![]() 23 Jun 2025
23 Jun 2025

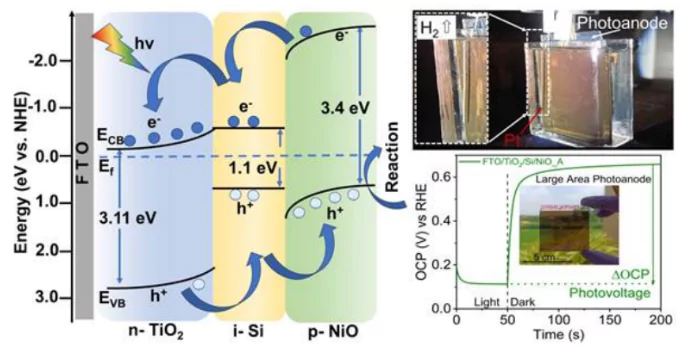
Indian researchers from the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), Bengaluru, have developed a scalable solar-driven device that generates green hydrogen using only sunlight and water.
It is a photoelectrochemical (PEC) water-splitting system that utilizes:
PWOnlyIAS ExtraEdge: About Green Hydrogen
Advantages
|
|---|

<div class="new-fform">
</div>