Recently, India ordered the expulsion of six Canadian diplomats and announced the withdrawal of its High Commissioner to Canada, along with other “targeted diplomats”.

Recent Events and Diplomatic Tensions
- Nijjar Killing
- Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau informed Parliament on September 18, 2023, of “credible allegations” linking Indian government agents to the killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar.
- A Canadian citizen and pro-Khalistan activist involved in promoting separatism in India.
- India refuted the allegations, accusing Canada of allowing its citizens to promote violent separatism (Khalistan movement).
- Escalation into Political Tensions
- Initially confined to diplomatic discussions, the issue escalated into personal political attacks. This shift complicates future diplomatic efforts.
- Trudeau publicly discussed the matter, including a meeting between Indian National Security Advisor Ajit Doval and his Canadian counterpart in Singapore on October 12, 2024.
- Diplomatic Fallout
- Canada asked India to lift the diplomatic immunity of six Indian diplomats, a request India denied.
- In retaliation, India recalled the diplomats and expelled six Canadian diplomats.
- Earlier, India had also asked Canada to reduce its diplomatic presence in India.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Issues and Discrepancies in relation
- Diplomatic Immunity & Allegations
- Canada claims the six Indian diplomats were involved in illegal intelligence gathering.
- India strongly condemned this as baseless and “propagandistic,” highlighting that diplomatic immunity is a standard norm.
- Khalistan Movement
- India criticises Canada’s leniency towards Khalistan supporters, viewing their activities as threats to India’s territorial integrity.
- Canadian officials argue that these activities, while concerning, are lawful under Canada’s free speech laws.
- Western Democracies’ Double Standards
- The irony of Western nations, including Canada, that often disregard fundamental freedoms when their security interests are at risk.
- Trudeau’s previous comments on India’s domestic issues are seen by India as violations of international norms.
Diplomatic Immunity
- Diplomatic Immunity: Principle of international law as per which foreign government officials are not subject to jurisdiction of local courts and other authorities for both their official and personal activities.
- Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, 1961: Extends privileges and immunities to diplomatic staff.
- India acceded to it in 1965 and ratified in 1972 through Diplomatic Relations (Vienna Convention) Act of 1972.
- Termination of Diplomatic Relations: Convention outlines the procedures for the termination of diplomatic relations between states Including the withdrawal of a diplomatic agent and the closure of a diplomatic mission.
- Consular Relations: Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, adopted in 1963, complements the VCDR by establishing rules for consular relations between states.
- While the VCDR primarily deals with diplomatic missions
- Convention on Consular Relations focuses on consular missions and officers.
|
Impacts and Concerns due to recent Issues
Impact on Economic Relations
- Canadian Investments in India:
- Canada has around $75 billion invested in India’s economy, especially in infrastructure, financial services, fintech, real estate, etc.
- Major investors include Canadian Pension Plan Investment Board (CPPIB) and Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec (CDPQ).
- 600 Canadian companies are present in India, and more than 1,000 Canadian firms are pursuing business.
- Missed Trade Deal:
- Negotiations on a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between India and Canada have been stalled.
- The FTA would have enhanced exports of Indian garments, pharmaceuticals, and machinery, along with greater collaboration in services.
- Minimal Trade Impact: Despite political tensions, the private sector has maintained trade flow.
- No major trade restrictions have been introduced by either country so far.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Strategic Concerns
- Geopolitical Shift: India’s attempt to deepen economic ties with other Western countries, including the European Union and the UK, could offset any negative impact from deteriorating relations with Canada.
- Western Support: India is likely to engage with key Western allies to counter Canadian accusations and build international consensus.
Potential Future Impact
- Long-Term Diplomatic Fallout: Escalation may lead to worsening of ties, impacting bilateral business engagements, trade, remittances, and educational cooperation.
- Investment Shifts: Despite tensions, the Indian market remains attractive for global investors, and Canadian investments could be rerouted via other countries like Singapore or UAE.
Principle of reciprocity in diplomatic relations
- The principle of reciprocity in international law involves treating foreigners on par with citizens to the extent provided and regulated by specific intergovernmental agreements.
- It involves permitting the application of the legal effects of specific relationships in law when these same effects are accepted equally by foreign countries.
- In international law, reciprocity means the right to equality and mutual respect between states.
- It is based on the idea that actions and concessions made by one party should be met with a similar response from the other.
|
Bilateral Relations
- India established diplomatic relations with Canada in 1947.
- Canada was among the first countries associated with India’s nuclear programme, but the relationship ruptured after India’s nuclear tests in 1974.
- In April 2015, the bilateral relation was elevated to a strategic partnership.
- Bilateral Mechanisms: Both sides pursue bilateral relations through the dialogue mechanisms such as
- Ministerial level- Strategic, Trade and Energy dialogues;
- Foreign Office Consultations; and
- Other sector specific joint working groups (JWG).
- Consular Matters: Signed Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty in 1994 and Extradition Treaty in 1987.
- Nuclear Cooperation Agreement: Signed in 2010 under which the Joint Committee on Civil Nuclear Cooperation was instituted.
- Trade Statistics and Dependencies
- India was Canada’s 10th largest trading partner.
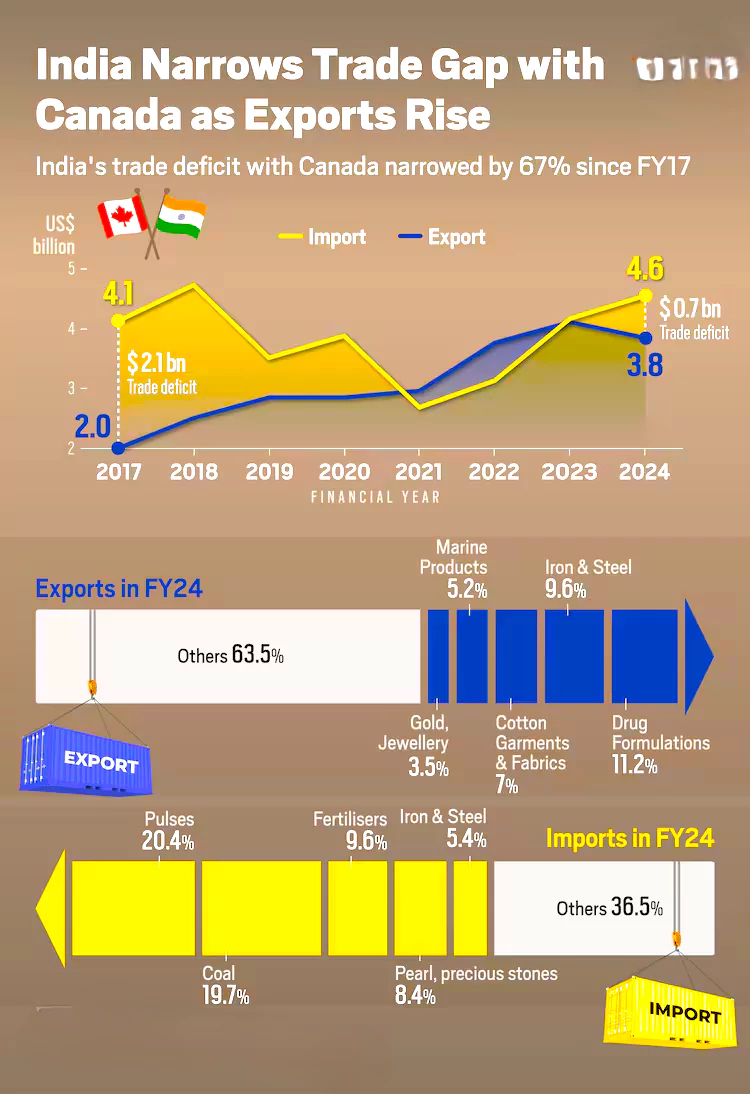
- Bilateral trade in FY 2024: $8.4 billion.
- Showed declining trend in 2023 (USD 7.65 billion from USD 10.50 billion in 2022).
- India’s Total exports to Canada: US$ 4.10 billion in 2022-23
- Major items of India’s Exports to Canada: Gems, Jewellery and Precious stones, Pharmaceutical products, Ready-made garments, Mechanical appliances, Iron and Steel articles, etc.
 India’s Imports from Canada: US$ 4.05 billion in 2022-23 (Nearly Equal to Exports)
India’s Imports from Canada: US$ 4.05 billion in 2022-23 (Nearly Equal to Exports)
- India’s imports from Canada: Pulses, Newsprint, Wood pulp, asbestos, potash, iron scrap, copper, minerals, and industrial chemicals, etc.
- Canada Investment in India: 18th-largest foreign investor in India which is 0.5 per cent of the total foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows into India.
- Canadian pension funds have cumulatively invested around US $55 billion in India.
- Cumulative FDI from Canada since 2000 is about US$4.07 billion.
- Services and infrastructure together accounted for close to 41 per cent of Canadian FDI into India.
- Both sides are engaged in technical negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) including trade in goods, services, investment, trade facilitation etc.
- Science and Technology Cooperation:
- IC-IMPACTS (the India-Canada Centre for Innovative Multidisciplinary Partnerships to Accelerate Community Transformation and Sustainability) is the only Canada-India Research Centre of Excellence as a Centre dedicated to the development of research collaborations between Canada and India.
- Department of Earth Science and Polar Canada have started a programme for exchange of knowledge and scientific research on Cold Climate (Arctic) Studies
- Space Cooperation:
- ISRO and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) have signed MOUs for cooperation in the field of exploration and utilisation of outer space and two Implementation Arrangements specifically addressing satellite tracking and space astronomy have also been signed.
- ANTRIX, the Commercial arm of ISRO has launched many Canadian Satellites.
- ISRO launched its 100th Satellite from PSLV in 2018, also flew Canadian first LEO (Low earth Orbit) satellite.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Indian Diaspora and Remittances
- Canada hosts one of the largest Indian diasporas in the world, numbering 16 lakh people of Indian origin, accounting for more than 3 percent of the total Canadian population and 700,000 NRIs.
- As per the 2021 Canadian census, Sikhs account for 2.1 per cent of Canada’s population, and are the country’s fastest growing religious group.
 After India, Canada is home to the largest population of Sikhs in the world.
After India, Canada is home to the largest population of Sikhs in the world.
- Indian Students:
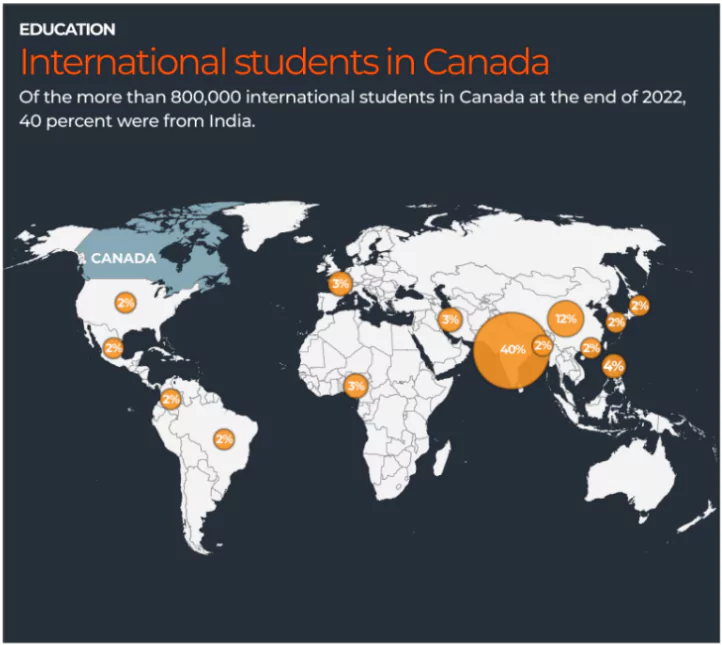
- India became the top source of foreign students (nearly 40 per cent of all international students in Canada) studying in Canada — 2.3 lakh, according to 2022 data.
- Indian students are studying in Canada, contributing significantly to remittance flows and Canada’s economy.
- Remittances from Canada: Canada Contributed 0.6 per cent of the total inward remittances in 2021-22.
Possible Measures by India
- Impact on Education Sector:
- India could restrict Indian students from studying in Canada.
- Could cripple Canada’s education system, given that nearly 25% of foreign students in Canada are Indian.
 OCI (Overseas Citizen of India) Card Cancellations:
OCI (Overseas Citizen of India) Card Cancellations:-
- India could cancel OCI cards of pro-Khalistan Canadian citizens of Indian origin, forcing them to reconsider involvement in the movement.
- Property and Visa Measures:
- India could suspend property rights for Khalistani supporters.
- Delay visas or increase scrutiny on Canadian citizens of Indian descent involved in separatist activities.
- India may also suspend multiple-entry visas for suspected Canadian citizens of Indian descent.
- Trade Sanctions:
- India could impose trade restrictions on Canada.
- Canada is a top-10 trading partner of India, but India has a trade surplus with Canada.
- India could freeze Canadian financial institutions’ investments in India (Canadian pension funds have large stakes in India’s economy).
Way Forward for India-Canada Relations
- Diplomatic Engagement and Dialogue: Both nations should prioritise quiet diplomacy and back-channel talks to de-escalate tensions.
- Continued engagement through multilateral forums like the G20 and UN could offer opportunities for constructive dialogue.
- Addressing Mutual Security Concerns: Canada must take concrete action against anti-India elements, such as pro-Khalistan activists, operating on its soil. India, in turn, should engage with Canadian authorities on the evidence they have presented and ensure transparency in addressing allegations.
- People-to-People Ties: Despite diplomatic strains, the Indian diaspora in Canada plays a vital role in maintaining strong bilateral ties. Both countries should ensure that students, skilled workers, and businesses are not adversely impacted by political tensions.
- Reaffirming Trade and Investment Relations: Resuming discussions on the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and exploring new avenues for economic cooperation can help stabilize relations.
- Canada’s investments in India and vice versa should be kept insulated from political conflicts to ensure mutual economic benefits.
- Collaborating on Global Issues: India and Canada can work together on shared concerns such as climate change, sustainable development, and global security.
- Leveraging common ground in multilateral settings can help maintain cooperation in non-controversial areas.
- Maintaining a Balanced Approach: India should continue engaging with its Western allies to explain its position and avoid diplomatic isolation.
- Canada, on its part, must weigh the long-term geopolitical consequences of allowing domestic politics to dictate foreign policy, particularly with a rising global power like India.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
The current strain in India-Canada relations can only be addressed through sustained diplomacy, mutual respect for sovereignty, and practical cooperation on shared interests. Both nations should focus on long-term strategic benefits, ensuring that political differences do not undermine their historically strong ties and economic partnerships.
![]() 16 Oct 2024
16 Oct 2024

 India’s Imports from Canada: US$ 4.05 billion in 2022-23 (Nearly Equal to Exports)
India’s Imports from Canada: US$ 4.05 billion in 2022-23 (Nearly Equal to Exports)
 After India, Canada is home to the largest population of Sikhs in the world.
After India, Canada is home to the largest population of Sikhs in the world. OCI (Overseas Citizen of India) Card Cancellations:
OCI (Overseas Citizen of India) Card Cancellations: