As per the latest data released from the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), the total renewable energy installed capacity has increased by an impressive 24.2 GW (13.5%) in a year.
About Renewable Energy
- It is the source of energy which is derived from natural sources which are renewable in nature as it gets constantly replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed and will never exhaust.
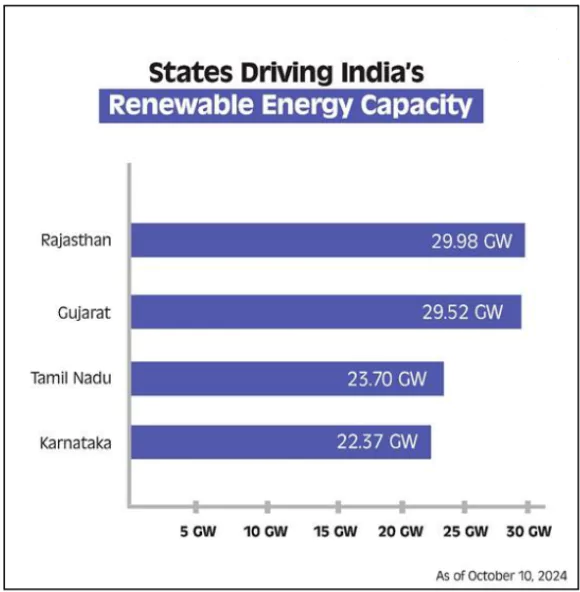 Sources:
Sources:
- Solar Energy: Solar technologies convert sunlight into electrical energy either through photovoltaic panels or through mirrors that concentrate solar radiation.
- India’s solar energy potential is estimated to be 748 GWp as estimated by National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE).
- Wind Energy: It harnesses the kinetic energy of moving air by using large wind turbines located on land (onshore) or in sea- or freshwater (offshore).
- Hydropower Energy: It harnesses the energy of water moving from higher to lower elevations. It can be generated from reservoirs and rivers.
- Bioenergy: It is produced from a variety of organic materials, called biomass, such as wood, charcoal, dung and other manures for heat and power production, and agricultural crops for liquid biofuels.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
About India’s Renewable Energy Sector
- As per the REN21 Renewables 2024 Global Status Report, India ranks 4th globally in Renewable Energy Installed Capacity (4th in Wind Power capacity & 5th in Solar Power capacity).
- Total Installed Renewable Energy Capacity: As of October 2024, India’s total renewable energy installed capacity stands at 203.18 GW from 178.98 GW in October 2023
- Total Non-Fossil Fuel Capacity: It stands at 211.36 GW in 2024, compared to 186.46 GW in 2023 also including Nuclear Energy.
- Contribution: Renewable Energy accounts for 46.3 percent of the country’s total installed capacity which has reached 452.69 GW
- Target: India plans to enhance its renewable energy capacity target to 500 GW by 2030 at the COP26 as part of a key pledge under the Panchamrit targets.
- Status of Renewable Energy Projects: As of October 2024, projects of 143.94 GW is under implementation and 89.69 GW are already tendered.
- The projects saw an increase from 99.08 GW under implementation and 55.13 GW tendered as of October 2023.
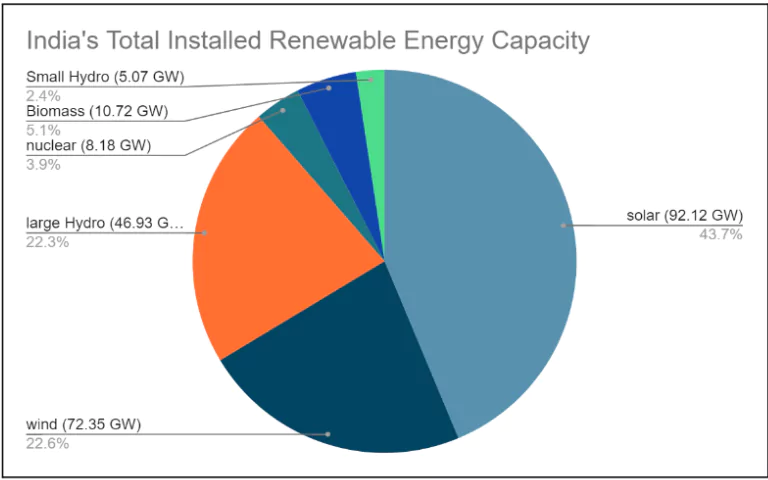 Policies and Schemes:
Policies and Schemes: -
- Governmental Pledges: India has committed to reduce the carbon intensity of the nation’s economy by less than 45% by 2030, and achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2070.
- Foreign Direct Investment permitted up to 100 percent under the automatic route to attract investments.
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: India aims to produce 5 Mn Tonnes of green hydrogen by 2030 revolutionising the green transport sector. The National Green Hydrogen Mission was approved with a budget of INR 19,744 Cr.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM): It aimed to increase the income of farmers by installing solar irrigation pumps and provide sources of irrigation and de-dieselization the agricultural sector.
- PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: It aims to increase the share of solar rooftop capacity and empower residential households to generate their own electricity by providing subsidy of 60% of the solar unit cost for systems up to 2kW capacity.
- Significance:
- Limit Climate Change: Renewables are the cleanest, most viable solution to prevent environmental degradation as they do not emit greenhouse gases in energy generation processes.
- Inexhaustible Source: Clean energies being inexhaustible are essential for sustainable energy system allowing development today without risking that of future generations
- Reducing Energy Dependence: Dependence on fossil fuel imports results in subordination to the economic and political short-term goals of the supplier country, which can compromise the security of energy supply
- Example: The oil wars of the middle east.
- Increasing Competitiveness: Economies of scale and innovation are already resulting in renewable energies becoming at lightning speed the most sustainable solution, not only environmentally but also economically, for powering the world.
- Maintenance: Renewable energy systems, like solar panels, require less maintenance than traditional energy systems.
- Local resilience: Renewable energy can provide electricity close to where it’s used, which can help with local energy resilience
![]() 14 Nov 2024
14 Nov 2024

 Sources:
Sources:
 Policies and Schemes:
Policies and Schemes: