India has made remarkable progress in expanding social security coverage, rising from 19% in 2015 to 64.3% in 2025, according to the International Labour Organisation (ILO).
Key Highlights of the Report
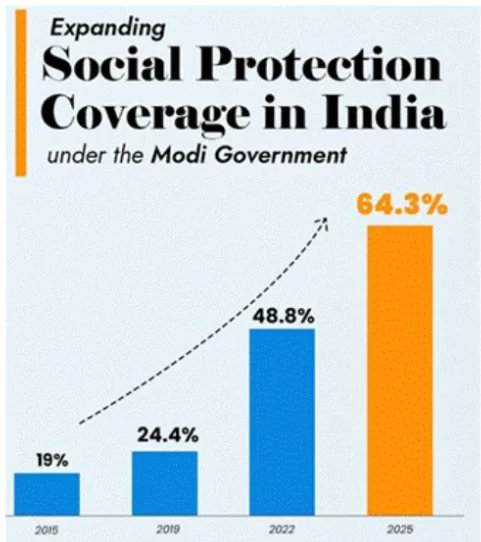
- India’s social protection coverage has grown at an unprecedented pace, marking the fastest expansion globally.
- Over 94 crore (940 million) Indians now have access to at least one social security benefit.
- India ranks second in the world in terms of the number of beneficiaries.
Causes for the boost in Social Security in India
- Government Schemes Expansion: Major schemes like PM-KISAN, PM-SYM, PMJJBY, PMSBY, Atal Pension Yojana, and eShram brought unorganised and informal workers under coverage.
- Formalisation of Economy: GST implementation, digital payments, and labour reforms encouraged formal employment.
- Formal jobs typically come with social security benefits like PF, ESIC, etc.
- Digital Infrastructure: Platforms like Aadhaar, Jan Dhan Yojana, UMANG, and eShram Portal enabled identification, registration, and delivery of benefits to crores of people.
- Policy Push & Labour Codes: Four new labour codes consolidate 29 laws and mandate social security even for gig/platform workers and unorganised sectors.
What is Social Security?
- Social Security refers to government programs that provide financial support to individuals and families in times of need.
- Protection Against Life Risks: It offers protection during unemployment, old age, disability, illness, or loss of a breadwinner.
- Government-Funded or Mandated: Funded by the state, employers, or workers, it ensures a safety net for all.
- Examples include pensions, health insurance, maternity benefits, and unemployment aid.
- Promotes Inclusive Growth: It reduces poverty and inequality by ensuring basic income security for vulnerable groups.
Key Social Security Programmes and Initiatives
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): For unorganised sector workers; government co-contribution for eligible subscribers.
- Ayushman Bharat – PM Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY): ₹5 lakh health insurance per family per year for the poor and elderly.
- Employees’ State Insurance (ESI) Scheme: Health and maternity benefits for workers in the formal sector.
- Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY): Promotes institutional delivery for poor pregnant women.
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): Life insurance of ₹2 lakh.
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Accidental insurance of ₹2 lakh.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): Zero-balance bank accounts with accidental insurance and pension linkages.
- Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008: Framework for social security for informal workers.
- e-Shram Portal: National database for unorganised workers to ensure targeted delivery of benefits.
- PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana: Voluntary pension scheme for unorganised workers.
|
![]() 12 Jun 2025
12 Jun 2025

