From the lunar surface to the International Space Station, India’s strides in space are reshaping identity, policy, and aspiration.
Historic Milestones in India’s Space Journey
- India’s Lunar (Chandrayaan) Program:
-
- Chandrayaan-1 (2008): India’s first lunar mission. Its orbiter and Moon Impact Probe (MIP) helped confirm the discovery of water/hydroxyl molecules on the Moon.
- It stopped communicating in 2009.
- Chandrayaan-2 (2019): Composite lunar mission launched with orbiter, lander (Vikram), and rover (Pragyan). The orbiter succeeded and is still operational, but the lander crashed during its descent to the surface.
- Chandrayaan-3 (2023): A follow-on mission focused on demonstrating a safe soft landing and roving.
- It successfully landed near the lunar south pole on August 23, 2023, deploying the Vikram lander and Pragyan rover.
- Mangalyaan (Mars Orbiter Mission-2014): India reached Mars orbit on its first attempt, becoming the first Asian nation to do so.
- Indian Astronaut on ISS (2025): Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla flew to the International Space Station on Axiom Mission 4 (launched June 2025), conducting experiments and gaining experience for India’s human spaceflight programme.
- SpaDeX: Orbital Docking Success (2025): ISRO demonstrated autonomous spacecraft docking, joining an elite group of nations (US, Russia, China).
- NISAR: Joint NASA-ISRO Earth observation satellite launched (July 2025), now in science phase.
- Aditya-L1 (2023): Studying the sun’s corona and space weather.
- Positioned at the Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 1 (L1), it provides uninterrupted observations of the Sun, advancing our understanding of solar activities and space weather.
- XPoSat (2024): XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite) is India’s first dedicated astronomy mission to study the polarisation of cosmic X-rays.
Upcoming Goals of ISRO
- Gaganyaan Programme: India’s first indigenous human spaceflight, targeted for 2027.
- Shukrayaan: Venus Orbiter Mission (2028).
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): Indian space station by 2035.
- Indian Human on the Moon: Goal set for 2040.
Future Lunar Missions
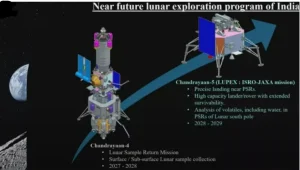
- Chandrayaan-4: It is a Lunar sample return mission planned for 2027-2028.
- Key Objective: Land near the south pole, collect ~3 kg of surface and subsurface soil/rock, and bring it back to Earth for analysis.
- Major Technology Firsts: First Indian mission to demonstrate Earth and lunar orbit docking, ascent from the Moon, and safe Earth re-entry with samples.
- Chandrayaan-5 (LUPEX): It is a Lunar polar exploration mission with both lander and rover slated for 2028-2029.
- Key Objective: In-situ study of water ice and volatiles in a Permanently Shadowed Region (PSR) near the south pole.
- International Collaboration: Major joint mission with JAXA (Japan).
International Cooperation in Space Sector
- South Asia Satellite: Provides communication capacity to neighbours in South Asia.
- G20 Satellite (2023): For climate/environment monitoring, data shared globally.
- Joint Missions: NISAR (with NASA), TRISHNA (with CNES, France), LUPEX (with JAXA, Japan), Proba-3 (with European Space Agency).
- Guided by the ethos of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” (the world is one family).
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- ISRO is India’s national space agency, responsible for developing space technology and its applications for national development,
- Establishment: Founded in 1969, superseding the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR), established in 1962.
- Headquarter: Bengaluru.
- It operates under the Department of Space (DoS), directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India.
Economic and Societal Impact of ISRO
- Budget: ₹13,416 crore for 2025-26, nearly tripled since 2013-14.
- Space Economy: Valued at ~$9 billion in 2025, projected to reach $44 billion by 2033.
- Private Sector: Over 300 startups; reforms via IN-SPACe and NSIL drive innovation.
- Applications: Satellites support disaster management, agriculture, navigation (NavIC), and connectivity.
|
![]() 1 Jan 2026
1 Jan 2026


