Context: This article is based on the news “India Skills Report finds Kerala the most preferred State to work” which was published in the Hindu. The talent assessment agency Wheebox recently unveiled India Skills Report 2024: “Impact of AI on the Future of Work, Skilling & Mobility”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India Skills Report 2024, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), National Skill Development Mission (NSDM), and SANKALP.
Relevancy for Mains: Skill Development in India: Challenges, Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
India Skills Report 2024: Key Highlights
- State of Employability in India: It has improved with 51.25% of the assessed youths found to be employable with the required skills.
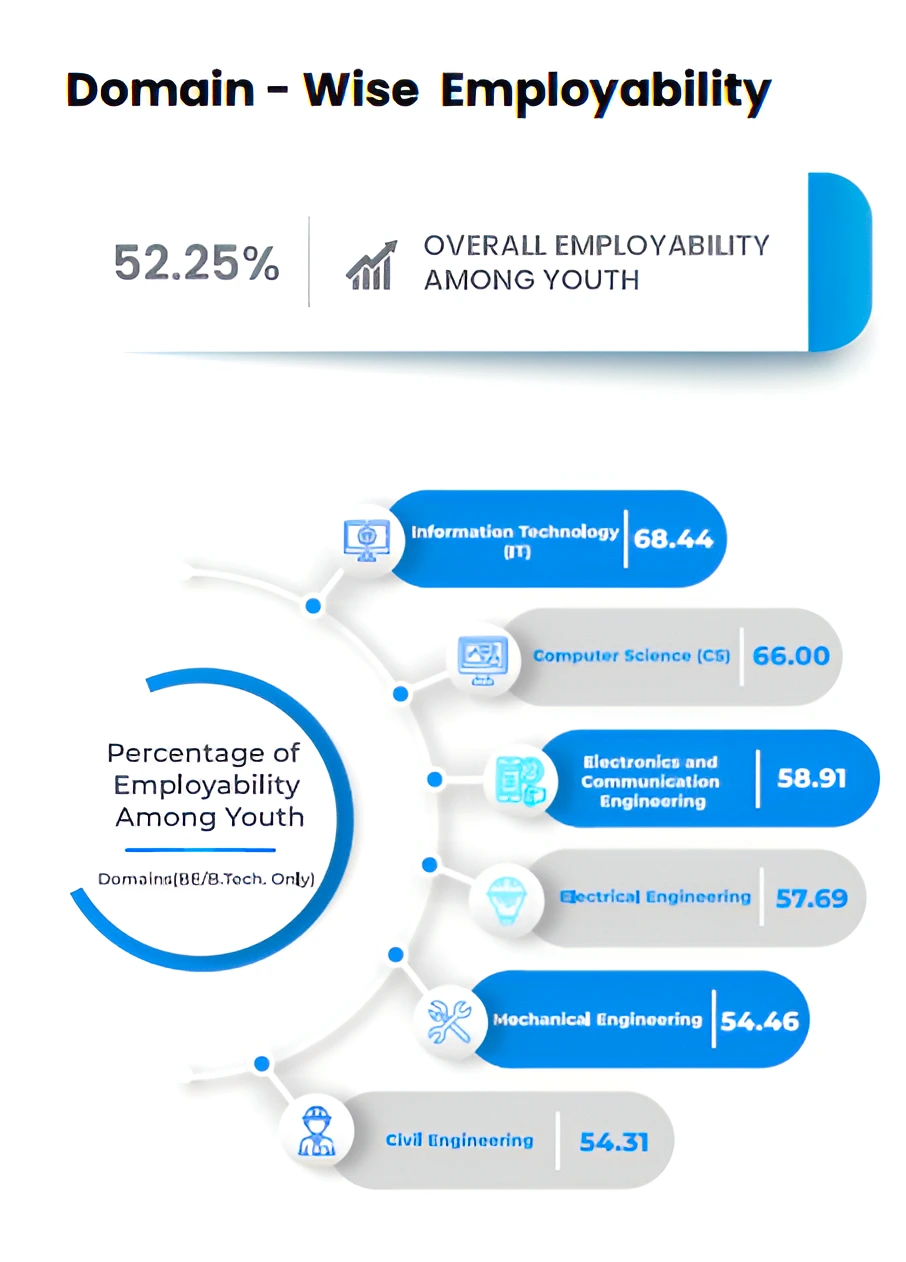 State with Maximum Employability in India Skills Report 2024: Telangana has the highest concentration of employable talent in the age group of 18-21 where 85.45% were found employable.
State with Maximum Employability in India Skills Report 2024: Telangana has the highest concentration of employable talent in the age group of 18-21 where 85.45% were found employable.- Status of Young Employability in India Skills Report 2024:
- Age Range of 18-21 years: Haryana stands out as a top performer in youth employability development, with an impressive 76.47% of test takers scoring above 60% on their WNET tests.
- Haryana is followed by Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, and Telangana have the highest concentration of highly employable youth.
- Age range of 22 to 25 years: Uttar Pradesh stands out with the highest talent concentration at 74.77%, followed closely by Maharashtra at 71.97%.
- Computer Skills: Thiruvananthapuram claimed the first position among cities for nurturing computer skills while Kerala came third overall among States.
- Skill Penetration: India stands at first position in AI skill penetration and talent concentration.
- Increase in Female LFPR: There is a consistent increase in female labor force participation(LFPR), fostering healthy competition and gradually correcting gender imbalances across societal and cultural realms.
- LFPR is defined as the percentage of persons in the labour force (i.e. working or seeking or available for work)in the population.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About the India Skills Report
- The India skills report has been launched by Wheebox in association with various agencies including All India Council for Technical Education, Confederation of Indian Industry and Association of Indian Universities.
- This eleventh edition of the India skills report is based on the extensive Wheebox National Employability Test (WNET) with 3.88 lakh participants and insights from 152 corporations.
- It unfolds key highlights that underscore India’s leadership in the AI domain.
|
Skills Distribution Across States and Cities in India
- English as a Second Language: Karnataka emerged as a leader with 73.33% proficiency, reflecting the state’s emphasis on language skills.
- It is followed by Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra showcasing a diverse geographic spread of English proficiency.
- Numerical Skills : Telangana witnessed numerical skills at 78.68%, emphasizing the state’s focus on quantitative abilities.
- Uttar Pradesh and Bihar excelling in numerical skills exhibit diverse proficiency levels in other domains.
- Bengaluru and Vijayawada lead in cities, indicating strong numerical capabilities in major urban hubs.
- Proficiency in numerical skills is vital for roles in finance, data analytics, and STEM fields.
- Critical Thinking : Telangana tops in critical thinking with 37.70%, showcasing a culture valuing analytical thinking.
- Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh closely follow, indicating a trend of developing critical thinking skills.
- Computer Skills : Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and Kerala lead in computer skills, underscoring their commitment to technological advancements.
- Bengaluru emerged as a technology hub, leading among cities.
Growth Story of Kerala: All Round Talent Hub
- Most Preferred Place to Work: It emerged the most preferred State to work.
- Overall Employability: It secured the second position in overall employability among the 18-21 age group reaffirming its status as a robust talent pool in India.
- Nurturing Future Skills:It has been credited for ensuring a balanced approach towards education and nurturing skills.
- Most Preferred Cities: Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram have come second and fourth respectively among cities where both men and women prefer to work regardless of their age.
- Thiruvananthapuram witnessed a growing pool of highly skilled individuals in various regions of Kerala migrating to the State capital.
- Employable Talent: Kerala ranked third in terms of highest concentration of employable talent in the B.E./BTech and polytechnic domains, as well as for highest availability of English skills.
- Diverse Skill Pool: It showcased a well-rounded talent pool that has enabled its performance across different skills.
- This trend challenges the conventional norm that employability is confined to major urban centers, signifying a broader dispersion of talent across the country.
Additional Skill Acquisition Program (ASAP) Kerala
- It is an initiative by the Higher Education Department of the Government of Kerala, focusing on equipping youth with the necessary industry-relevant skills required to enhance their employability.
- It imparted skills to over 2.5 lakh higher secondary students in the last decade.
- It established community skill parks and centres of excellence which have been recognized as exemplary models for training in advanced technologies across the nation.
|
Transformative Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on the India’s Workforce
- AI Skills: With an installed talent base of 416K AI professionals as of August 2023, the nation is well positioned to meet the current demand of approximately 629K.
- This demand is projected to escalate to 1 million by the year 2026.
- The Indian AI industry is projected to reach USD 28.8 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 45%.
- This is propelled by the widespread adoption of AI across diverse sectors such as healthcare, finance, retail agriculture, and manufacturing.
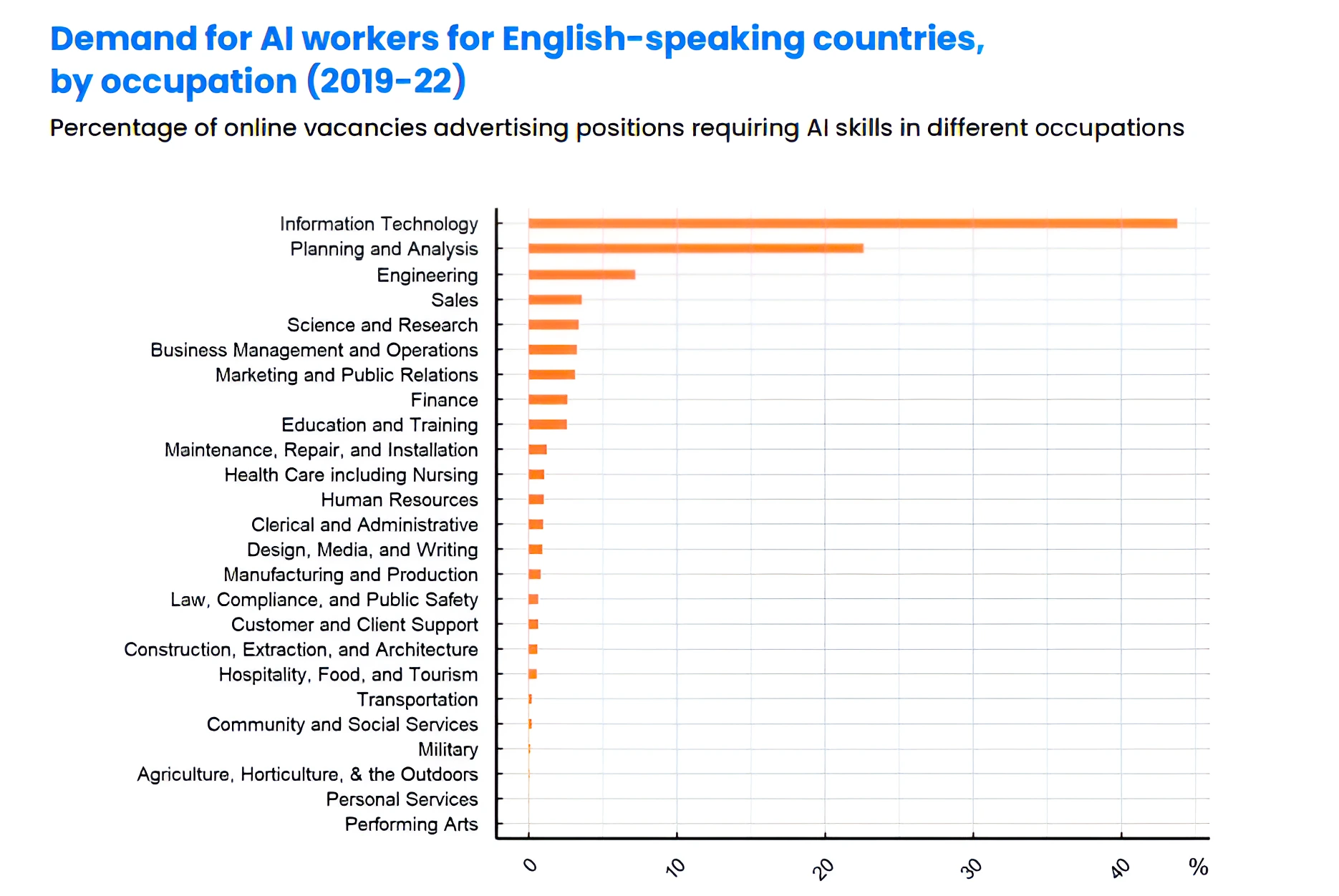
- Escalating demand for AI professionals in India: There is a 14-fold increase in AI-skilled individuals within the country from January 2016 to June 2023.
- India stands among the top five nations witnessing a significant rise in AI talent, alongside Singapore, Finland, Ireland, and Canada.
- Skill Penetration: India has a relative AI skill penetration three times the global average.
- AI Skill Gap: India currently has a 60% to 73% gap between demand and supply in crucial roles like ML engineer, data scientist, DevOps engineer, and data architect.
Challenges with Skill Development in India
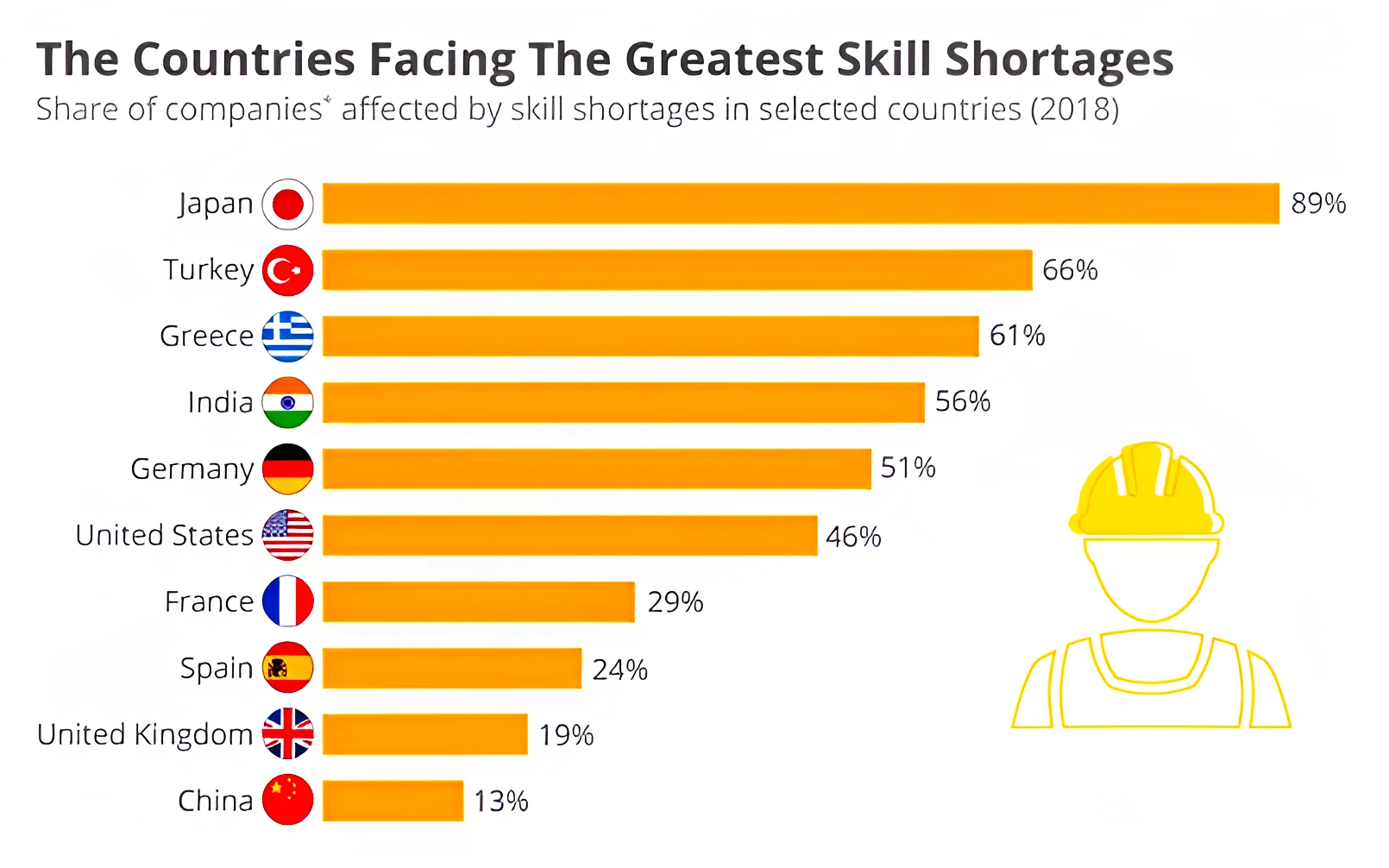
- Skill Gap: In India, there exists an enormous skill gap between the demand from industries and the skillset of the young people acquired through education and training.
- Around 31% is illiterate, only 13% had a primary education, and only 6% were college graduates. Further, only about 2% of the workforce had formal vocational training, and only 9% had non-formal, vocational training.
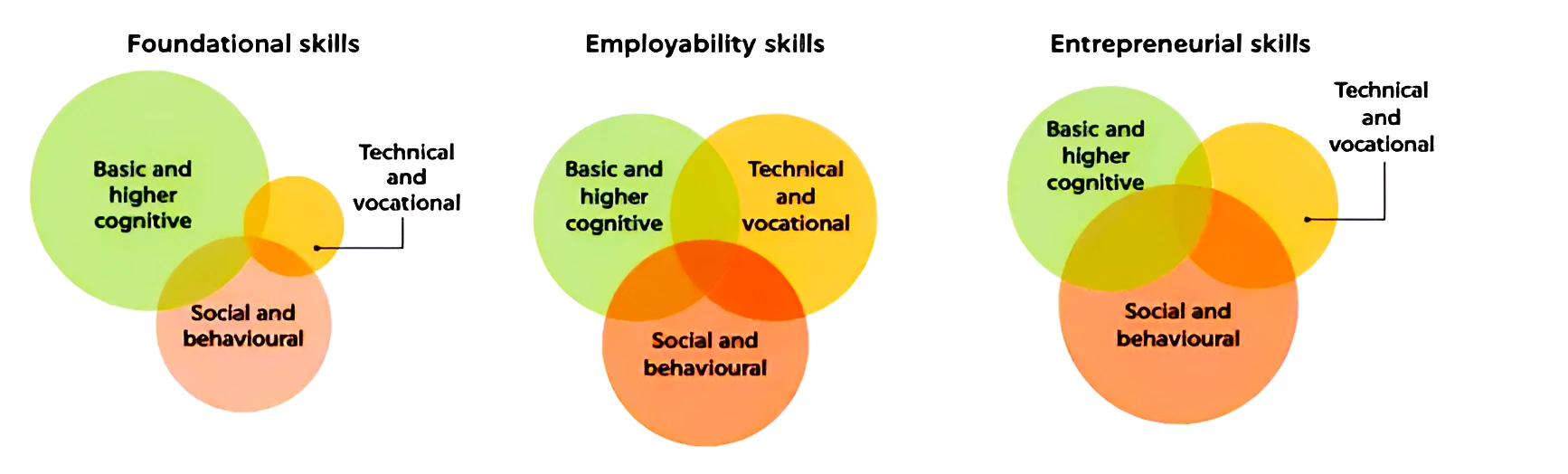
Types of skills
- Cognitive Skills: Basic skills of literacy and numeracy, applied knowledge and problem-solving aptitudes and higher cognitive skills such as experimentation, reasoning and creativity.
- Technical and vocational skills: Physical and mental ability to perform specific tasks using tools and methods in any occupation.
- Social and Behavioural Skills: Include working, communicating, and listening to others.
- Different levels of these three types of skills can be combined to further classify skills into foundational, employability, and entrepreneurial skills.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Skills Mismatch: There is lack of industry-faculty interaction because of which the skill sets provided by the educational and training institutes suit the employers’ requirements.
- As a result, though the people may be skilled but they do not get employment.
- Informal Workforce: Over 90% of India’s workforce is in the informal sector.
- According to researchers at the NCAER, India is trapped in a vicious cycle where informality of the workforce leads to lower incentives to acquire new skills. Majority of Indians who work in agriculture do not have the skills to take up industrial or services sector jobs.
- National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) is India’s oldest and largest independent, non-profit, economic policy research think tank.
- Poor Quality of Skill Training: The Government skill programs suffer from no training centres to poor training, no certification, no placement or forced placement, lack of trainers, and no assurance of a decent wage for those trained.
- As per the government data, between 2015 and March 2023, of the 10 million (1,37,24,226) people trained under the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, less than 20 percent were “reported as placed”.
- Poor Industrial Linkage: It results in a lack of understanding of the current demands and trends. This gap prevents the alignment of curriculum with the practical needs of the job market.
- Lack of Curriculum Standardization: There is no standardization of the course curriculum making it difficult to compare courses across different training institutes creating ambiguity among the students about skills which will be imparted.
Skilling Efforts by India
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): It aims to enable Indian youth to take up industry-relevant skill training that will help them secure a better livelihood.
- Skill India Mission: It aims to provide skill training to millions of youth nationwide. It focuses on sectors such as manufacturing, construction, healthcare, tourism, and information technology.
- National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC): It plays a role in fostering skill development initiatives by collaborating with training partners, industry bodies, and vocational training providers to enhance skilling efforts.
- National Skill Development Mission (NSDM): It aims to create an end-to-end implementation framework that provides opportunities for quality short and long-term Skill Development (SD), leading to productive employment and career progression that meets the aspirations of trainees.
- Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion (SANKALP): It aims to strengthen institutional mechanisms for skill development and increase access to quality and market-relevant training for youth across the country.
- Sector Skill Councils (SSC): These were set up as interfacing organizations between the industry and the Government.
- National Migration Policy (NMP): The government is working to develop a NMP to protect the rights of migrant workers and facilitate their mobility as well as access to resources.
- The number of Indian workers migrating to other countries for work has increased by 20% in the past five years.
Must Read: Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Annual Report 2022
Way Forward
- Upskilling and Reskilling the workforce: There should be an emphasis on upskilling the existing workforce to adapt to the changing technological landscape.
- The emergence of new-age technologies like AI, automation, robotics and analytics has created a high demand for professionals with emerging skills.
- Equipping students with the necessary skills for the future job market by focusing on practical experiences, industry collaboration, and leveraging technology.
- Government, Academia, and Corporate Sector Collaboration: It will help design and implement comprehensive skill development programs, promote employee skill development and create a talent pool per the industries’ requirements.
- These initiatives should focus on traditional engineering skills and cutting-edge digital technologies, enabling the workforce to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving industry.
- Promoting Vocational Education and Apprenticeship Programmes: It will create a steady pipeline of skilled manpower.
- These initiatives can align the curriculum with the specific needs of the infrastructure sector by engaging with educational institutions and industry experts.
- Promoting Consultancy Sector: It can address the demand for specialized expertise. Engaging experienced professionals in consulting roles will enhance project efficiency and quality.
- Career Counselling: Setting up career counseling and guidance in secondary schools to provide the necessary exposure to students to vocational education at an early age.
- Awareness Creation: Raising awareness and engaging students in emerging technologies such as automation, Artificial Intelligence, data analytics, robotics etc.
- Integration of distance and regular education: It will provide flexibility and wider access to learners from diverse backgrounds based on their preferences and requirements.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Conclusion:
The India Skills Report 2024 highlights improvements in employability, the transformative impact of AI, and challenges in skill development, emphasizing the need for comprehensive collaboration and proactive measures to bridge the skill gap and prepare the workforce for the evolving job market.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
 State with Maximum Employability in India Skills Report 2024: Telangana has the highest concentration of employable talent in the age group of 18-21 where 85.45% were found employable.
State with Maximum Employability in India Skills Report 2024: Telangana has the highest concentration of employable talent in the age group of 18-21 where 85.45% were found employable.


