India stands at the cusp of a major transformation as Industry 5.0 reshapes global manufacturing and innovation.
- By combining human creativity with advanced technologies, this new era demands a future-ready workforce equipped with both technical expertise and human-centric skills.
- Industry 5.0 emphasizes collaboration between humans and intelligent machines, requiring a workforce skilled in emerging technologies and human-centric competencies to drive India’s industrial and innovation goals.
What is Industry 5.0 ?
- Definition: Industry 5.0, or the Fifth Industrial Revolution, represents a human-centric phase of industrialization.
- Focus: Partnership between humans and machines to drive efficiency, sustainability, personalization, resilience, and ethical outcomes.
- Difference from Industry 4.0:
-
- Industry 4.0: Prioritised automation, efficiency, and smart systems.
- Industry 5.0: Restores the human role, ensuring creativity, adaptability, and ethics are central to industrial processes.
- Relevance to India: Supports self-reliance, global competitiveness, and inclusive industrial growth.
- Aligns with “Vocal for Local,” Atmanirbhar Bharat,” and vision of Viksit Bharat 2047.
Evolution of Industrial Revolutions
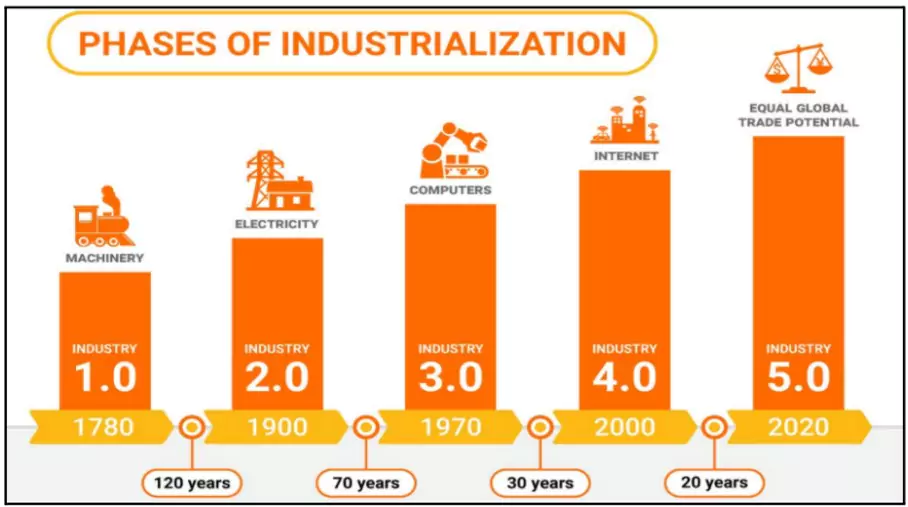
- Industry 1.0: Mechanisation using water and steam power.
- Industry 2.0: Mass production enabled by electricity.
- Industry 3.0: Automation using electronics and IT.
- Industry 4.0: Digital transformation with IoT, AI, and cyber-physical systems.
- Industry 5.0: Human-machine collaboration, focusing on well-being, sustainability, and inclusivity.
Key Features of Industry 5.0
- Human-centricity: Workers are not displaced but empowered by machines.
- Collaboration: Cobots (collaborative robots) working with humans.
- Sustainability: Green technologies, resource optimisation, waste reduction.
- Resilience: Ability to withstand disruptions (pandemics, geopolitical shocks).
- Customization: Shift from mass production to personalized products and services.
Industry 5.0 Applications
- Manufacturing: Cobots assist workers in customised production with higher safety.
- Healthcare: AI-driven medical devices and personalised treatment (e.g., predictive health apps).
- Automotive & Electronics: Tailor-made designs and consumer-specific innovations.
- Education & Services: AI-human collaboration enabling personalised learning and efficient service delivery.
- Sustainability: Circular economy practices, renewable energy integration, and eco-friendly production.
Key Technological Shifts Driving IR 5.0
- AI & Robotics: Automating repetitive tasks, enabling humans to focus on creativity.
- Edge Computing: Data processed closer to the source, ensuring speed and privacy.
- 5G/6G & Brain-Computer Interfaces: New communication modes and faster connectivity.
- IoT & Big Data: Predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and smarter decisions.
- 3D Printing & Blockchain: On-demand customised production and supply chain transparency.
- Remote Work Ecosystems: Rise of “cloud people” and virtual industries.
Challenges in Implementation of Industry 5.0
- Adoption Gaps: Traditional industries resist change due to cultural and cost factors.
- Skill Gaps: Workforce lacks interdisciplinary training in tech + human-centric skills.
- Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology between urban-rural areas and large vs small firms.
- Financial Barriers: High initial investment in advanced technologies.
- Ethical & Governance Issues: AI bias, job displacement, data privacy, and cybersecurity.
Government Initiatives in India
- Skill Development: Skill India Mission, PM Kaushal Vikas Yojana, National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme for workforce upskilling.
- AICTE Initiatives:
-
- Integration of AI in curricula, 2025 as “Year of AI”.
- ATAL Faculty Development Programmes, Hackathons, KAPILA Startup Policy.
- Institution’s Innovation Councils to boost entrepreneurship.
- Digital India & Make in India: Building digital infrastructure and manufacturing competitiveness.
- PLI Schemes (Production Linked Incentives): Encouraging advanced manufacturing and innovation.
Way Forward
- National Industry 5.0 Roadmap: Set milestones for adoption, policy, and innovation clusters.
- Skill Ecosystem Reforms: Blend STEM education with creativity, ethics, and soft skills.
- Strengthen Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities: Build regional innovation hubs using local talent.
- Sustainability Integration: Embed green tech and circular economy models in industry.
- Public-Private-Academia Collaboration: Ensure coordinated progress in R&D, skilling, and infrastructure.
- Ethical & Regulatory Framework: Guidelines for AI governance, cybersecurity, and responsible innovation.
Conclusion
Industry 5.0 is not about replacing humans but about empowering them through intelligent technologies. It complements Industry 4.0 by balancing automation with human creativity, adaptability, and ethics. For India, embracing Industry 5.0 is critical to achieve Atmanirbhar Bharat, sustainable growth, and the vision of a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
![]() 29 Aug 2025
29 Aug 2025

