pivot: The IMF suggests a three-part policy approach to respond to the global economic challenges:
- Neutral monetary policy stance: A shift towards balanced monetary policies, which many countries are currently adopting.
- Fiscal consolidation: Building fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy.
- Structural reforms: To boost growth and productivity, address the ageing population, and tackle the climate transition
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Key Highlights On Indian Economy
- This outlook highlights India’s position as one of the fastest-growing major economies, though there are challenges to sustaining high growth rates amid global uncertainties.
- India’s growth rate at 7% remains higher than global growth projections, with the world economy projected to grow at 3.2% for 2024 and 2025.
- For the following year, FY 2025-26, the growth rate is expected to be 6.5%.
- The decline from 8.2% in 2023 is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand from the pandemic period, as the economy reconnects with its potential.
- In contrast, the U.S. economy is expected to grow at 2.8% this year and 2.2% next year.
About IMF
- Established in the aftermath of the Great Depression of the 1930s at Bretton Woods Conference in 1944.
- It is one of the United Nations (UN) specialised agencies.
- Main objectives: Include supporting global monetary cooperation, securing financial stability, facilitating international trade, promoting high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reducing poverty.
- Economic surveillance : IMF keeps track of the economic health of its member countries, alerting them to risks on the horizon and providing policy advice.
- Lender of last resort: Lends to countries with balance-of-payments difficulties.
- It also provides technical assistance and training to help countries improve economic management.
- Headquarter : Washington, DC.
- Reports by IMF: Following reports are usually prepared twice a year April and October.
- Global Financial Stability Report.
- World Economic Outlook.
IMF Quota Subscription
- Quota Subscription: Each IMF member contributes a financial amount based on its economic size and wealth.
- Quota Review: Quotas are reviewed every five years and are linked to each country’s wealth and economic performance.
- Quota Formula:
- GDP (50%)
- Openness (30%)
- Economic Variability (15%)
- International Reserves (5%)
- Richer Countries: Countries with larger economies, like the U.S., contribute more to the IMF. The U.S. has the largest quota, reflecting its economic dominance.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDR): Quotas are denominated in Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), an international reserve asset created by the IMF.
- SDR Value: Determined from a weighted basket of major global currencies, including:
- U.S. Dollar
- Euro
- Japanese Yen
- Chinese Yuan
- British Pound
- Quota’s Role:
- Loanable Funds Pool: Quotas contribute to a pool of funds that IMF members can borrow from.
- Borrowing and Voting Power: The size of a country’s quota influences how much it can borrow and its voting power in IMF decisions.
- Reserve Tranche Position: Reserve Tranche (also called “Gold Tranche”) is a portion of a member’s quota that can be accessed without stringent conditions or service fees.
- Calculation: The Reserve Tranche Position is the difference between the IMF’s holdings of a country’s currency and the country’s IMF quota.
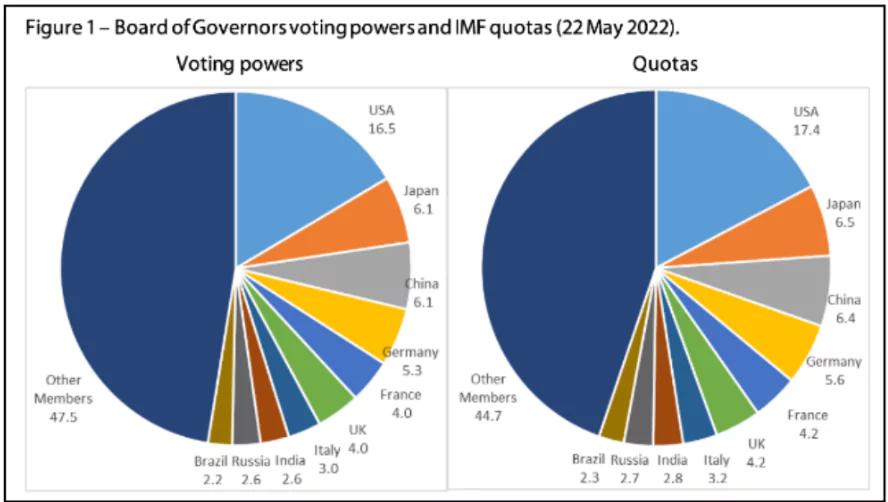
- Voting Powers and IMF Governance:
- Quota-Determined Voting: A country’s quota dictates its voting power. Votes are comprised of:
- One vote per 100,000 SDRs of quota
- Basic votes: Each member receives a fixed number of basic votes.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Governance Setup of IMF
- Board of Governors: Each IMF member country appoints one governor and one alternate governor.
 Key Responsibilities of Board of Governors:
Key Responsibilities of Board of Governors:-
- Electing or appointing executive directors to the Executive Board.
- Approving quota increase and SDR allocations.
- Admitting new members or enforcing the compulsory withdrawal of members.
- Executive Board: It is composed of 24 members, elected by the Board of Governors.
- Oversees the daily operations of the IMF.
- IMF Membership: Membership is open to any state, including non-UN members, under the conditions set by the IMF’s Articles of Agreement and the Board of Governors.
![]() 23 Oct 2024
23 Oct 2024

 Key Responsibilities of Board of Governors:
Key Responsibilities of Board of Governors: