Vietnamese Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh is on a three-day visit to India.
Vietnamese Prime Minister Stance
- He emphasized the need for closer cooperation between Vietnam and India in various areas, including semiconductor technology, digital transformation, green hydrogen, pharmaceuticals, renewables, and biotechnology.
- He stressed the role of both governments in promoting business ties and strategic cooperation across supply chains, strategic resources, climate action, environmental technology, human resources, defense, and security.
- He also highlighted that bilateral trade could increase from the current $15 billion to $20 billion in the coming years.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Highlights and Outcomes of the Bilateral Meeting
- Strategic partnership: Both the prime ministers discussed increasing comprehensive strategic partnership between India and Vietnam.
- Both leaders focused on areas such as trade, defence, and maritime security.
- Defence cooperation: 14th India and Vietnam defence policy revolved around emerging areas such as cyber security and military medicine.
- Vietnam suggested cooperation in five areas – delegation exchanges, staff talks, service-to-service cooperation, education and training, and defence industry collaboration.
- The leaders agreed to expedite the implementation of the Implementing Arrangement on Hydrography and form a Joint Committee to oversee these efforts, enhancing collaboration across multiple domains.
- Economic and Trade Relation: Both nations agreed to increase trade and economic cooperation, keeping the vision to increase two-way trade beyond the current $15 billion.
- Trade Barriers: They discussed removal of trade barriers and establishment of economic diplomacy dialogue for improving trade relations.
- Maritime Security: Both the nations (India and Vietnam) emphasised on maritime security cooperation especially in south china sea.
- They agreed to collaborate to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight in the region.
- Credit line agreement: An agreement of $300 million credit line was signed to add up Vietnam maritime security.
- This initiative is crucial for bolstering Vietnam’s maritime security, enabling it to safeguard its interests in the contentious waters of the South China Sea.
- Cultural and Educational Exchange: Both sides shed light on the significance of Cultural and Educational Exchange to enhance people to people connections.
India-Vietnam Relations
- Diplomatic Ties: India and Vietnam established diplomatic relations in 1992, and since then, their ties have grown stronger.
- Historical Background : Both countries share similar historical experiences, particularly in their struggles for independence from colonial rule.
- Bilateral Relations: India and Vietnam have a long-standing and friendly relationship, making it one of India’s most important partnerships in Southeast Asia.
- Strategic and Comprehensive Partnership
- The relationship between India and Vietnam was elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2007.
- In 2016, the partnership was further enhanced to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, reflecting the deepening ties between the two nations.
- Economic Cooperation: Over the last 20 years, trade between India and Vietnam has increased significantly, rising from $200 million in 2000 to $12.3 billion in the 2019-2020 financial year.
- For the fiscal year 2023-24, bilateral trade reached approximately $14.82 billion.
- Trade Breakdown:
- India’s exports to Vietnam were around $5.47 billion.
- Imports from Vietnam to India totaled about $9.35 billion.
- Defence Cooperation
-
- India and Vietnam signed the ‘Joint Vision Statement on India-Vietnam Defense Partnership towards 2030′ and an MoU on Mutual Logistics Support.
- Vietnam-India Bilateral Army Exercise (VINBAX): A regular joint military exercise.
- Gifting of INS Kirpan: India gifted the in-service missile corvette INS Kirpan to Vietnam.
Impact of India and Vietnam Trade on Indian Economy
Benefits for the Indian Economy
- Job Creation: Increased trade often leads to more jobs in sectors like manufacturing, transportation, and logistics. As India exports more to Vietnam, it can create employment opportunities for Indian workers.
- Economic Growth: Higher exports mean more money coming into the Indian economy. This can boost overall economic growth and development.
- Foreign Investment: Vietnam’s growing economy and increasing trade with India could attract more foreign investment into India, providing capital for businesses and infrastructure projects.
- Technology Transfer: Cooperation in areas like semiconductors, digital transformation, and green technology can lead to knowledge sharing and technology transfer, benefiting India’s technological advancement.
- It will help in areas like e-commerce, fintech, and artificial intelligence.
- Reduced Trade Deficit: While India currently has a trade deficit with Vietnam, increased exports can help to reduce this gap and improve India’s trade balance.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Challenges
- Trade Imbalance: There’s a risk of trade imbalances if imports from Vietnam increase faster than exports to Vietnam, potentially leading to a higher trade deficit for India.
- Competition: Indian businesses might face tougher competition from Vietnamese products, especially in areas like textiles, electronics, and agriculture.
- Regulatory Barriers: Differences in regulatory standards and practices between the two countries can create obstacles for businesses entering each other’s markets.
- Logistics and Infrastructure: Insufficient logistics and infrastructure could hinder the efficient flow of goods and services between India and Vietnam.
- Quality Standards: Ensuring that products meet the quality standards of both countries can be challenging, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical issues, especially those involving China, can impact trade relations and introduce uncertainties.
Way forward
To achieve the target of $20 billion trade between India and Vietnam, both nations can take various steps.
- Strengthening Trade Agreements: Enhance existing trade agreements and formulate rules to reduce the burden of tariff and non-tariff barriers.
 Streamline regulatory frameworks for establishing smooth customer procedure.
Streamline regulatory frameworks for establishing smooth customer procedure.
- Development of Infrastructure: Invest in infrastructure projects that increase connectivity between two nations such as ports, highways, and logistics networks.
- There should be promotion of digital infrastructure too to support e-commerce and digital trade.
- Capacity Building:
- Training Programs: Organize workshops and training sessions to improve skills in quality standards, market access, and export readiness.
- Knowledge Exchange: Foster technical cooperation and knowledge sharing between countries to enhance expertise.
-
Policy Support
- Supportive Policies: Ensure that government policies consistently promote trade and investment.
- Address Bottlenecks: Identify and resolve any policy issues that may be obstructing trade growth.
-
Cultural and Educational Exchanges
- Promote Exchanges: Encourage cultural and educational programs to build strong relationships and understanding between people.
- Language and Culture: Support language learning and cultural awareness initiatives to make business interactions smoother.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
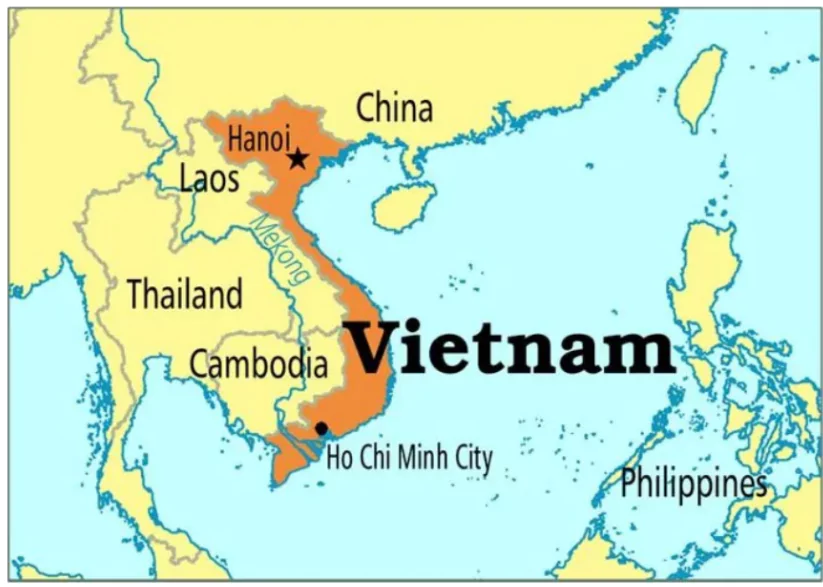
Overview of Vietnam
- Location:
- Situated in Southeast Asia.
- Bordered Regions:
- North: China
- Northwest: Laos
- Southwest: Cambodia
- East and South: The South China Sea
- Capital: Hanoi
- Major Rivers:
- Mekong River in the south.
- Red River in the north.
- Both rivers flow into the South China Sea.
- Currency: Vietnamese Dong (VND)
|
![]() 3 Aug 2024
3 Aug 2024
 Streamline regulatory frameworks for establishing smooth customer procedure.
Streamline regulatory frameworks for establishing smooth customer procedure.