![]() 11 Feb 2026
11 Feb 2026

The Union Health Minister launched the Annual Nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Campaign for eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) across 12 endemic States.
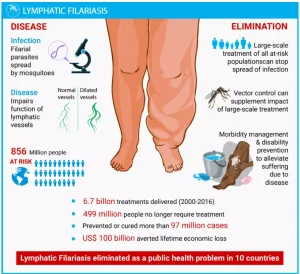 Cause and Transmission:
Cause and Transmission:| Hydrocele surgery, or hydrocelectomy, is a medical procedure performed to remove or repair a hydrocele, a fluid-filled sac that forms around the testicle, causing swelling in the scrotum. |
|---|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
| National Deworming Day is observed on 10 February and 10 August. |
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
