Context:
Centre directs officials to upscale efforts for ‘better utilization’ of river waters in J&K under Indus Water Treaty
| Probable Question:
Q. The implementation of the Indus water treaty augurs well between India-Pakistan, despite so many challanges. Evaluate |
About Indus Water Treaty:
- The Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) was signed by former Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and then President of Pakistan, Ayub Khan in 1960 by mediation of World Bank.
- Water Allocation:
-
- All the water of the eastern rivers – Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi was allocated to India for unrestricted use.
- The waters of western rivers — Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab — were assigned largely to Pakistan.
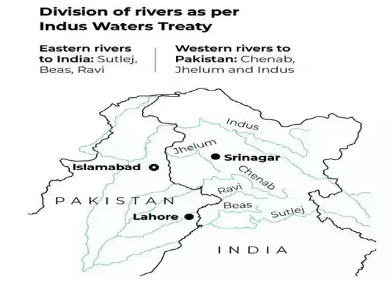
Image Source: The Indian Express
- India has been given the right to generate hydroelectricity through run of the river projects on the western riverabject to specific criteria for design and operation.
- The Treaty also gives the right to Pakistan to raise objections on the design of Indian hydroelectric projects on western rivers.
- Pakistan roughly got 80% of the water in the Indus drainage system.
- Setting up of Permanent Indus Commission: It mandated both the countries to establish a Permanent Indus Commission for resolution of conflicts.
- IWT does not have a unilateral exit provision, and is supposed to remain in force unless both the countries ratify another mutually agreed pact.
India’s Perspective:
- India is unhappy with the treaty because it prevents building storage systems on the western rivers.
- The Indus Treaty allows for the building of storage systems under certain circumstances, but India complains that Pakistan is blocking such efforts due to political tensions.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 27 May 2023
27 May 2023
