Context:
This article is based on the news “Union Minister for Civil Aviation Shri Jyotiraditya M Scindia inaugurates Asia’s largest Aviation Expo-Wings India 2024” which was published in the PIB. According to the Union Civil Aviation Minister, the government is working to make India the third largest aviation sector in the world in the next three years from the fifth position currently.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Civil Aviation Sector, Wings India 2024, Make in India, DGCA, Centre for Aviation (CAPA)UDAN Scheme, and RCS UDAN.
Relevancy for Mains: Indian Civil Aviation Sector: Status, Potential, Challenges, Government Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
Civil Aviation Sector: India Aims for 300 Million Domestic Air Passengers by 2030
- Increasing Domestic Passenger Market: The domestic passenger market will grow to 300 million by 2030.
- Increasing Aviation Capacity: On the sidelines of Wings India 2024 in Hyderabad, the Minister said that India should increase its aviation capacity to 2000 aircraft from the current 700 plus by 2030.
- Further, the Indian aviation sector had a purchase order of 150 aircraft at the Wings India 2024.
- Violation of the Standard Operative Procedures: According to the Minister, stringent action will be taken against airlines if they violate the Standard Operative Procedures as far as passenger amenities are concerned.
About Wings India 2024
- Wings India: It is the biennial aviation event which brings together business leaders and policymakers.
- Theme of Wings India 2024: Connecting India to the World in Amrit Kaal: Setting the Stage for India Civil Aviation @2047
- Objective: The event seeks to showcase India’s strengths in the aviation space and its rise as the third largest civil aviation market in the world.
- Organised By: Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA), Airport Authority of India (AAI) and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI).
|
Status of Indian Civil Aviation Sector
- Position of Indian Aviation Industry: According to the Civil Aviation Minister, India is the third largest domestic civil aviation market and seventh largest international civil aviation market. If both are combined, India is the fifth largest civil aviation market in the world.
 The civil aviation industry in India has emerged as one of the fastest growing industries in the country during the last three years and can be broadly classified into scheduled and non-scheduled air transport service.
The civil aviation industry in India has emerged as one of the fastest growing industries in the country during the last three years and can be broadly classified into scheduled and non-scheduled air transport service.-
- Scheduled services include domestic and international airlines and non-scheduled service consists of charter operators and air taxi operators, air cargo service, which includes air transportation of cargo and mail.
- Passengers Status:
- Domestic Passengers: The total number in 2014 was 60 Mn which doubled to 143 Mn in 2020 prior to Covid-19.
- International Passengers: They have increased from 43 Mn to 64 Mn (increase of almost 50%).
- Number of Aircrafts: The numbers have increased from around 400 in 2014 to 723 in 2023 despite the impact of Covid-19.
- Airports: Currently, the country has around 148 operational airports which includes 137 airports, 2 Water aerodromes and 9 Heliports.
- Among them there are 29 international, 92 domestic, and 10 custom airports.
Also Read: Passenger Raises Privacy Concern Over Digi Yatra Enrolment
Potential Opportunities in the Indian Civil Aviation Sector
- Sector is Becoming Profitable: According to IATA, the airline sector returned to profitability in 2023, with net profit expected at $23.3 billion on a 2.6% margin, and is set to reach $25.7 billion and a margin of 2.7% next year. The airline industry’s operating profit is expected to touch USD 49.3 billion in 2024 from $ 40.7 billion this year.
- In 2024, the total revenue is estimated to grow 7.6 per cent to $964 billion compared to 2023.
- Growing Airport Infrastructure: To augment the airport infrastructure the government aims to develop 100 airports by 2024 (under the UDAN Scheme) with 74 airports having been developed.
- Boosting Maintenance, Repair & Overhaul (MRO) Services: The projected upsurge in air travel in India further ignites the demand for MRO services. The Indian Civil Aviation MRO market is anticipated to grow to $4.33 Bn by 2025.
- Land allotment for entities setting up MRO facilities in India has been revised to a period of 30 years in September 2021, from 3-5 years as the government aims to make India a ‘Global MRO Hub”.
- Growing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV): Indian drone (UAV) industry is expected to have a total turnover of up to US$ 1.8 Bn by 2026. In June 2023, the US committed to creating a global hub for MRO for high-end drones in India.
- Rapidly Growing Passenger Traffic: India’s annual domestic air passenger traffic has been around high single- to double-digit growth for the past few years.
- According to the International Transport Association (IATA), India’s annual passenger traffic is expected to grow to around 500 million by 2037 from 141 million in 2017.
- Growing Fleet of Airplanes: According to the aviation minister, Indian airlines will have a cumulative fleet size of 1,500-2,000 planes by 2028, up 185% at the higher end of the estimate from the current count.
- Indian carriers together have ordered a total of 1,120 planes, Air India and IndiGo ordered 970 planes in 2023.
- Domestic Manufacturing: With ‘Make in India’ initiatives in this segment, it is estimated that the high procurement costs can be significantly reduced.
- For instance, the C-295 aircraft manufacturing facility in Gujarat laid the foundation of India’s first transport aircraft manufacturing facility in Vadodara in October 2022.
Tokyo’s Haneda Airport Accident
- A Japan Airlines Airbus A350 collided with a Japan Coast Guard Aircraft on the runway at Tokyo’s Haneda Airport. Both planes caught fire, and five people died.
- Rescue: The rescue of 367 passengers from the Airbus A350 following a collision shows the efficacy of textbook emergency-evacuation protocol and the importance of the 90-seconds rule.
- Major Issues in Air- Safety: The Haneda incident has brought into focus four core perennial issues threatening air safety:
- Improper crew training.
- Lack of passenger education.
- Change in materials used to make modern-day planes.
- Miscommunication between air traffic control (ATC) and pilots.
- Implication for India: India is the fastest-growing aviation market and as more flights take off from India’s major airports, there is a need to stay vigilant to ensure that a Haneda-like incident does not happen.
|
Also Read: Analyzing Aviation Accidents and DGCA’s Role in Enhancing Safety Measures
Challenges Associated with Indian Civil Aviation Sector
- Infrastructure: India’s airports face modernization needs due to age and challenging locations, causing congestion and safety concerns. Insufficient runway capacity and an outdated air traffic management system contribute to delays and congestion.
- The lack of night parking stands in Mumbai and New Delhi Air Port often forces airlines to fly the last flight of the day to smaller cities such as Ahmedabad and Lucknow Respectively.
- Regulation: The complex regulatory framework in India’s aviation industry, involving agencies like the Ministry of Civil Aviation, DGCA, AAI, etc. leads to challenges such as unclear policies and delays in obtaining permits.
- Skilled Workforce: The aviation sector faces challenges due to a shortage of skilled professionals, impacting safety and causing delays. High training costs and outdated training facilities in India contribute to a skills mismatch.
- For instance, many people rushed out of an IndiGo aircraft at Mumbai airport, some sitting on the tarmac and eating food as their diverted Goa-Delhi flight landed
- Dollar Dependency: Fluctuations in the dollar rate against the Indian Rupee can severely impact profits since major expenditures like aircraft acquisition, maintenance, and lease costs are dollar-denominated.
- Cutthroat Pricing: To attract passengers, airlines in India often resort to drastically reducing ticket prices, making it challenging to balance the cost, especially when operational costs remain high.
- For instance, Go First (also known as Go Air) has recently been grounded citing the shortage of funds and lack of supply of parts, similar to Jet Airways, Kingfisher, and many other airlines that once operated in India and are now defunct.
- Supply Chain Issues: According to Centre for Aviation (CAPA) India, more than 100 planes of various Indian carriers are on the ground due to supply chain and non-supply chain issues. Nearly 110 aircraft or 15% of India’s total fleet across four major airlines viz. Air India, SpiceJet, GoAir, IndiGo are grounded for want of maintenance or engine replacements.
- Comparatively Low Penetration: Despite the rapid growth witnessed in the passenger traffic, its per capita penetration is still significantly low versus global average.
- As per data compiled by the World Bank and Jeffries, India is at 0.13 seats deployed per capita (domestic air travel penetration) against 0.49 for China and 0.57 for Brazil.
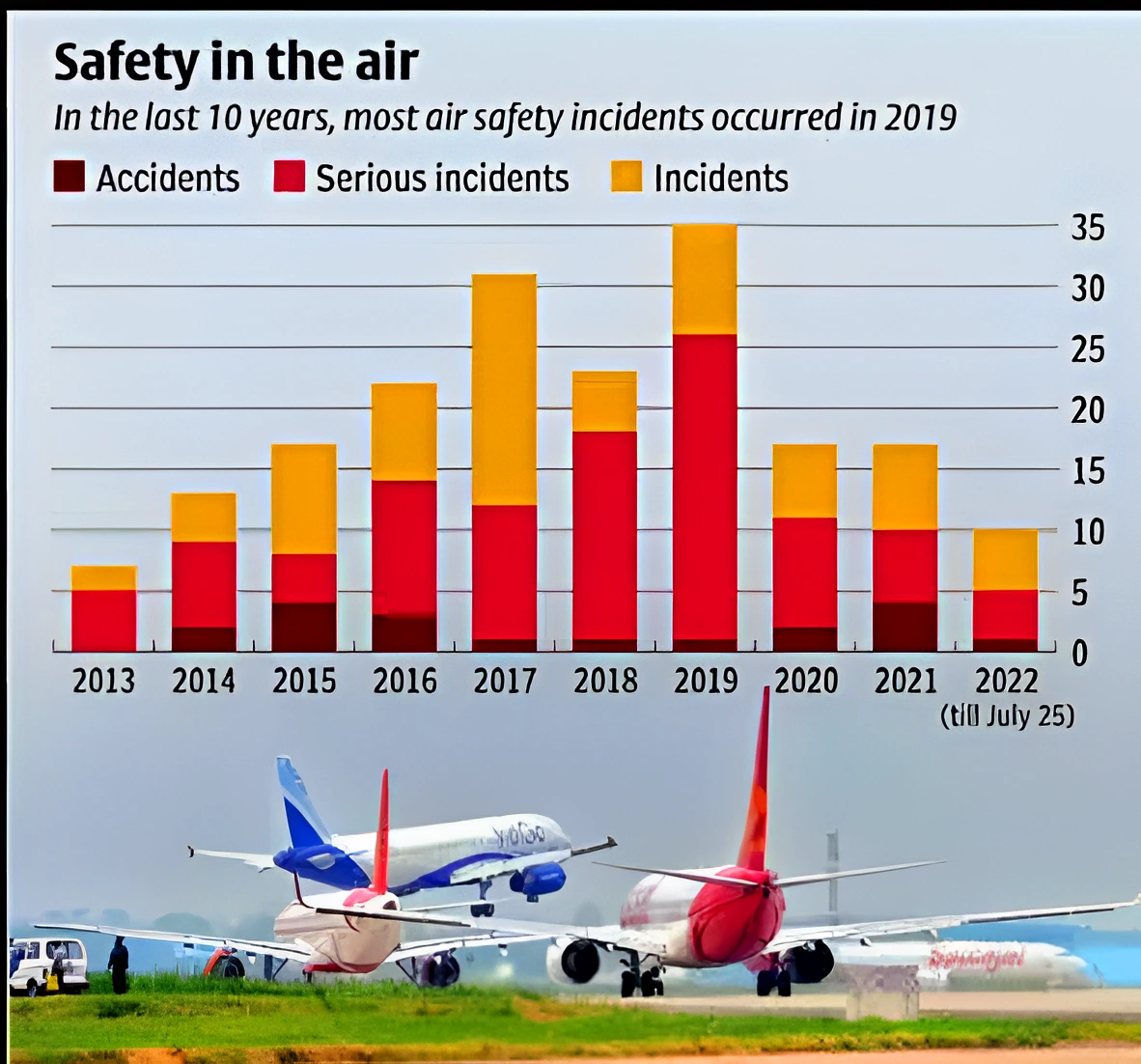 High Fuel Costs: In India, the cost of Aircraft Turbine Fuel (ATF) can account for 50-70 percent of an airline’s operational expenses.
High Fuel Costs: In India, the cost of Aircraft Turbine Fuel (ATF) can account for 50-70 percent of an airline’s operational expenses. - Safety Preparation:
- Mock Drill Frequency: According to a media report citing Japan Airlines’ public relations office, the carrier’s crew members are trained every year to evacuate passengers within 90 seconds under various scenarios, but the frequency of such mock drills in India is every three years.
- Misplaced Priorities: The cabin crew training in India is focused on customer service and handling of unruly passengers.
Also Read: First Flight Using Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
Government Policies Support to Indian Civil Aviation
- Increasing Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Up to 100% FDI under the automatic route is permitted in:
- Non-scheduled air transport services, Helicopter services and seaplanes.
- MRO for maintenance and repair organizations; flying training institutes; and technical training institutes.
- Ground Handling Services subject to sectoral regulations & security clearance.
- Brownfield Airport projects.
- National Civil Aviation Policy 2016 (NCAP): It promotes ease of doing business, deregulation, simplified procedures, and e-governance. For instance, in April 2020, the GST for MRO services rendered locally was reduced from 18% to 5%.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme or UDAN (‘Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik’): It is a vital component of NCAP 2016 and plans to enhance connectivity to India’s unserved and under-served airports and envisages to make air travel affordable and widespread.
- The Government has set a target to operationalize 1,000 UDAN routes and to revive/develop 100 unserved & underserved airports/heliports/water aerodromes by 2024.
- Digi Yatra Policy: It is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation for providing passengers seamless and hassle-free experience at airports without the need for verification of ticket and ID at multiple touch points.
- Monetising Assets: Airport Authority of India (AAI) has formed joint ventures in seven airports and awarded six airports viz. Ahmedabad, Jaipur, Lucknow, Guwahati, Thiruvananthapuram, Mangaluru for operations, management and development under public–private partnership (PPP) for a period of 50 years.
- As per National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP), 25 AAI airports have been earmarked for asset monetisation between 2022 and 2025.
- National Air Sport Policy (NASP) 2022: It lays out the vision of making India as one of the top sports nations by 2030, by providing a safe, affordable, accessible, enjoyable, and sustainable air sports ecosystem in India.
- Air sports encompasses various sports including sports like air-racing, aerobatics, aero modelling, hang gliding, paragliding, paramotoring and skydiving etc.
- Proliferation of Drones: The Government of India has taken several steps to make India a Drone Hub of the World. Government has approved the PLI scheme for drones and drone components as a follow-through of the liberalized Drone Rules, 2021 intended to catalyze growth in the upcoming drone sector.
- The total incentive of INR 120 crores and the total PLI per manufacturer is capped at INR 30 crores.
- Further, ten thousand self-help group women will be given free drone pilot training and substantial subsidy on drones with an aim to strengthen rural aviation skills.
- Disinvestment Of Air India: The process of strategic disinvestment of 100% stake of Government of India in Air India (AI) along with equity shareholding of Air India in Air India Express (AIXL) and AISATS has been completed.
- Carbon Neutrality Initiatives: The MoCA has standardised the Carbon Accounting and Reporting framework of Indian Airports. MoCA is encouraging developers of new Greenfield airports, in collaboration with respective state governments, to prioritize carbon neutrality and net zero emissions in their development plans.
- Airports like Delhi, Mumbai, Hyderabad, and Bengaluru have achieved Level 4+ as well as higher Airports International Council (ACI) Accreditation and have become Carbon neutral. Additionally, 66 Indian Airports are operating on 100% Green Energy.
Also Read: Airports In India
Way Forward to the Indian Civil Aviation
- Technological Impetus & Opportunities: Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), AR/VR, blockchain, big data, and machine learning (ML) will maximise operational effectiveness and cut costs.
- Advanced monitoring systems, quicker check-in procedures, effective luggage management, and enhanced flight services and maintenance will all be made possible by these technologies.
- New Passenger-Handling Manual for Delayed Flights: There is a need to modify rules and conduct of operations to avoid problems caused by long delays as a personal vendetta against them on the airlines’ part.
- For instance, fog in Delhi has delayed flights, leading to a passenger assaulting pilot announcing that the flight would be delayed.
- Ensuring Crew and Passenger Safety:
- Crew training: Ensuring the crew is well trained and holding regular drills to ensure safety of passenger and crew aboard the plane. As per the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations, aircraft manufacturers are required to demonstrate that all passengers and crew members can evacuate a plane within 90 seconds.
- Education: While Indian airlines do make the mandatory safety announcements, the whole process should be simplified, and the message needs to be conveyed in a more visual manner.
- Efficient Regulatory System: There’s a need for a more clear, consistent, and efficient regulatory system. Achieving enhanced transparency, accountability, faster reform, and increased engagement with industry stakeholders is crucial for the industry’s growth and development.
- Upskilling Workforce: Coordination between the industry and educational institutions is crucial to align training programs with industry requirements.
- For this, there is a need to improve training affordability, updating facilities, fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders and educational institutions.

 The civil aviation industry in India has emerged as one of the fastest growing industries in the country during the last three years and can be broadly classified into scheduled and non-scheduled air transport service.
The civil aviation industry in India has emerged as one of the fastest growing industries in the country during the last three years and can be broadly classified into scheduled and non-scheduled air transport service. High Fuel Costs: In India, the cost of Aircraft Turbine Fuel (ATF) can account for 50-70 percent of an airline’s operational expenses.
High Fuel Costs: In India, the cost of Aircraft Turbine Fuel (ATF) can account for 50-70 percent of an airline’s operational expenses. 