As India accelerates towards becoming a $5 trillion economy by 2027, the transportation and the logistics sector is set to play a pivotal role in this journey.
What Is Logistics?
- Logistics refers to the overall process of managing how resources are acquired, stored, and transported to their final destination.
- Logistics management involves identifying prospective distributors and suppliers and determining their effectiveness and accessibility.
Importance of Logistics
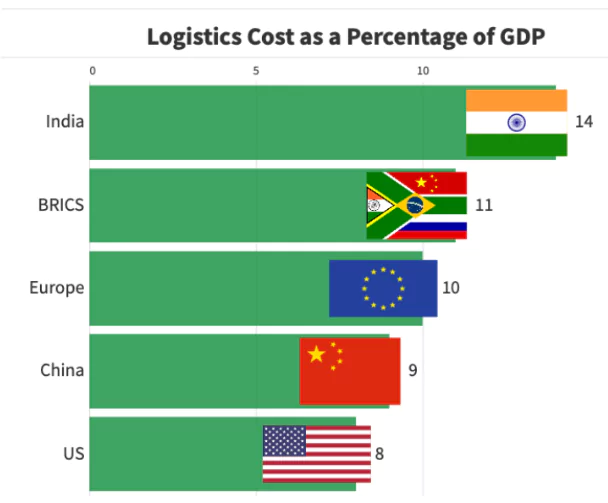
- Economic Contribution: Logistics contributes 13-14% to India’s GDP, showcasing its pivotal role in driving economic growth.
- Facilitates Trade and Commerce: A robust logistics sector supports domestic and international trade by enabling the seamless movement of goods.
- Job Creation and Employment: The logistics sector is one of the largest employment generators, providing jobs to over 22 million people in India.
- Additionally, it is projected to add 10 million jobs by 2027, contributing significantly to economic empowerment.
- Reduces Cost and Enhances Competitiveness: Efficient logistics operations reduce transportation and warehousing costs, allowing businesses to offer competitive pricing.
- For example, the introduction of GST reduced truck waiting times at state borders, decreasing logistics costs and increasing supply chain efficiency.
- Supports E-commerce Growth: The rise of e-commerce has increased the demand for efficient logistics solutions, including last-mile delivery and cross-border trade.
- For instance, platforms like Amazon and Flipkart rely on advanced logistics networks to meet customer demands for faster and reliable delivery.
- Boosts Supply Chain Efficiency: A well-functioning logistics sector ensures smooth and timely supply chain operations, reducing lead times and optimizing production.
- For example, the development of Multi-modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs) has improved freight handling, lowering overall supply chain costs.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Logistics Sector in India
- Global Standing: India’s logistics sector is one of the largest globally, ranked 38th among 139 countries in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index 2023, showcasing steady improvement in efficiency and infrastructure.
- Modes of Transport
-
- Road Transport: Accounts for 66% of cargo movement, but faces challenges like poor road conditions and congestion.
- Rail Transport: Handles 26% of freight but requires modernization and increased capacity.
- Air and Waterways: Contribute 1% and 3%, respectively, but hold potential for growth through government initiatives like Sagarmala.
- Technological Adoption: India is transitioning to a digitally integrated logistics ecosystem with technologies like AI, IoT, blockchain, and automation.
- However, the adoption rate is still lower compared to global standards.
- E-commerce and Trade Growth: The rise of e-commerce and cross-border trade has accelerated demand for logistics services.
- Companies like Amazon and Flipkart rely heavily on advanced logistics to meet customer expectations for faster delivery.
Challenges with Logistics Sector in India
- High Logistics Costs: Logistics costs in India account for 13-14% of the GDP, compared to the global benchmark of 8-10%.
- This increases the cost of Indian goods, making them less competitive in international markets.
- For instance, inefficiencies in transportation and warehousing contribute significantly to these high costs.
- Fragmented Industry Structure: The logistics sector is highly fragmented, with small, unorganized players dominating 80% of the market. This results in poor resource optimization and inefficiencies.
- For example, most trucking companies operate with fleets of fewer than five trucks, limiting scalability.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: India’s logistics infrastructure, including roads, railways, ports, and warehouses, is insufficient to handle the growing demand.
- Only 31% of freight moves through rail, despite it being more cost-efficient than road transport, which handles 66% of cargo.
- Skill Shortage: The sector faces a significant shortage of skilled workers in supply chain management and logistics technologies. Limited vocational training and industry-specific education exacerbate this issue.
- For example, despite the growing demand for advanced warehousing and technology-enabled logistics, training programs remain sparse.
- Regulatory Complexity: Complex and inconsistent regulatory frameworks, including multiple tax structures and compliance requirements, create operational barriers.
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has helped streamline some processes, but further harmonization is needed.
- Last-Mile Connectivity Issues: Last-mile delivery faces challenges such as poor road infrastructure, traffic congestion, and inadequate address mapping in urban and rural areas.
- For instance, delays in last-mile connectivity impact e-commerce deliveries, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
- Technological Gaps: While the sector is moving towards digitization, the adoption of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain is still limited compared to global standards.
Best Global Examples of Logistics Sectors
Singapore: A Global Logistics Hub
- Ranked consistently as the top performer in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index due to its efficient port infrastructure, advanced technology, and seamless trade facilitation.
- Best Practices: Integration of cutting-edge technologies like IoT and AI for real-time tracking, and a single-window platform for trade documentation.
- Singapore is well-connected to the world’s major markets, with daily sailings to every major port of call and over 6,500 weekly flights to 280 cities in 60 countries.
Netherlands: Gateway to Europe
- Rotterdam, Europe’s largest port, handles over 469 million tons of cargo annually, connecting global trade routes.
- Best Practices: Use of automated port operations and blockchain for customs and trade facilitation.
China: Scale and Innovation
- China leads in logistics scale, with advanced infrastructure including mega ports like Shanghai (the busiest in the world) handling over 47 million TEUs annually.
- Best Practices: Integration of AI and IoT in supply chain management, and significant government investment in infrastructure through the Belt and Road Initiative.
United States: Logistics Powerhouse
- Strong integration of road, rail, and air logistics systems, with companies like Amazon and FedEx leading innovation in e-commerce logistics and last-mile delivery.
- The Port of Los Angeles is a major gateway for trans-Pacific trade, handling over 9 million TEUs annually.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Government Initiatives for the Logistics Sector in India
- National Logistics Policy (NLP) 2022:
- The National Logistics Policy aims to reduce logistics costs to single digits, enhance India’s global competitiveness, and create a unified digital logistics platform.
- PM GatiShakti (2021):
- PM GatiShakti is a transformative initiative designed to provide multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- This initiative emphasizes multi-modal connectivity, reducing disruptions, and fostering infrastructure synergy for improved logistics efficiency.
- Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs)
- It was launched in 2017 under the Logistics Efficiency Enhancement Programme (LEEP).
- Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs) are transportation hubs that consolidate warehousing, storage, distribution, and other logistics services under one roof.
- The government is establishing 35 Multi-Modal Logistics Parks across strategic locations, with a total investment of ₹50,000 crores.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) are a network of railway tracks in India that are exclusively used for freight trains.
- The Ministry of Railways announced the DFC initiative in 2005-06.
- The 2,843-km-long DFC project, passing through 56 districts in seven states, is 96.4 per cent complete.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) (2017)
- The implementation of GST has streamlined the movement of goods by eliminating state border checkpoints.
- With GST creating a unified tax regime, businesses have been able to consolidate these into larger, centralized warehouses.
- For instance, e-commerce companies like Amazon and Flipkart have significantly benefited by setting up large regional fulfillment centers instead of smaller state-specific warehouses.
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) (2022):
- It was conceptualized by NITI Aayog and is operated by NICDC Logistics Data Services (NLDS), a joint venture between the Government of India and NEC Corporation.
- ULIP is a digital platform that integrates over 30 systems from ministries and logistics partners, providing real-time data for seamless coordination.
- It has streamlined cross-border trade, last-mile delivery optimization, and reverse logistics.
- Sagarmala Project (2015):
- It is a flagship initiative by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways of the Government of India to develop India’s maritime sector:
- Goal: To reduce logistics costs, improve port efficiency, and promote coastal community development.
- e-Way Bill System (2018):
- The e-Way Bill system digitizes inter-state goods transportation, eliminating the need for physical documentation and reducing delays caused by bureaucratic procedures at state borders.
- Required for the movement of goods valued at more than Rs. 50,000 under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
- Logistics Data Bank (LDB) (2016):
- The Logistics Data Bank app provides real-time tracking of export-import (EXIM) cargo, enhancing predictability, transparency, and reliability in the supply chain.
National Logistics Policy (NLP)
- The National Logistics Policy (NLP) was launched in September 2022 to complement PM GatiShakti National Master Plan (NMP).
- The NLP addresses the soft infrastructure and logistics sector development aspect, inter alia, including process reforms, improvement in logistics services, digitization, human resource development and skilling.
- Vision: To drive economic growth and business competitiveness of the country through an integrated, seamless, efficient, reliable, green, sustainable and cost-effective logistics network by leveraging best in class technology, processes and skilled manpower.
- Targets: The targets of the NLP are to:
- Reduce cost of logistics in India;
- Improve the Logistics Performance Index ranking – endeavor is to be among top 25 countries by 2030, and
- Create data driven decision support mechanism for an efficient logistics ecosystem.
Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP)
- To achieve these targets, a Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) as part of the NLP was launched covering eight action areas including
- Integrated Digital Logistics Systems;
- Standardization of Physical Assets and Benchmarking of Service Quality Standards;
- Logistics Human Resource Development and Capacity Building;
- State engagement;
- EXIM Logistics;
- Services Improvement Framework;
- Sectoral Plans for Efficient Logistics (SPEL); and
- Facilitation of Development of Logistics Parks.
|
Way Forward for the Logistics Sector in India
- Reduce Logistics Costs: Focus on reducing logistics costs to align with global benchmarks of 8-10% of GDP.
- This can be achieved through infrastructure modernization, promoting multi-modal transportation, and adopting cost-efficient technologies like automation and AI-driven analytics.
- Strengthen Infrastructure Development: Accelerate the development of dedicated freight corridors, multi-modal logistics parks, and coastal shipping networks.
- Investments in road and rail connectivity, especially for last-mile delivery, will significantly enhance logistics efficiency.
- Promote International Collaboration: Strengthen international partnerships to enable shared infrastructure, data exchange, and coordinated decision-making.
- For example, the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) aims to establish seamless connectivity between India and Europe through the Arabian Peninsula.
- Attract Investments and Enhance Private Sector Participation: Leverage initiatives like the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), which aims to mobilize ₹50 lakh crore (approximately $650 billion) for infrastructure projects.
- While 100% FDI is permitted in most transport infrastructure development initiatives, additional policy measures and incentives are needed to attract more private and foreign investments, ensuring the desired impact on infrastructure growth.
- Encourage Digital Transformation: Promote widespread adoption of technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) across logistics operations.
- These technologies can improve transparency, optimize routes, and reduce transit times.
- Policy Harmonization and Simplification: Further streamline regulations and simplify compliance through single-window systems like the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP).
- Harmonizing tax structures and regulatory frameworks across states can improve ease of doing business.
- Enhance Skill Development: Address the skill gap in the logistics sector by introducing specialized training programs in supply chain management, warehousing, and technology-enabled logistics.
- Public-private partnerships with educational institutions can bridge this gap.
- Focus on Sustainability: Encourage green logistics practices such as the adoption of electric vehicles, eco-friendly packaging, and carbon-neutral supply chains.
- The government and private players should invest in sustainable solutions to reduce the environmental impact of logistics operations.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
India’s logistics sector is on the brink of transformation, driven by government reforms, technological advancements, and infrastructure development. By addressing challenges like high costs and fragmentation, and adopting global best practices, India can position itself as a globally competitive and sustainable logistics hub, boosting trade and economic growth.
![]() 31 Dec 2024
31 Dec 2024


