Context:
Murmansk, often referred to as the capital of the Arctic region and the starting point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is currently experiencing a notable increase in Indian participation in cargo transportation.
- During the initial seven months of 2023, India secured a significant portion, amounting to 35%, of the eight million tonnes of cargo that passed through the Murmansk port.
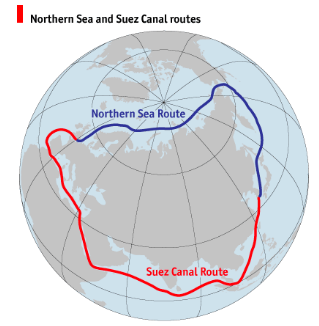
What is NSR?
- It is the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles four seas of the Arctic Ocean.
- Running to 5,600 km, the Route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
NSR Development:
- NSR Development Targets:
- The Russian government has approved a development plan for the NSR until 2035.
- Targets include reaching cargo traffic volumes of 80 million tonnes by 2024 and 150 million tonnes by 2030.
- Russian-Indian Collaboration:
- In March 2023, a Russian delegation engaged with the Indian business community in New Delhi and Mumbai to discuss NSR development.
- The delegation pledged to ensure the availability of essential components for year-round NSR operation.
Factor for India’s participation in the development of the NSR:
- Rising Cargo Traffic Growth: India’s increasing imports of crude oil and coal from Russia make the NSR an attractive and reliable transportation route for these vital energy resources.
- Geographical Significance: India’s strategic geographical location near major sea trade routes makes the NSR an important transit route for its trade.
- Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC): The CVMC project, stemming from a memorandum of intent signed between India and Russia in September 2019, is being explored as a way to connect with organized international container transit through the NSR.
- The 10,500 km-long CVMC, passing through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea, and Malacca Strait, significantly reduces transport time to 12 days compared to existing routes.
- Geostrategic Considerations: Experts highlight the potential for China and Russia to collectively influence the NSR, making India’s engagement in its development an essential strategic move.
About Arctic Region:
- Arctic, northernmost region of Earth, centred on the North Pole and characterized by distinctively polar conditions of climate, plant and animal life, and other physical features.
Significance of Arctic Region for India:
- Climate Impact: Vulnerability to Arctic climate changes affects India’s climate patterns, impacting agriculture and water resources.
- Natural Resources: The Arctic holds vast unexplored hydrocarbon reserves, estimated at over 40% of global oil and gas reserves, along with coal, zinc, and silver potential.
- India’s Arctic policy aligns with UN Sustainable Development Goals, emphasizing responsible and sustainable development in the region.
India’s Arctic Policy Six Pillars:
- Science and research.
- Environmental protection.
- Economic and human development.
- Transportation and connectivity.
- Governance and international cooperation.
- National capacity building.
India’s engagement with the Arctic:

|
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 25 Aug 2023
25 Aug 2023

