Recently, the Indian PM broke with the tradition of India’s new Prime Minister traveling first to a neighbouring country by choosing Russia for his first bilateral visit in his 3rd term.
Significance of Indian PM Visit to Russia
- First Visit Since Ukraine War: 22nd India-Russia Annual Summit is the first Modi-Putin meet since the Ukraine war.
- 21st Summit: It was held in Delhi in December 2021, just before Russian President Vladimir Putin launched “special operations” on Ukraine.
- Agreement & MOUs Signed: During Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s two-day visit to Russia, New Delhi and Moscow signed nine MoUs and agreements in several sectors, including trade, climate and research.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Order of Saint Andrew the Apostle, conferred upon PM Modi
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi was awarded Russia’s highest civilian honour, the Order of Saint Andrew the Apostle, during his visit to the country.
- Award for the PM was announced in 2019, for “exceptional services in promoting special & privileged strategic partnership between Russia and India and friendly relations between the Russian and Indian peoples.”
- Story Behind the Name: Its name comes from Saint Andrew, who is believed to be one of the apostles or 12 original followers of Jesus.
- After Christ’s crucifixion, the apostles are said to have travelled great distances to spread his message.
- Saint Andrew travelled to Russia, Greece, and other places in Europe and Asia, and founded the Church of Constantinople, which later led to the establishment of the Russian Orthodox Church.
- Foreign leaders who have been honoured in the past: It includes Chinese President Xi Jinping in 2017, and the former President of Kazakhstan, Nursultan Nazarbayev.
|
Key Points of the 22nd India-Russia Annual Summit
Bilateral economic cooperation between Russia and India is planned to be developed including in the following key areas:
- Trade over USD 100 billion by 2030: India and Russia have agreed to enhance bilateral trade to over USD 100 billion by 2030, with a focus on investments, national currency usage for trade, and cooperation across various sectors such as energy, agriculture, and infrastructure
- India to balance bilateral trade: This includes increased supplies of goods from India to balance bilateral trade and invigorating investment activities within special investment regimes.
- Boosting Agricultural and Energy Trade
-
- Agriculture Sector: The agreement includes plans to raise the volume of bilateral trade in agricultural products, food, and fertilizers.
- Both sides aim to maintain an intensive dialogue to remove veterinary, sanitary, and phytosanitary restrictions and prohibitions.
- Energy Sector: They agreed to cooperate in nuclear energy, oil refining, and petrochemicals, and to expand forms of cooperation and partnership in energy infrastructure, technologies, and equipment.
Need To Advance The India-Eurasian Economic Union Trade And Goods Agreement
Senior officials of India and the five-nation Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) blocs formally start negotiations for a free trade agreement to boost economic ties early this year
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) is an international economic union and free trade zone comprising countries locatedin central and northern Asia and Eastern Europe.
- Member countries: Russia, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
|
- Elimination of Trade Barriers: Focus on reducing non-tariff barriers and exploring an EAEU-India Free Trade Area.
- Bilateral Cooperation in the Russian Far East: India and Russia inked a program for bilateral cooperation in trade, economic, and investment spheres in the Russian Far East from 2024 to 2029, including cooperation principles in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Nostro & Vostro Account
- Russia becomes first country to facilitate rupee-based export-import transactions
- Nostro account: It is an account held by a bank in another bank.
- It allows the customers to deposit money in the bank’s account in another bank. It is often used if a bank has no branches in a foreign country.
- Vostro account: It is held by a bank that allows the customers to deposit money on behalf of another bank.
- A Nostro account is a Vostro account for the bank that opens the account.
|
- Development of a bilateral Currency settlement system: It is a key part of the joint statement.
- Implementing national currencies for trade to simplify transactions. This arrangement allows India to pay for Russian imports, such as crude oil, in Indian rupees.
- Russia can then use these rupees to pay for Indian exports. The same system applies vice versa with Russian rubles.
- New Trade Routes: The leaders agreed to increase cargo turnover by launching new routes like the North-South International Transport Corridor, the Northern Sea Route, and the Chennai-Vladivostok Sea Line. This will be a game changer for India-Russia trade and people-to-people connect.
- Help in Trade Boost: The development of new trade routes like the Eastern Maritime Corridor and the Northern Sea Route will also be of interest in deepening trade ties.
- The two countries are also discussing the possibility of launching a trans-Arctic container shipping line and processing facilities along the Northern Sea Route.
- Defence and Technology Cooperation:
- Make-in-India program: Both Sides agreed to encourage joint manufacturing in India of spare parts, components, aggregates and other products for maintenance of Russian origin arms and defence equipment under Make-in-India program through transfer of technology
IRIGC-MTC
- The India-Russia Inter-Governmental Commission on Military Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-MTC), set up in 2000, is at the apex of this structure.
- The two Defence Ministers meet annually, alternately in Russia and India, to discuss and review the status of ongoing projects and other issues of military and military technical cooperation.
|
-
- Establishing a new Working Group on Technological Cooperation: Setting up of joint ventures for meeting the needs of the Indian Armed Forces as well as subsequent export to mutually friendly third countries by the Sides’ approval. In this regard, the Sides agreed on establishing a new Working Group on Technological Cooperation
- 21st round of IRIGC-M&MTC: Both side agreed to hold the 21st round of IRIGC-M&MTC in Moscow in the second half of 2024.
- International Cooperation:
- India’s bid for Permanent seat in UNSC: Russia appreciated India’s 2021-22 term as non-permanent member of the UN Security Council and India’s UNSC priorities and efforts towards reformed multilateralism, UN peacekeeping and counter-terrorism.
- Both Sides highlighted that India’s presence in the UNSC provides a valuable opportunity to further coordinate on most pressing issues at the UN.
- BRICS: Sides stressed the importance of strengthening their strategic partnership and close coordination within BRICS, and welcomed the decision to expand the membership of BRICS that was taken at the XV summit in Johannesburg.
- SCO: Sides noted with satisfaction their fruitful cooperation within SCO on key areas like countering terrorism, extremism, separatism, drug trafficking, cross-border organized crime, and information security threats.
- They welcomed Iran and Belarus as new members of SCO.
- G20: The Sides emphasized that the important practical legacy of India’s G20 Presidency was the consolidation of the priorities of the countries of the Global South in the agenda of the main platform for international economic and financial cooperation
- Entry of the African Union into the ranks of full members of the forum.
- Voice of Global South : Both Sides also welcomed the holding of the Voice of Global South virtual summits under the auspices of the Indian Presidency in 2023, which sent an important signal in favor of building a multipolar world order and strengthening the position of developing countries in global affairs.
How INSTC Can Revolutionise India’s Trade
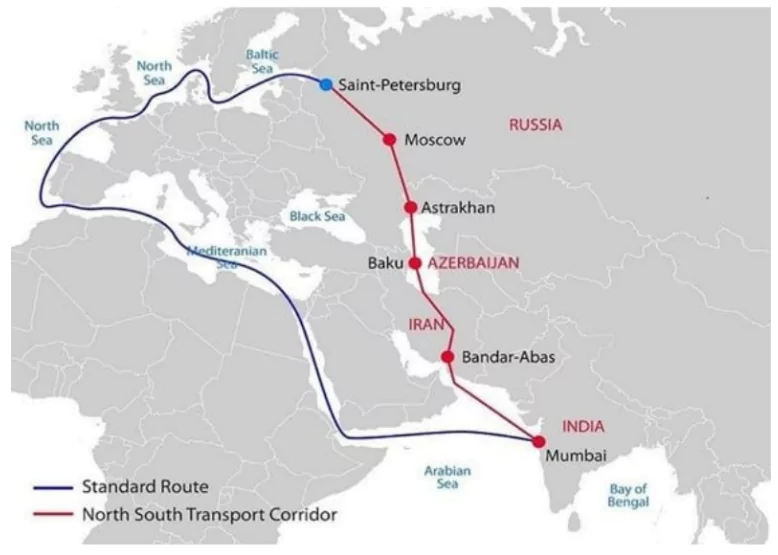
- Alternative to BRI: The Corridor assumes even more economic and strategic importance, especially when India sees it as an alternative to China’s ambitious Belt and Road Initiative.
- Ease and More Cost-effective: INSTC will allow Indian traders to reach Central Asia with greater ease and more cost-effectively.
- Trade experts explain that this will mean efficient access to Iran, Russia, Azerbaijan, and the Baltic and Nordic countries — and not just the 11 countries in Central Asia.
- Reduce transit time: The INSTC significantly cuts transit times to around 25 days from the usual 45 days via the Suez Canal route and reduces freight costs by 30%.”
- High Energy Dependence: Energy, pharmaceuticals, information technology, health, agriculture, textiles, and gems and jewellery can benefit greatly once India starts leveraging Chabahar port for the INSTC route
- Reliability on Trade from Choke points: The INSTC can also help India source energy from the Central Asian countries. Citing India’s huge energy imports from Central Asian countries via trade choke points of the Red Sea and Strait of Hormuz
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
New Trade Routes
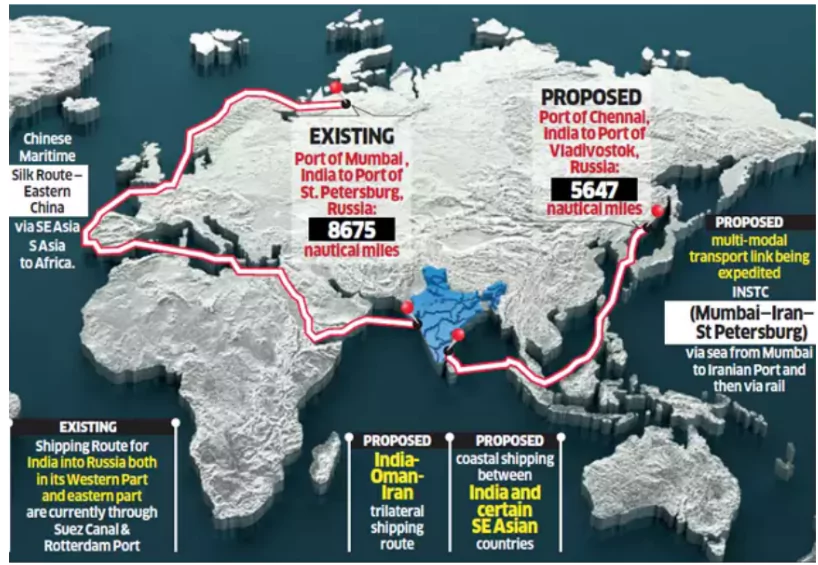
International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
- It is the ship, rail, and road route for moving freight between India, Russia, Iran, Europe, and Central Asia.
- The primary goal of INSTC is to enhance connectivity and promote trade and economic cooperation among these regions
Northern Sea Route(NSR):
- The NSR, the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles the Four Seas (Barents, Kara, Laptev and East Siberian Sea) of the Arctic Ocean.
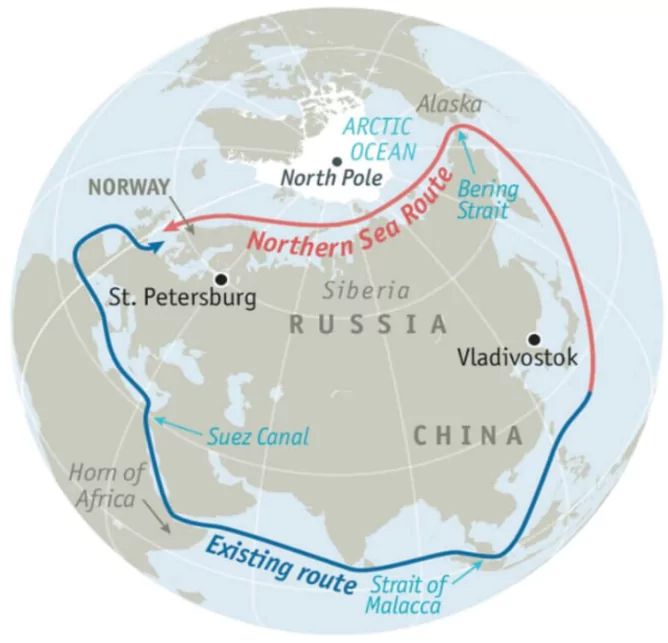 The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and France. The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and France.
- Running to 5,600 km, the Route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
- It offers potential distance savings of up to 50% compared to traditional routes through the Suez or Panama Canals.
Chennai-Vladivostok Sea Line.
- The Vladivostok-Chennai sea route is a maritime trade route that connects the Indian port of Chennai with the Russian port of Vladivostok in the Far East.
- It is part of the Eastern Maritime Corridor and aims to provide cost-effective access to export-import trade between India and Russia.
|
- Infrastructure and Industrial Collaboration: Both countries will strengthen interactions in infrastructure development, transport engineering, automobile production, shipbuilding, space, and other industrial sectors.
-
- They plan to facilitate the entry of Indian and Russian companies into each other’s markets by creating subsidiaries and industrial clusters.
- Humanitarian Cooperation: The summit also emphasized expanding humanitarian cooperation in education, science and technology, culture, tourism, sports, healthcare, and other areas.
-
- Both sides instructed the Russian-Indian Intergovernmental Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technical, and Cultural Cooperation to study these priority areas and assess progress at its next meeting.
- MOUs Signed
-
- Climate Change and Low-Carbon Development MoU: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of India and the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation signed an MoU on climate change and low-carbon development, establishing a Joint Working Group and facilitating information exchange and research.
- Polar Research and Logistics MoU: India’s National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research and Russia’s Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute signed an MoU on cooperation in research and logistics in polar regions.
- Geographical Survey MoU: Survey of India and the Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography of the Russian Federation signed an MoU to enhance collaboration in geographical surveys.
- Broadcasting Cooperation MoU: Prasar Bharati and ANO “TV-Novosti” (Russia Today TV Channel) signed an MoU on cooperation and collaboration in broadcasting.
India-Russia Relations: Recent Challenges
- Defence relationship with Russia
- Historically: Russia has been a key supplier of military hardware to India. In the early 1990s, the Soviet Union provided a significant portion of India’s military arsenal
- It includes 70 per cent of its army weapons, 80 per cent of its air force systems, and 85 percent of its naval platforms.
- India’s first aircraft carrier: INS Vikramaditya, acquired from Russia in 2004, exemplifies this robust defence relationship.
- Important Bilateral projects: It include the supply of S-400, licensed production of T-90 tanks and Su-30 MKI, supply of MiG-29 and Kamov helicopters, production of Ak-203 rifles in India and BrahMos missiles, etc.
- Ukraine conflict: It has disrupted Russia’s defence supply chain, prompting India to diversify its military procurements.
- Fallout on defense deliveries: There are concerns about the fallout on defence deliveries and spares from Russia.
- New defence partnerships with the United States, Israel, France, and Italy reflect India’s strategic shift towards reducing its reliance on Russian arms.
- Complexity of Triangular Relationship: Partnership between India and Russia faces new challenges as Moscow deepens its ties with China, India’s main rival.
- SCO Meet: Complexity of this triangular relationship was evident when PM Modi skipped a summit of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), a security alliance spearheaded by Russia and China. I
- PM Modi sent his foreign minister to represent India at the meeting in Astana, Kazakhstan, which was attended by both Putin and Chinese President Xi Jinping.
- Trade Imbalance: The skewed trade balance has been an area of concern between the two countries.
- For example: Russia is the top trading partner of India in the bloc, with bilateral trade worth USD 49.4 billion in FY23. India’s exports to Russia stood at USD 1.14 billion in 2022-23, while imports were USD 46.2 billion due to an increase in crude oil imports.
- Challenges in Rupee- Ruble Trade: Payment in rubles is also a challenge because there is no fixed exchange rate for the currency.
- Refiners would rather pay in the United Arab Emirates dirham which is pegged to the dollar.
- Internationalization of the rupee: India is betting on internationalization of the rupee to reduce dollar demand and make its economy less vulnerable to global shocks after current account deficit, the broadest measure of trade in goods and services
- Indian recruitments by the Russian army: Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) said two more Indian nationals serving with the Russian Army were killed in the Russia-Ukraine conflict, taking the number of such deaths to four.
- Russia has broadly heeded to India’s call to end the recruitment of Indians as support staff to the Russian military and ensure the return of those still operating in the force
Way Forward
- Addressing Trade Imbalance: A huge imbalance in trade heavily towards Russia is an issue in the Rupee-Ruble trade.
- To solve this problem, Russia is keen to import manufacturing equipment including machinery from India.
- Recently, the Russian President called for increasing mutual investments in pharmacy, manufacturing, and industry.
- Countering China: India would do well to take steps to shore up its relations with Russia to prevent it from becoming more dependent than it is already on China.
- Improving Rupee-Ruble Trade: To tackle the accumulation of Indian currency in Russia, increasing Rupee trade with third countries common to both India and Russia, where India has trade surplus can help in ensuring seamless money flow while solving the problem.
- For this, India has taken steps to de-dollarise trade while pushing for the internationalisation of Indian Rupee.
- Russia has also pitched for more use of national currencies in bilateral trade and called for ensuring smoother financial transactions between India and Russia.
- India as China’s Alternative to Russia: Since the start of the Russia- Ukraine conflict, Russian raw material exports to China and imports of Chinese goods have sharply increased. Sanctions from Western countries made Russia vulnerable, which has prompted China to use its economic leverage, forcing humiliating and one-sided concessions.
- However, India provides Russia with a choice of reliable partners, capable of ensuring the inflow of necessary goods to the Russian market.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Conclusion
Prime Minister Modi’s visit to Russia will be a focal point of how India leverages its multi-polar and non-aligned stance to foster dialogue and diplomacy, potentially contributing to resolving the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
![]() 11 Jul 2024
11 Jul 2024

