The recent train tragedy in Jalgaon, Maharashtra has brought to light critical issues surrounding passenger safety and negligence in Indian Railways.
- The Standing Committee on Railways, in its latest report, has highlighted several concerns regarding the operational and financial health of Indian Railways.
Indian Railways at a Glance
- The history of Indian Railways dates back to over 160 years ago.
- On 16th April 1853, the first passenger train ran between Bori Bunder (Bombay) and Thane, a distance of 34 km.
- Network Size: Indian Railways operates over 67,000 km of track across the country, making it the 4th largest rail network in the world (after the United States, Russia, and China).
- Number of Stations: There are more than 7,300 railway stations across the country.
- Passenger Traffic: Indian Railways carries over 8 billion passengers annually.
- Freight Traffic: Indian Railways handles around 1,200 million tonnes of freight every year, making it one of the largest freight carriers in the world.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
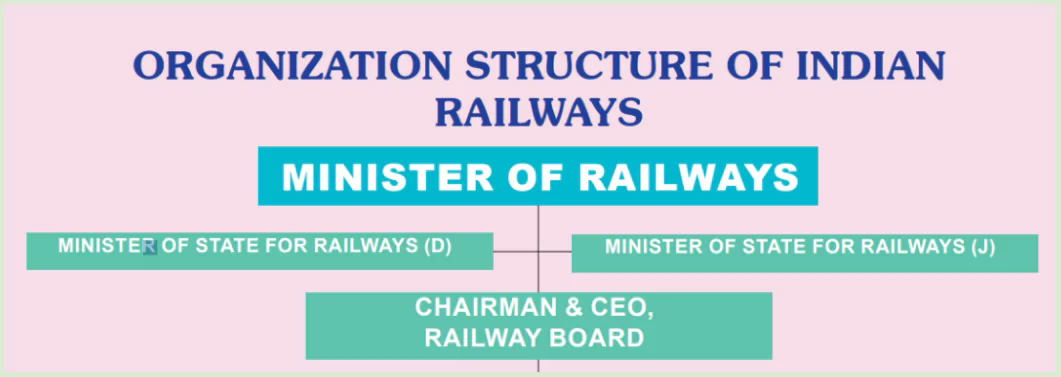
Organizational Structure of Indian Railways
- Indian Railways (IR) is one of the largest rail networks in the world, and its organizational structure is complex, with multiple layers designed to manage its vast operations.
- Ministry of Railways: At the top of the hierarchy is the Ministry of Railways.
- The Ministry of Railways is headed by the Minister of Railways and assisted by the Minister of State for railways.
- Railway Board: The Railway Board is the apex body responsible for framing policies and overseeing the implementation of programs and projects across Indian Railways.
- The Railway Board reports to parliament through the Ministry of Railways.
- The board’s structure includes Chairman and several members with specific areas of responsibility.
|
Key Issues Highlighted by the Standing Committee on Railways
- Low Average Speed of Freight Trains:
- The average speed of freight trains over the last 11 years has been only 25.14 km/h.
- This slow speed is seen as a major bottleneck in increasing the earnings of Indian Railways.
- Freight services contribute significantly to IR’s revenue.
Steps taken to improve Low Average Speed of Freight Trains
- Construction of two Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):
- Eastern DFC (Ludhiana to Sonnagar – 1,337 km) is completed.
- Western DFC (JNPT, Mumbai to Dadri – 1,506 km) is partially completed, with 102 km remaining, expected by December 2025.
- The Committee urged the Railways Ministry to speed up work on new DFCs.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
- Revenue from Freight Services:
- Freight services are the major source of income for Indian Railways.
- In 2023-24, IR earned Rs. 1,68,293 crore, with a target of Rs. 1,80,000 crore for 2024-25.
- Higher freight speeds and improved logistics are essential to meet revenue targets.
- Slow Progress in ‘Kavach’ Safety System Implementation:
- Kavach is an Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system that helps prevent collisions by automatically applying brakes if a loco pilot fails to do so.
- Underutilization of Research & Development Funds
- Research Design & Standards Organization (RDSO) is responsible for R&D of Indian Railways.
- Budget allocation of R&D for FY 2024-25 is Rs. 72.01 crore, which is relatively low.
- Funds utilization in previous years has been poor:
- 2022-23: Out of Rs. 107 crore, only Rs. 39.12 crore was spent.
- 2023-24: Out of Rs. 66.52 crore, only Rs. 28.34 crore was spent.
- The Committee stressed that R&D is a long-term investment and the Railways should ensure proper utilization of funds.
- Declining Net Revenue of Indian Railways:
-
- The committee noted that Indian Railways’ net revenue has been negligible in recent years:
- 2022-23 and 2023-24: Net revenue was minimal.
- 2024-25: The budget estimate for net revenue is just Rs.2,800 crore.
- The primary reason for this is low revenue from the passenger segment, particularly AC classes.
- The committee recommended a review of passenger fares and strategies to reduce losses in this segment.
Other Issues Faced by Indian Railways
- Overburdened Tracks: Around 60% of routes operate at over 100% capacity, leading to delays and accidents.
- Train Accidents: Derailments, collisions, and level-crossing accidents continue despite safety measures.
- In the 2023-24 financial year, there were 313 passenger deaths and four railway employee fatalities in 40 train accidents.
- Outdated Signaling System: Many sections still use manual signaling, leading to inefficiencies.
- Slow Adoption of AI & Automation: Unlike global rail networks, IR lags in AI-based predictive maintenance.
- The Shift2Rail program, part of the EU’s initiative to modernize rail transport, has used AI for Predictive maintenance to monitor the health of train components, Real-time monitoring of rail infrastructure and Optimizing train scheduling and route planning.
- Environmental Concerns: Expansion projects often lead to ecological damage.
- Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link has seen protests from environmentalists due to their impact on local flora and fauna.
- Project Delays & Bureaucratic Hurdles: Infrastructure projects often face land acquisition delays, litigation, and bureaucratic inefficiencies.
- Political Interference: Decision-making is influenced by regional and electoral considerations rather than national interest.
Steps Taken by the Government to Enhance Passenger Safety in Railways
- Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK): Introduced in 2017-18 with a corpus of Rs. 1 lakh crore for five years to replace, renew, and upgrade critical safety assets.
- Electrical/Electronic Interlocking Systems: Installed at stations to prevent accidents caused by human error.
- Retro-reflective Sigma Boards: Installed on masts to warn loco pilots about signals ahead during foggy weather.
- Elimination of Unmanned Level Crossings (UMLCs): All Broad Gauge (BG) UMLCs were eliminated by January 2019.
- Rolling Block Concept: Introduced in November 2023, this system plans maintenance, repair, and replacement work up to 52 weeks in advance on a rolling basis.
- Kavach – Automatic Train Protection (ATP) System: Kavach is a highly advanced ATP system that automatically applies brakes if the loco pilot fails to do so.
Committees made to Enhance Railway Safety
- Kakodkar Committee (2001): The Kakodkar Committee was set up by the Indian government in 2001 to review the safety measures of Indian Railways.
- The committee’s focus was on identifying the causes of rail accidents and recommending corrective actions to improve safety.
- Vinod Rai Committee (2012): The Vinod Rai Committee was formed after a series of rail accidents and aimed at improving the safety of railway operations.
- Bibek Debroy Committee (2014): The Bibek Debroy Committee was tasked with recommending reforms for the Indian Railways, with a specific focus on improving efficiency and safety.
|
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Way Forward
- Infrastructure Modernization: Implement Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) and High-Speed Rail projects.
- The Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train, supported by Japan’s Shinkansen technology, will reduce travel time between the cities from 8 hours to 2 hours.
- Financial Reforms: Rationalize fares, explore PPP models, and improve operational efficiency.
- UK’s Network Rail has implemented several PPPs for infrastructure development and station upgrades, leading to improved efficiency and investment in the rail sector.
- Safety Enhancements: Expand Kavach (anti-collision system), modern signaling, and better staff training.
- Europe’s ETCS (European Train Control System) provides real-time speed control and automatic braking to prevent accidents, contributing to one of the safest rail networks in the world.
- Passenger-Centric Reforms: Improve hygiene, ticketing systems, and station amenities.
- The Swachh Rail, Swachh Bharat campaign focuses on cleanliness and has introduced more waste bins and cleanliness inspectors in trains and stations.
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme aims to upgrade more than 500 stations, providing better facilities like waiting lounges, free Wi-Fi, and clean toilets.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focus on electrification, solar-powered stations, and waste management.
- The Indian Railways has set a target of becoming a “Net Zero” entity by 2030 by completing electrification of all railway tracks.
Conclusion
While Indian Railways remains a vital part of India’s economy, addressing these challenges through modernization, financial restructuring, and technological advancements is crucial for its long-term sustainability and efficiency.
Kavach: India’s Automatic Train Protection System
- Kavach is an indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system designed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) in collaboration with the Indian industry.
- It was tested by South Central Railway (SCR) to enhance safety in train operations across Indian Railways.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
| Privatisation of Indian Railways |
| Pros |
Cons |
| Increased Efficiency: Privatization can lead to better management, improved services, and operational efficiency due to competition. |
Loss of Accessibility: Private players may focus on profitable routes, neglecting less profitable, remote, or rural areas. |
| Better Infrastructure: Private companies may invest in modern technology and upgrade facilities, leading to improved infrastructure and passenger experience. |
Higher Fares: Privatization could lead to fare increases, making travel less affordable for certain sections of society. |
| Innovation & Technology: Private operators may introduce innovative technologies, like high-speed trains, modern ticketing systems, and better maintenance protocols. |
Job Losses: There could be job cuts or changes in labor conditions, affecting the livelihood of current railway employees. |
| Boost to Economic Growth: Enhanced efficiency and infrastructure could result in increased trade, tourism, and economic activity. |
Profit Motive Over Public Good: Private operators may prioritize profits over passenger welfare, compromising service quality and safety. |
| Reduced Government Burden: The government may be able to reduce the financial burden by transferring the responsibility of maintenance and development to private entities. |
Safety Concerns: Privatization could lead to safety risks if cost-cutting measures are taken at the expense of proper maintenance and regulations. |
| Current Scenario:
The Indian government has taken steps towards partial privatization and corporatization of certain services within Indian Railways. For example:
- Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC): A subsidiary of Indian Railways, IRCTC handles catering, tourism, and online ticketing. It has been partially privatized and is listed on the stock exchange.
- Private Trains: The government has introduced private train operators on certain routes to improve service quality and efficiency.
- Lucknow – New Delhi Tejas Express, which was inaugurated is India’s first train operated by private operators, IRCTC.
- Station Modernization: Private players have been invited to participate in the modernization and development of railway stations.
|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 29 Jan 2025
29 Jan 2025
